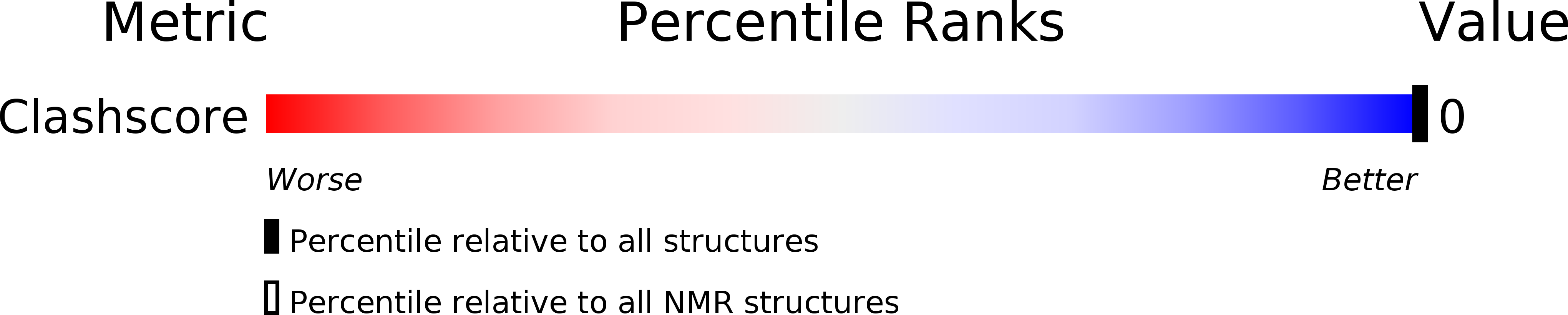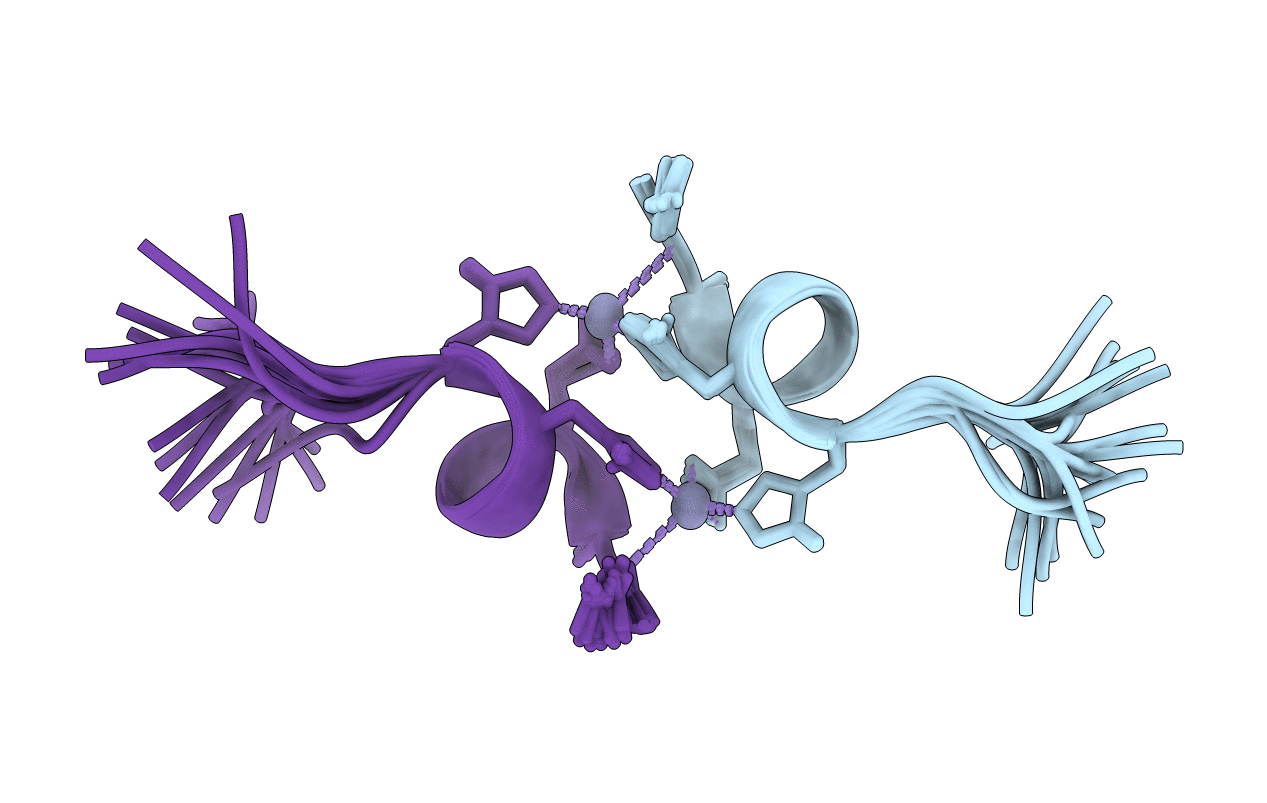
Deposition Date
2016-07-05
Release Date
2017-08-23
Last Version Date
2024-11-13
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
5LFY
Keywords:
Title:
Zinc bound dimer of the fragment of human amyloid-beta peptide with Alzheimer's disease pathogenic Taiwanese mutation D7H
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
50
Conformers Submitted:
20
Selection Criteria:
structures with the least restraint violations