Deposition Date
2016-06-21
Release Date
2017-02-15
Last Version Date
2024-01-10
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
5LCH
Keywords:
Title:
VIM-2 metallo-beta-lactamase in complex with (S)-1-allyl-2-(3-methoxyphenyl)-3-oxoisoindoline-4-carboxylic acid (compound 42)
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Pseudomonas aeruginosa (Taxon ID: 287)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
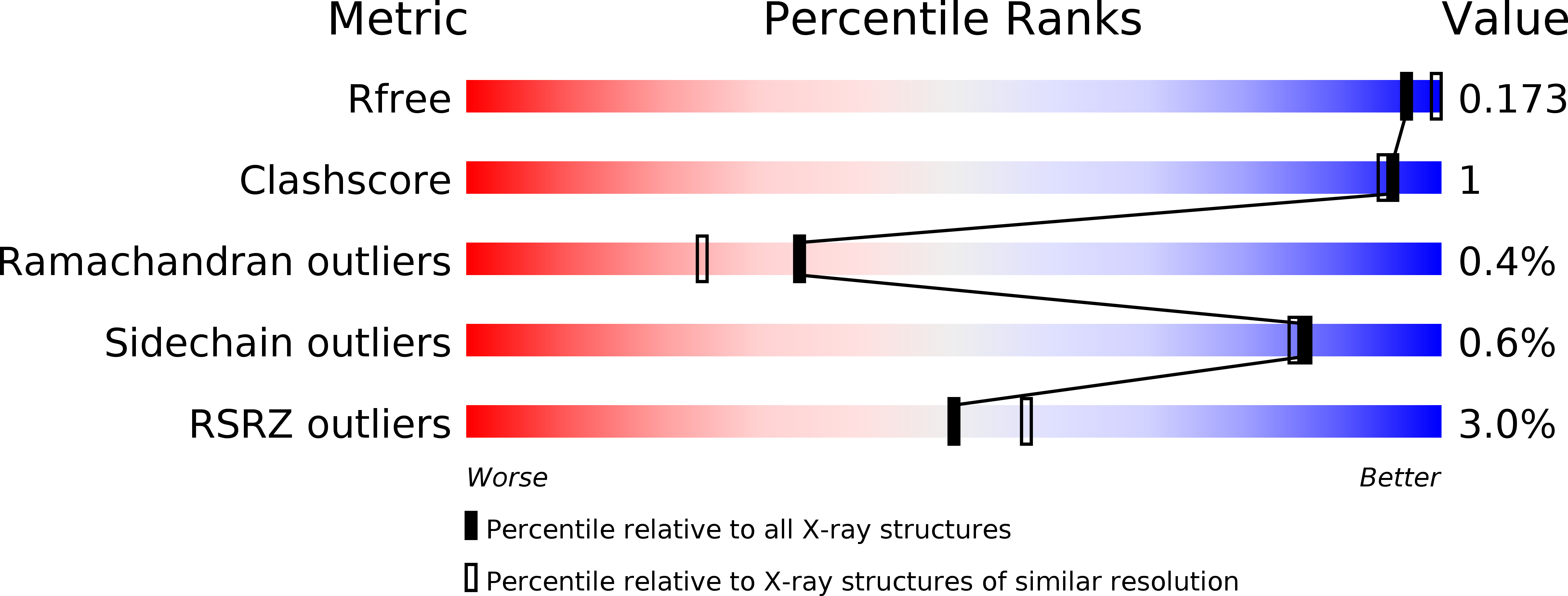
Resolution:
1.94 Å
R-Value Free:
0.16
R-Value Work:
0.12
R-Value Observed:
0.12
Space Group:
P 1 21 1


