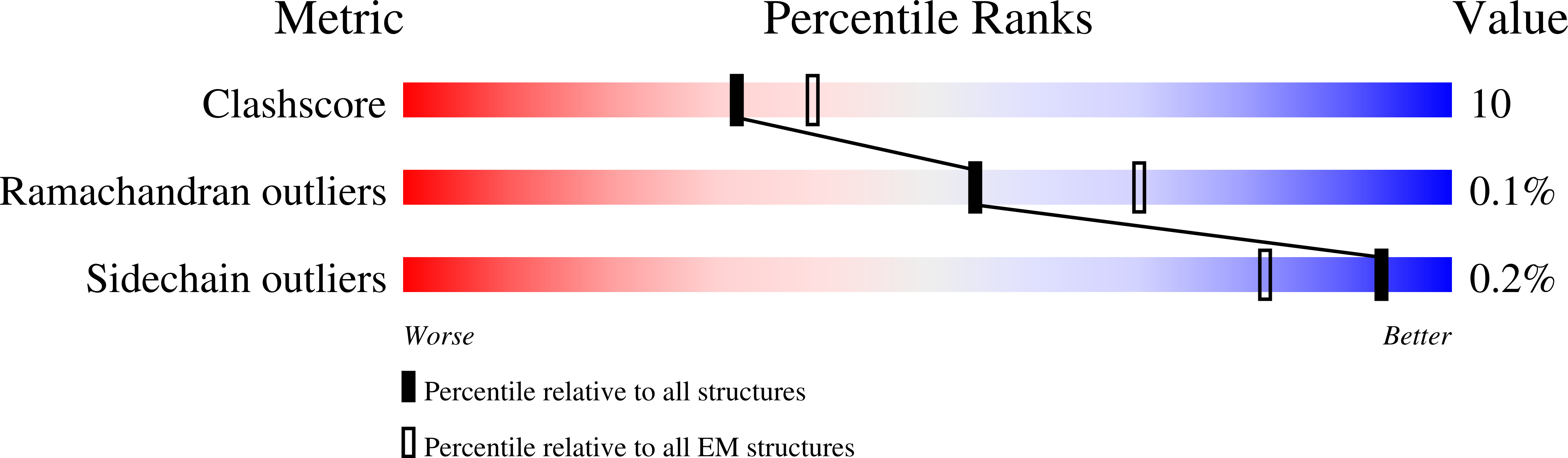
Deposition Date
2016-12-08
Release Date
2018-08-08
Last Version Date
2025-07-02
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
5MM7
Keywords:
Title:
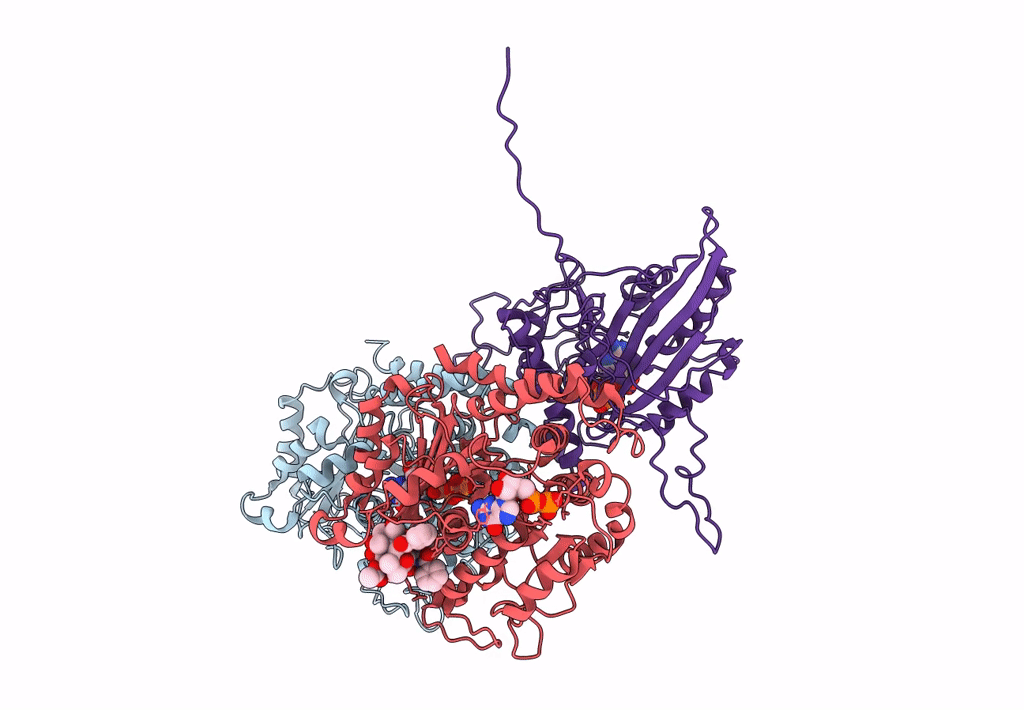