Deposition Date
2017-03-16
Release Date
2017-06-14
Last Version Date
2024-10-23
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
5NFV
Keywords:
Title:
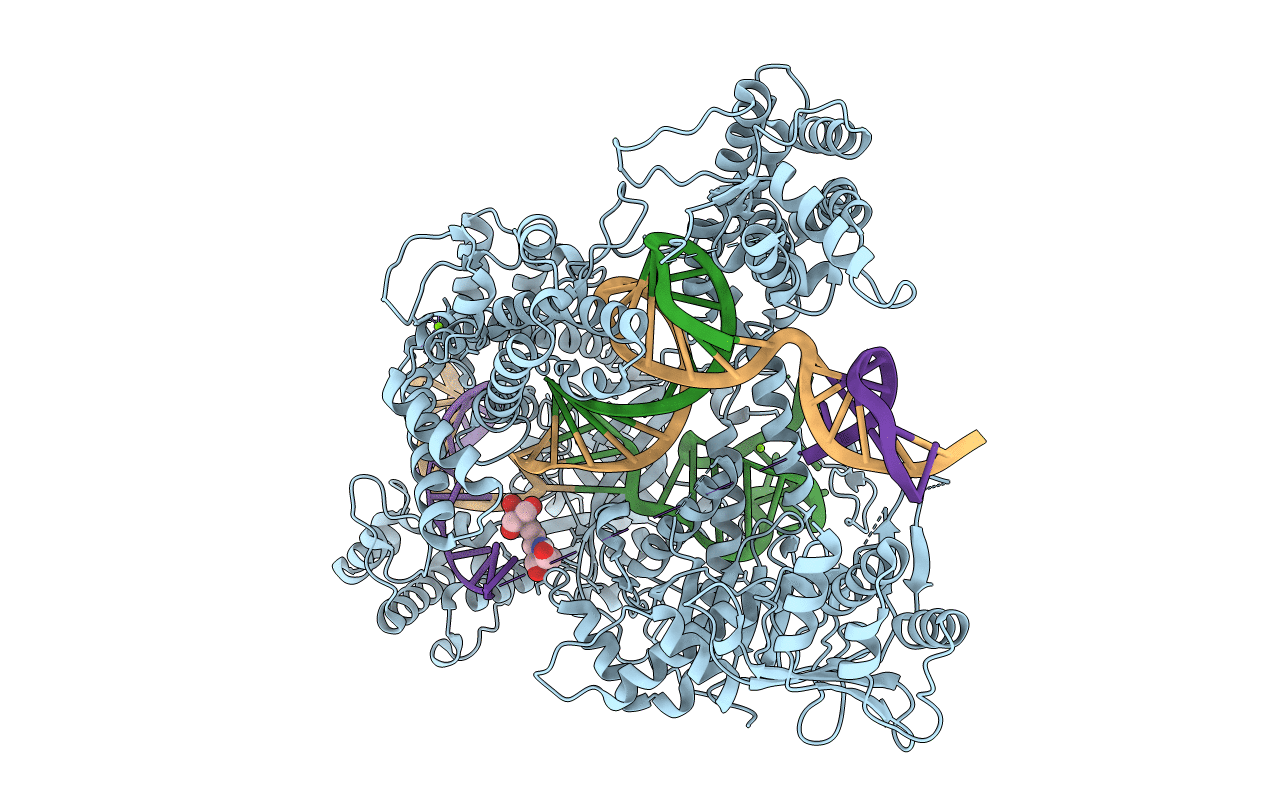
Crystal structure of catalytically inactive FnCas12 mutant bound to an R-loop structure containing a pre-crRNA mimic and full-length DNA target
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Francisella tularensis subsp. novicida (strain U112) (Taxon ID: 401614)
synthetic construct (Taxon ID: 32630)
synthetic construct (Taxon ID: 32630)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
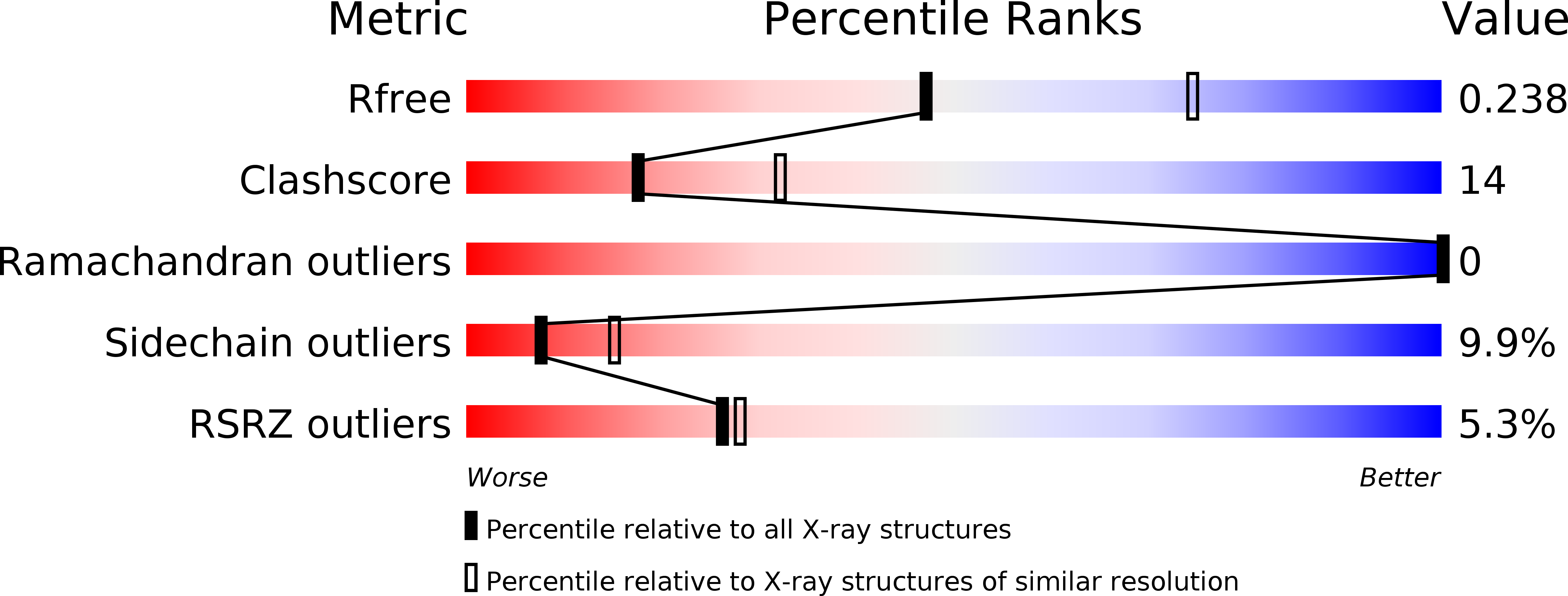
Resolution:
2.50 Å
R-Value Free:
0.23
R-Value Work:
0.20
R-Value Observed:
0.20
Space Group:
P 1 21 1