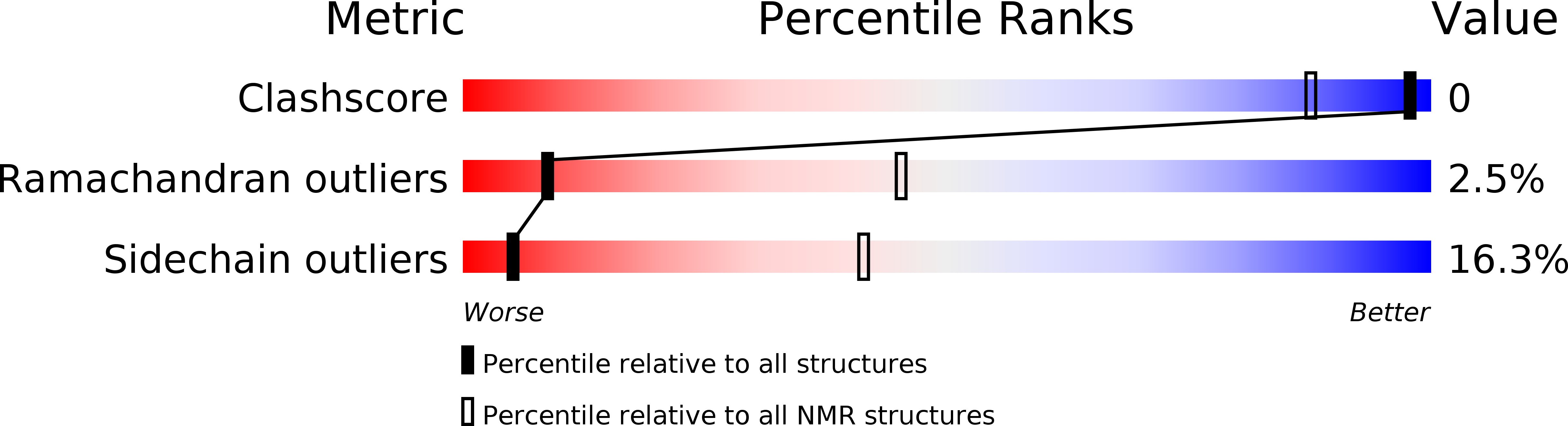
Deposition Date
2017-06-09
Release Date
2018-02-07
Last Version Date
2024-06-19
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
5O7J
Keywords:
Title:
Structural insights into the periplasmic sensor domain of the GacS histidine kinase controlling biofilm formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Pseudomonas aeruginosa (Taxon ID: 287)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
20
Conformers Submitted:
20
Selection Criteria:
all calculated structures submitted