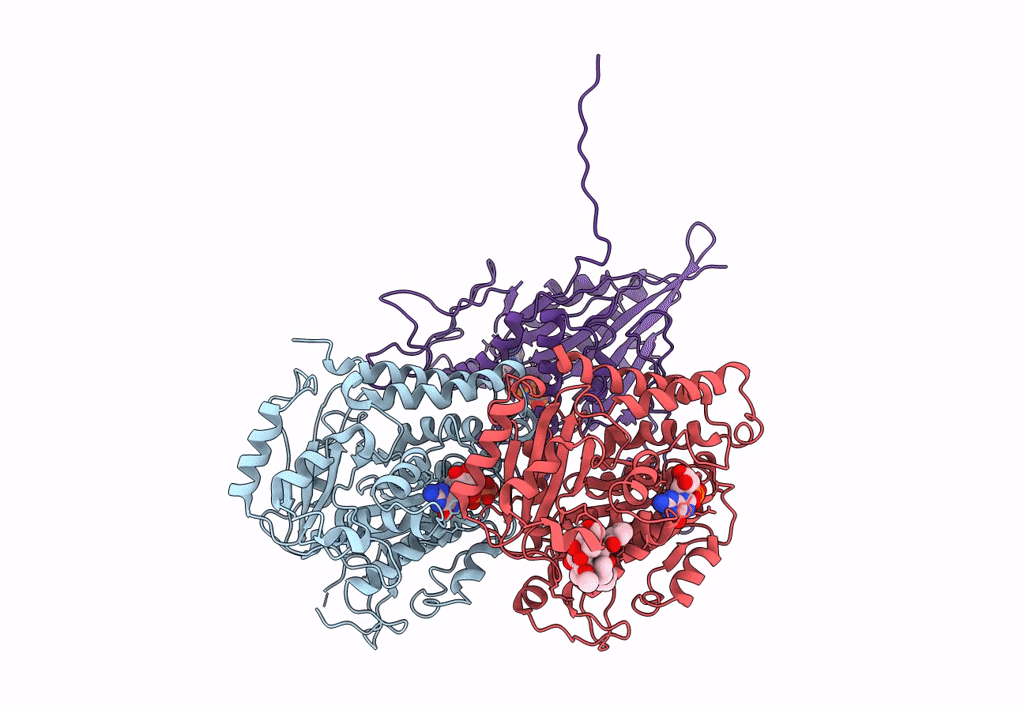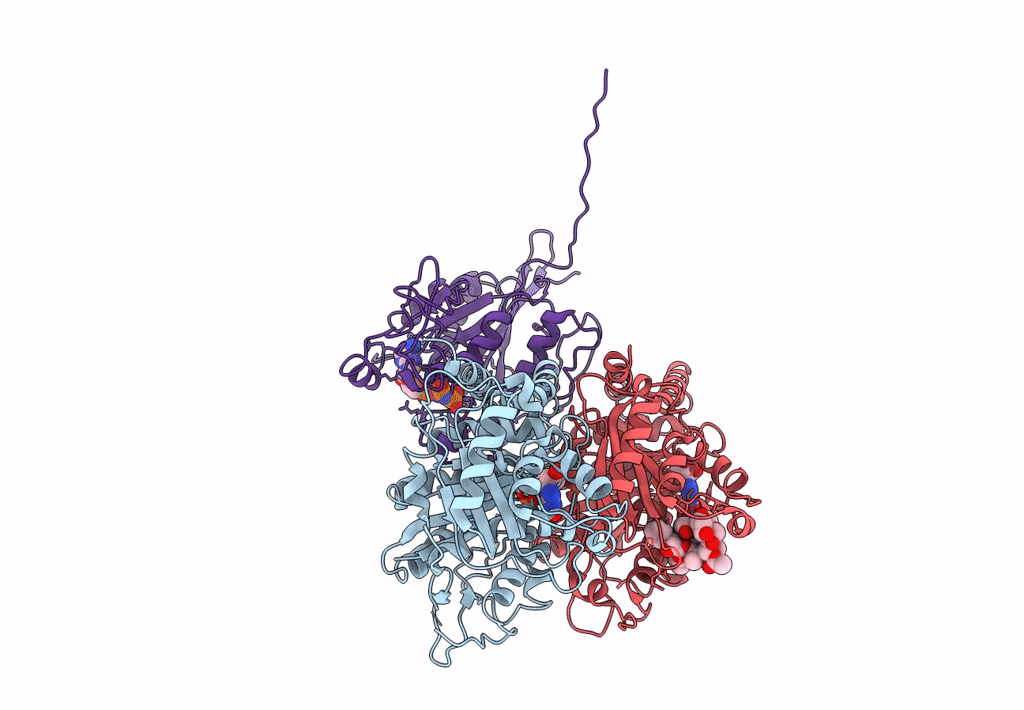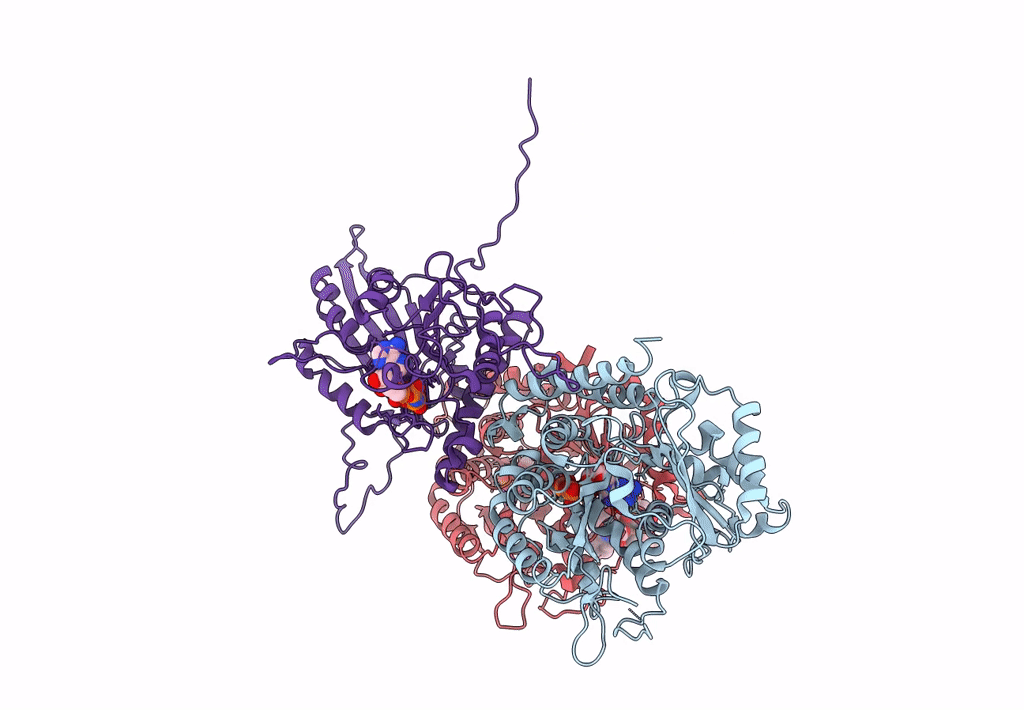
Ustilago maydis kinesin-5 motor domain with N-terminal extension in the AMPPNP state bound to microtubules
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Ustilago maydis (Taxon ID: 5270)
Sus scrofa (Taxon ID: 9823)
Sus scrofa (Taxon ID: 9823)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
5.10 Å
Aggregation State:
HELICAL ARRAY
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE