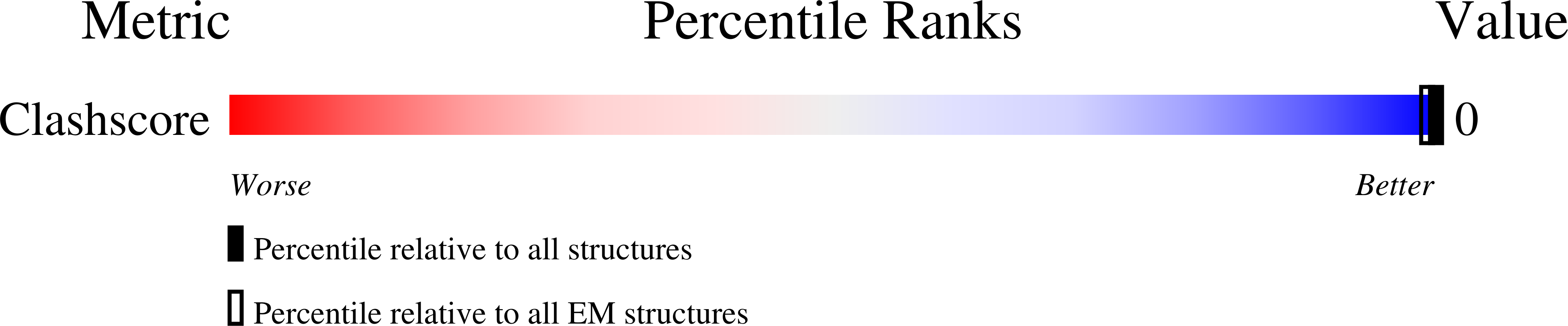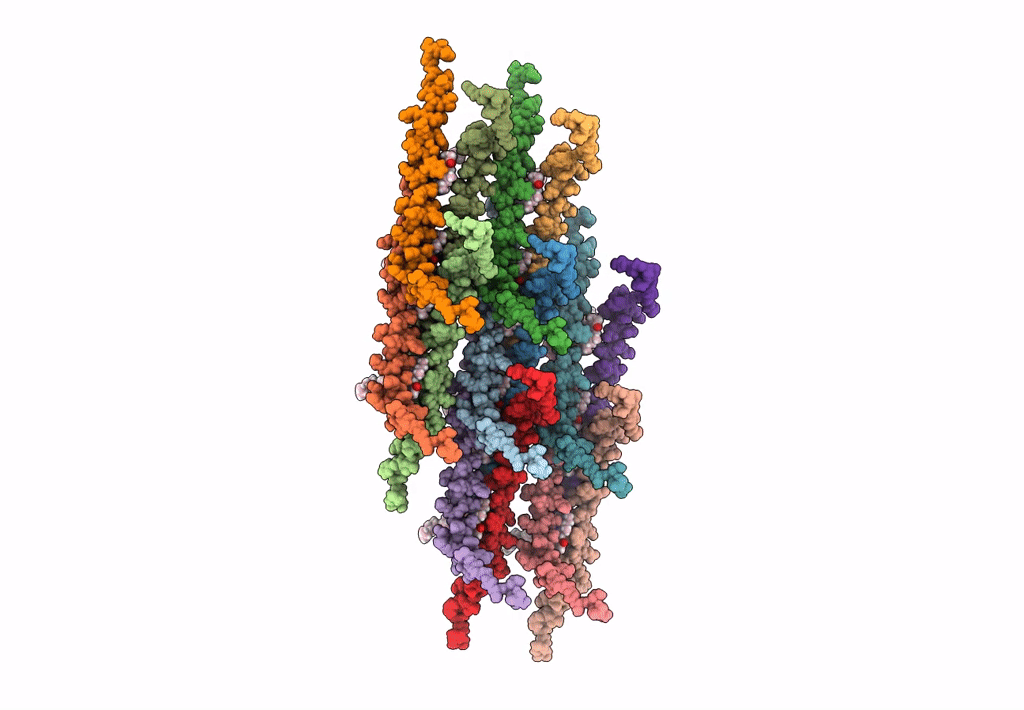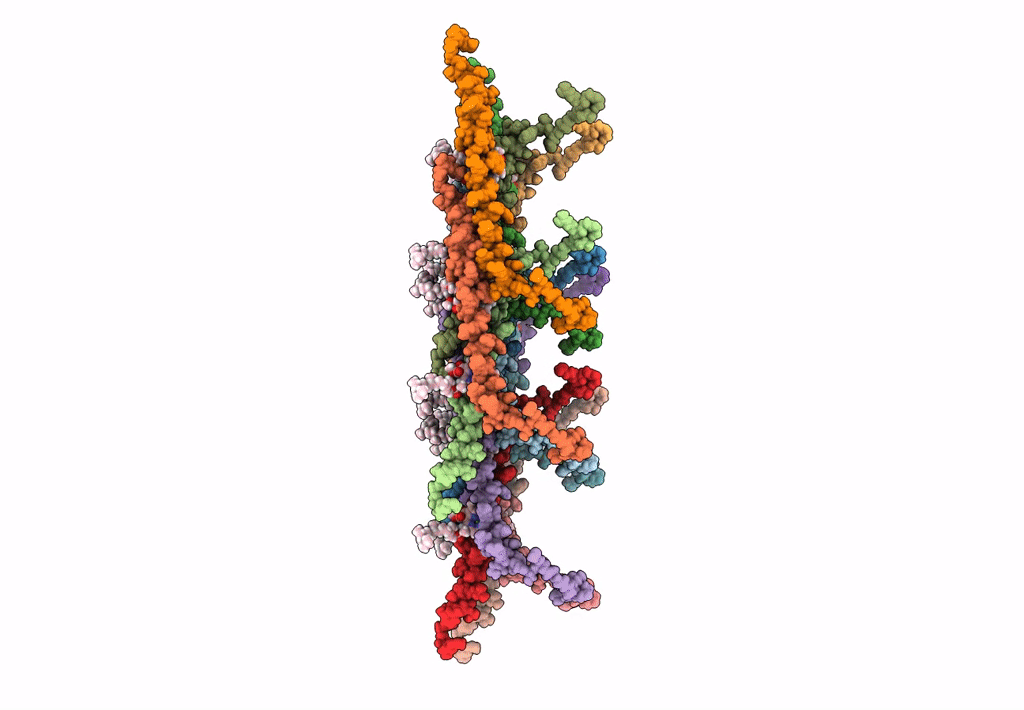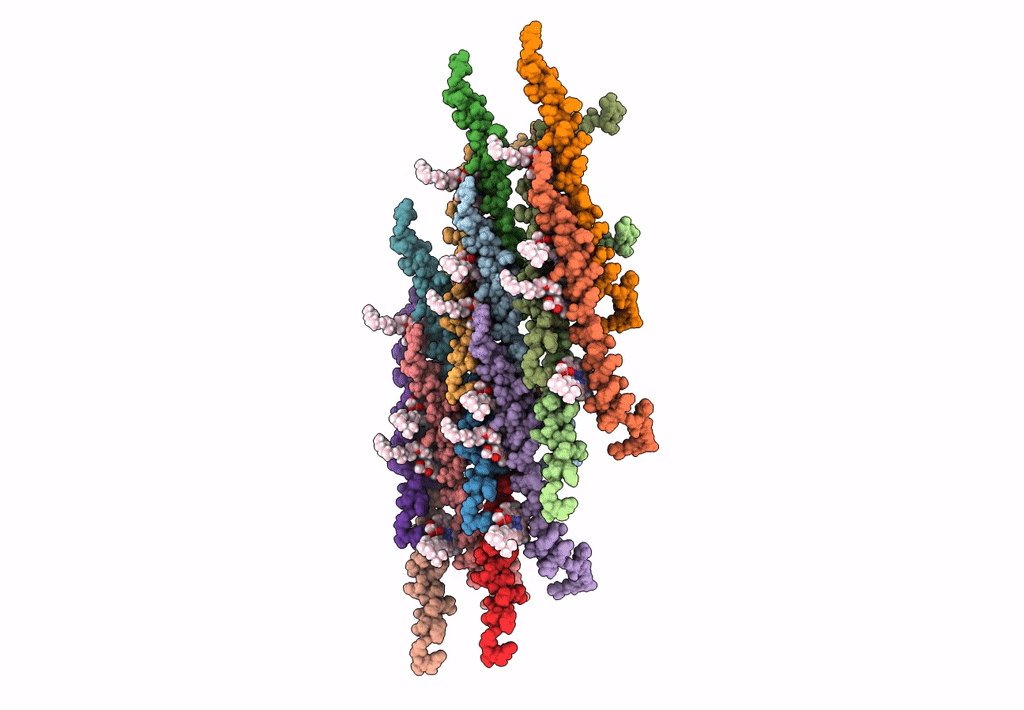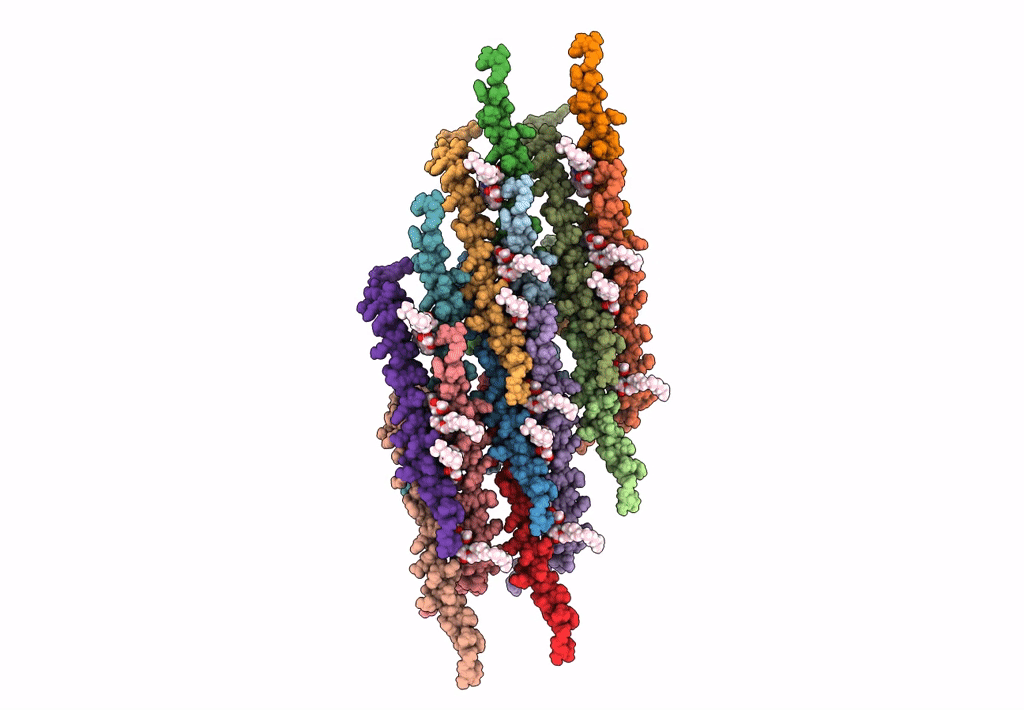
Deposition Date
2016-06-20
Release Date
2016-07-27
Last Version Date
2025-05-07
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
5LCB
Keywords:
Title:
In situ atomic-resolution structure of the baseplate antenna complex in Chlorobaculum tepidum obtained combining solid-state NMR spectroscopy, cryo electron microscopy and polarization spectroscopy
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
26.50 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE