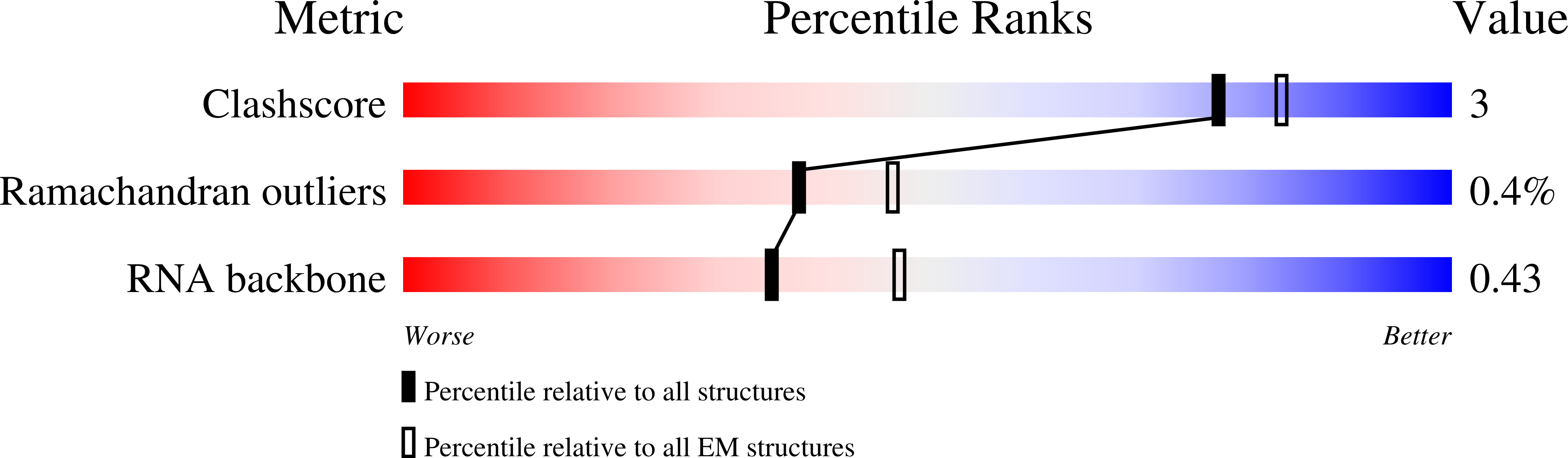
Deposition Date
2016-12-29
Release Date
2017-05-03
Last Version Date
2024-05-15
Entry Detail
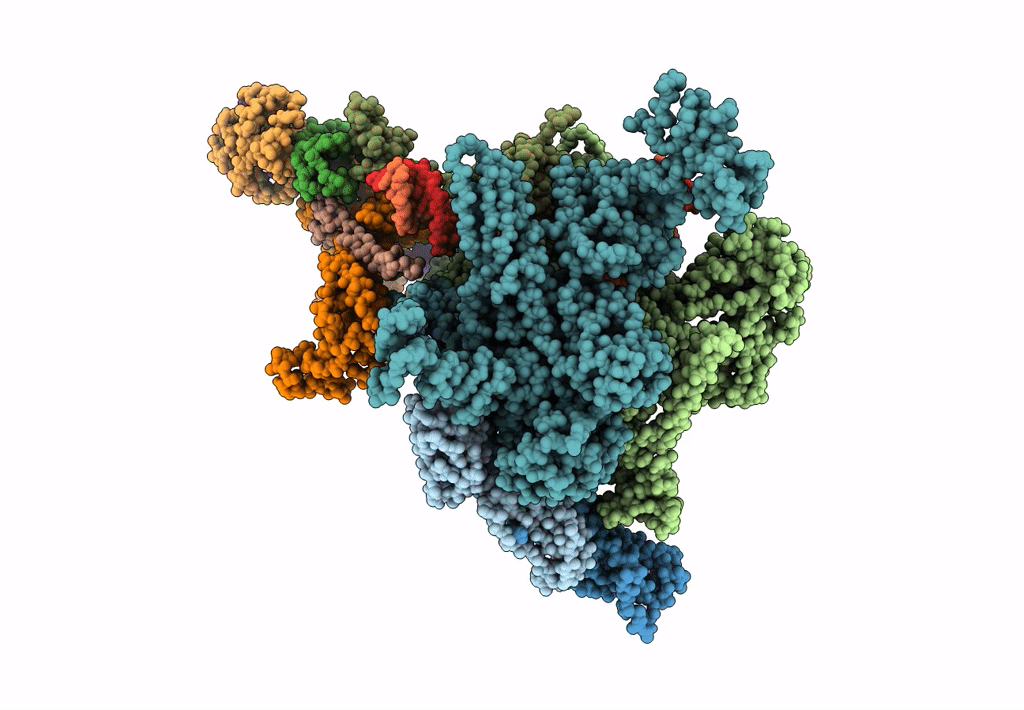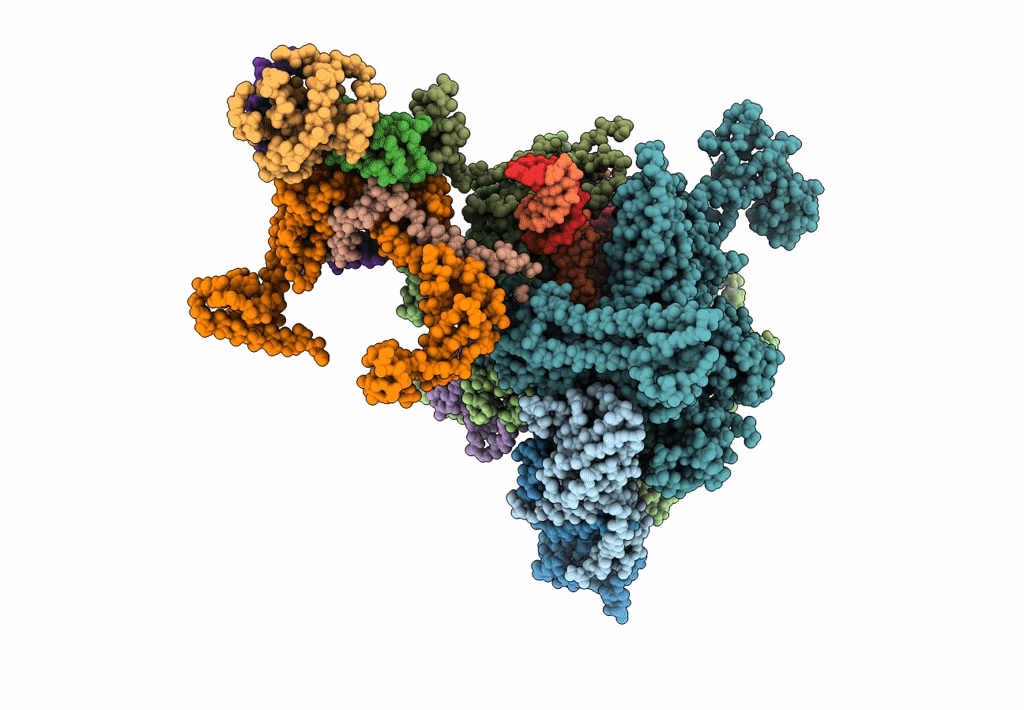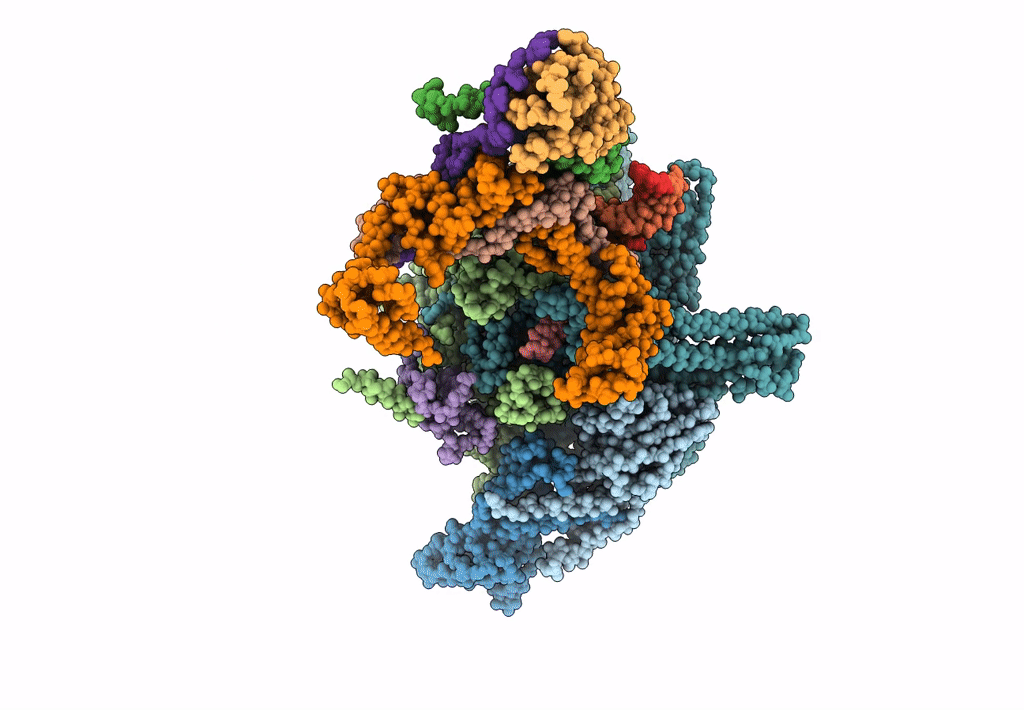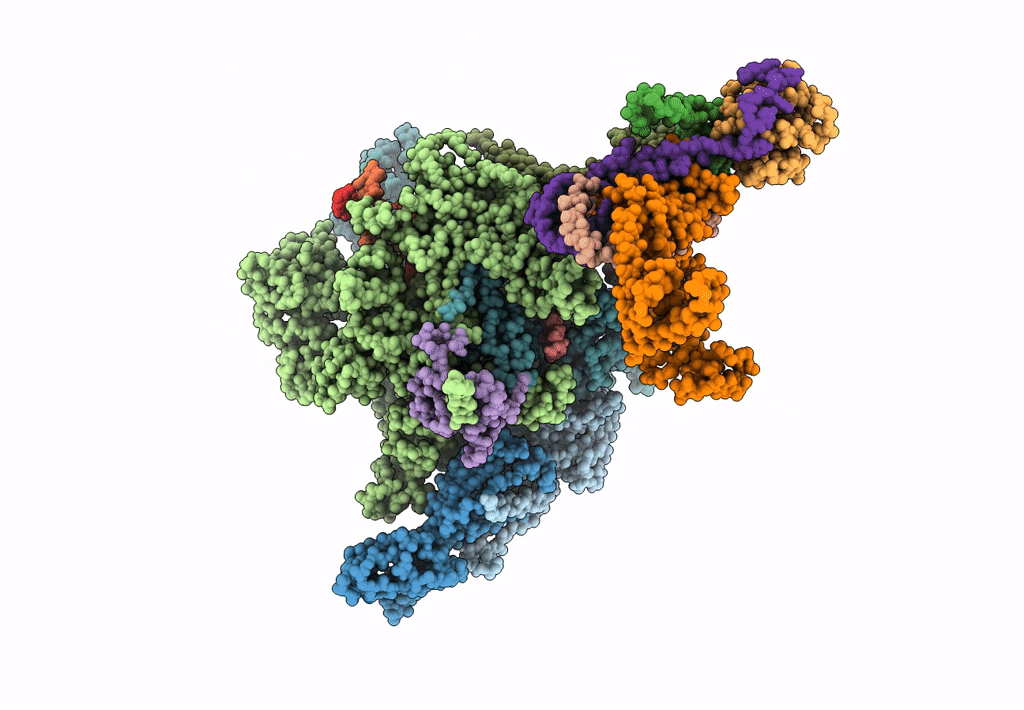
PDB ID:
5MS0
Keywords:
Title:
pseudo-atomic model of the RNA polymerase lambda-based antitermination complex solved by cryo-EM
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Escherichia phage lambda (Taxon ID: 10710)
Escherichia coli (Taxon ID: 562)
Escherichia coli K-12 (Taxon ID: 83333)
Escherichia coli (Taxon ID: 562)
Escherichia coli K-12 (Taxon ID: 83333)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
9.80 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE