Deposition Date
2016-06-28
Release Date
2017-06-14
Last Version Date
2024-10-16
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
5KNM
Keywords:
Title:
Human leukocyte antigen F (HLA-F) presents peptides and regulates immunity through interactions with NK-cell receptors
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
Trichoplusia ni (Taxon ID: 7111)
Trichoplusia ni (Taxon ID: 7111)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
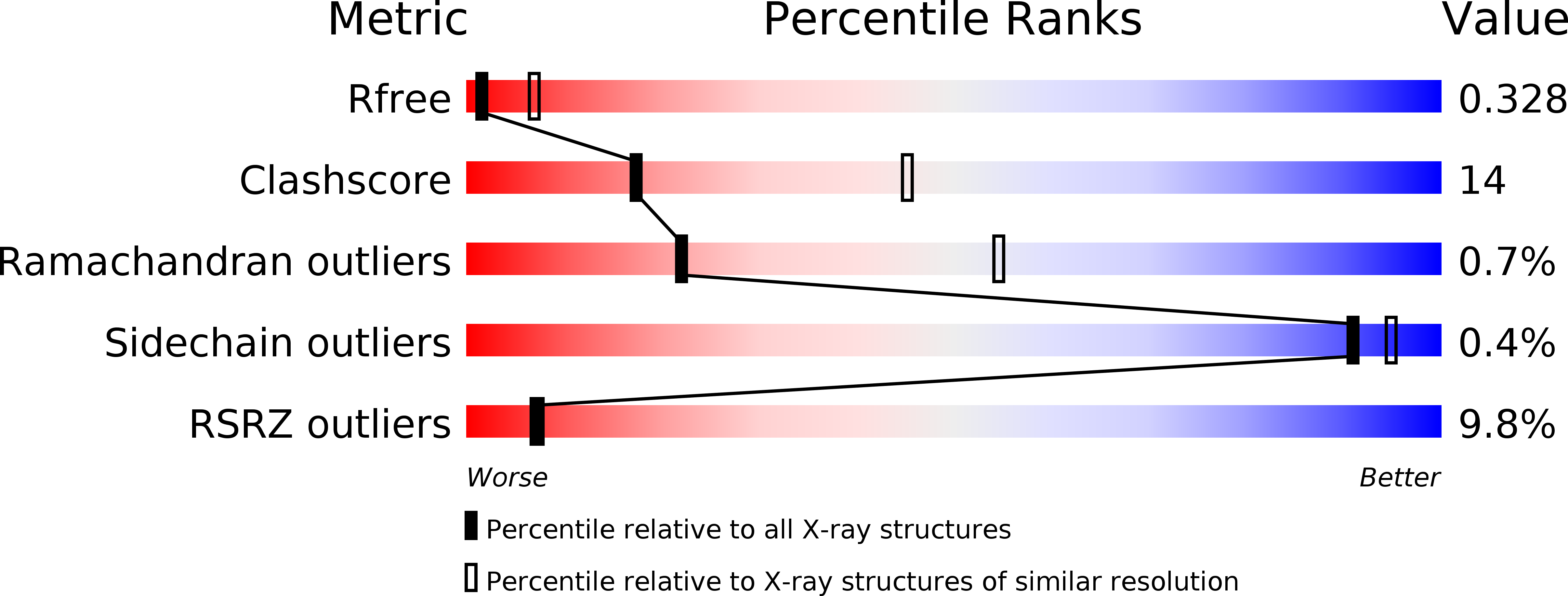
Resolution:
3.30 Å
R-Value Free:
0.32
R-Value Work:
0.30
R-Value Observed:
0.30
Space Group:
P 6 2 2