Deposition Date
2016-09-13
Release Date
2016-10-19
Last Version Date
2024-05-08
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
5LV9
Keywords:
Title:
Crystal structure of thermophilic tryptophan halogenase (Th-Hal) enzyme from Streptomycin violaceusniger.
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Streptomyces violaceusniger (Taxon ID: 68280)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
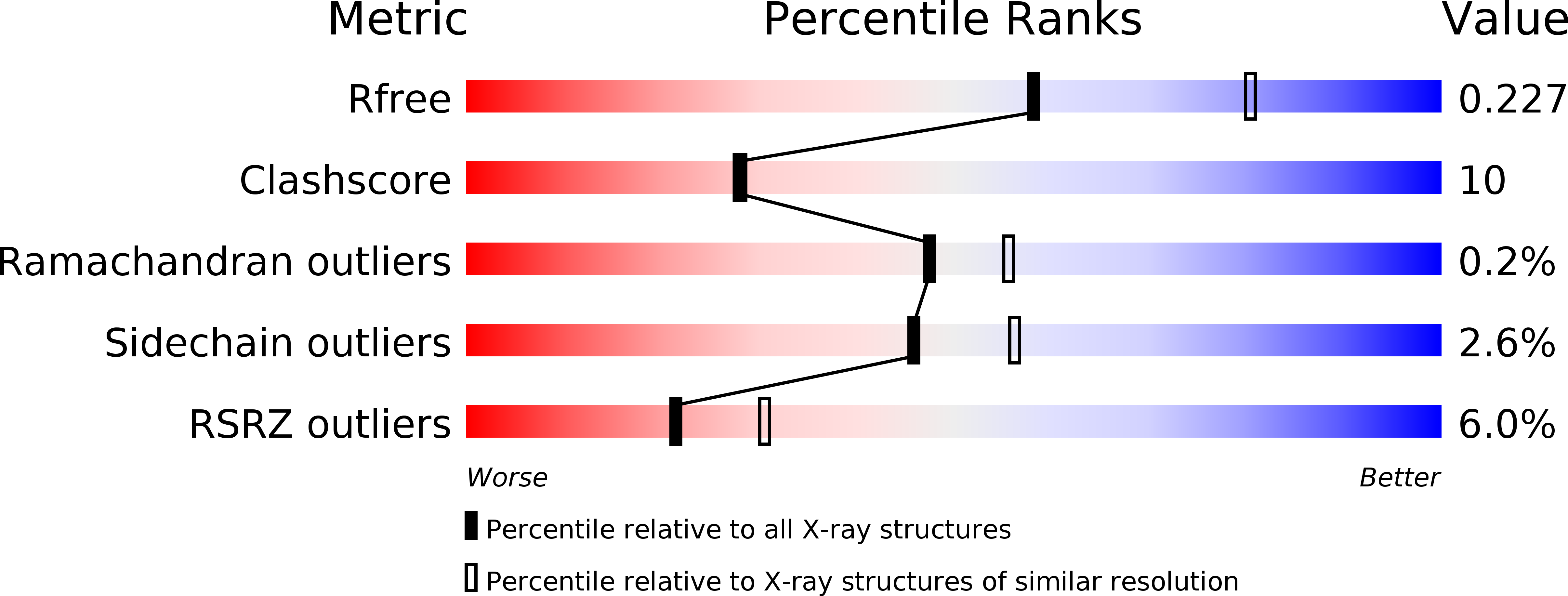
Resolution:
2.33 Å
R-Value Free:
0.22
R-Value Work:
0.17
R-Value Observed:
0.18
Space Group:
P 65