Deposition Date
2017-06-22
Release Date
2018-02-21
Last Version Date
2024-01-17
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
5OAK
Keywords:
Title:
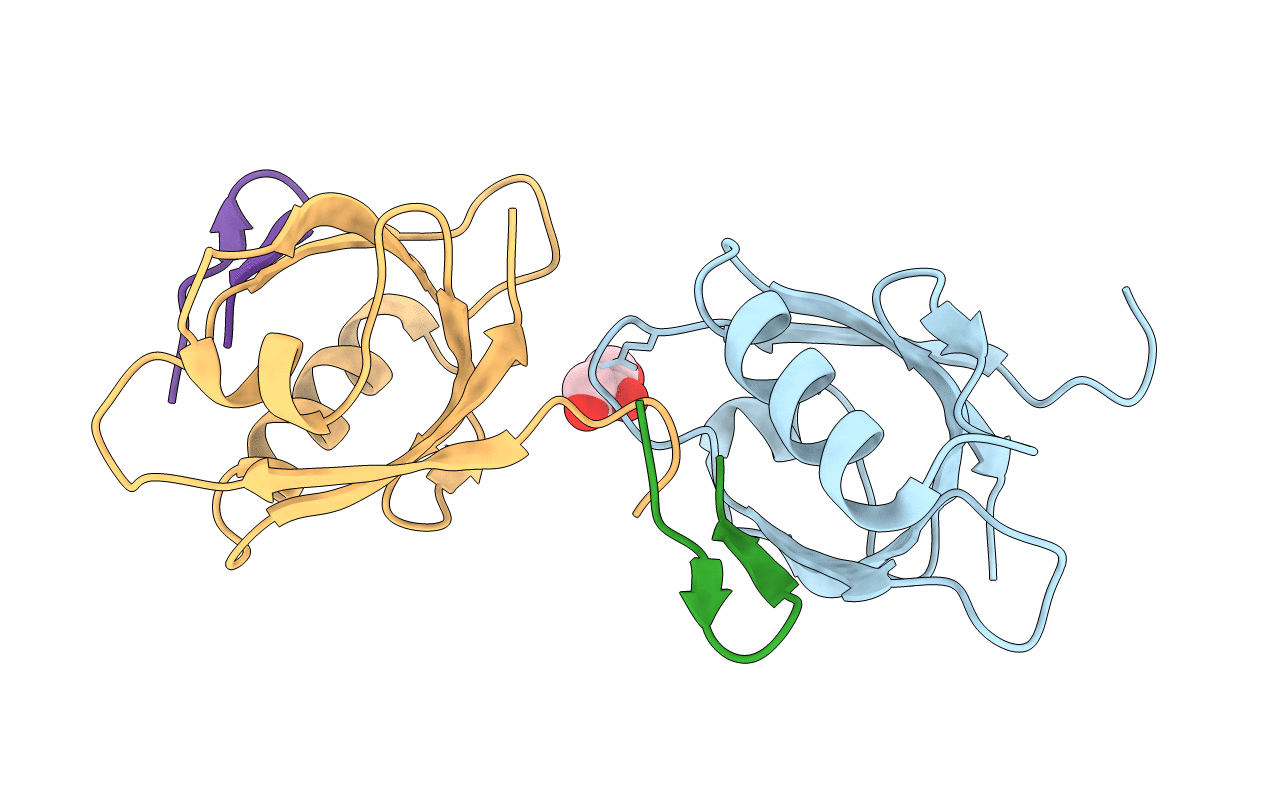
Structure of the dmPar3 PDZ1 domain in complex with the dmPar6 PBM
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Drosophila melanogaster (Taxon ID: 7227)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
1.50 Å
R-Value Free:
0.16
R-Value Work:
0.14
R-Value Observed:
0.14
Space Group:
P 31


