Deposition Date
2016-06-13
Release Date
2016-07-27
Last Version Date
2024-11-13
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
5KGF
Keywords:
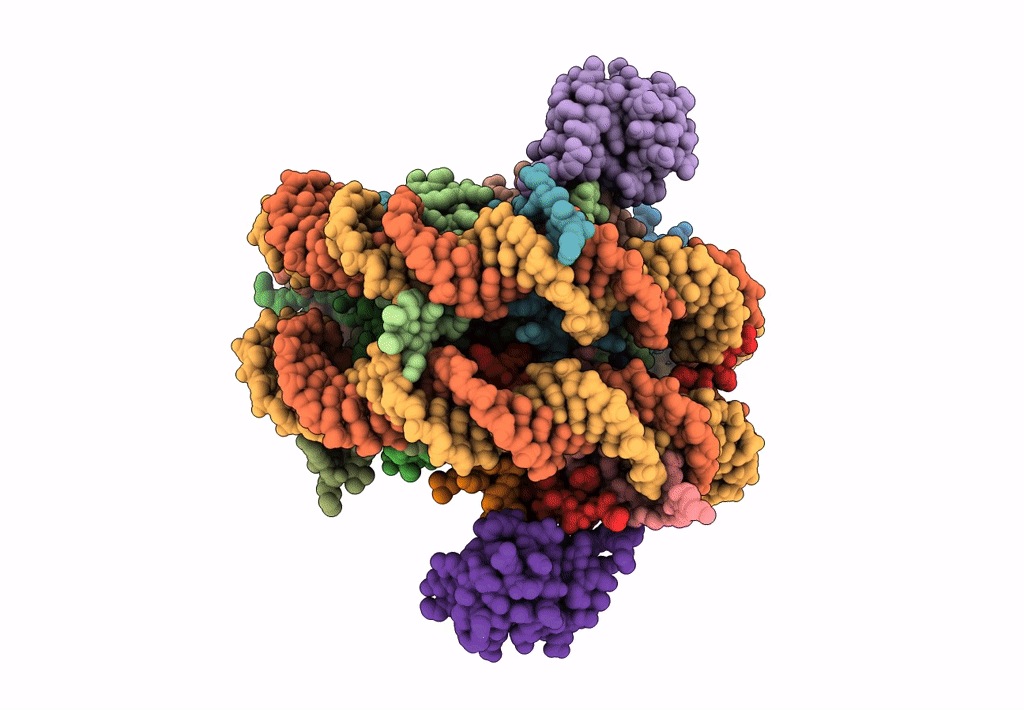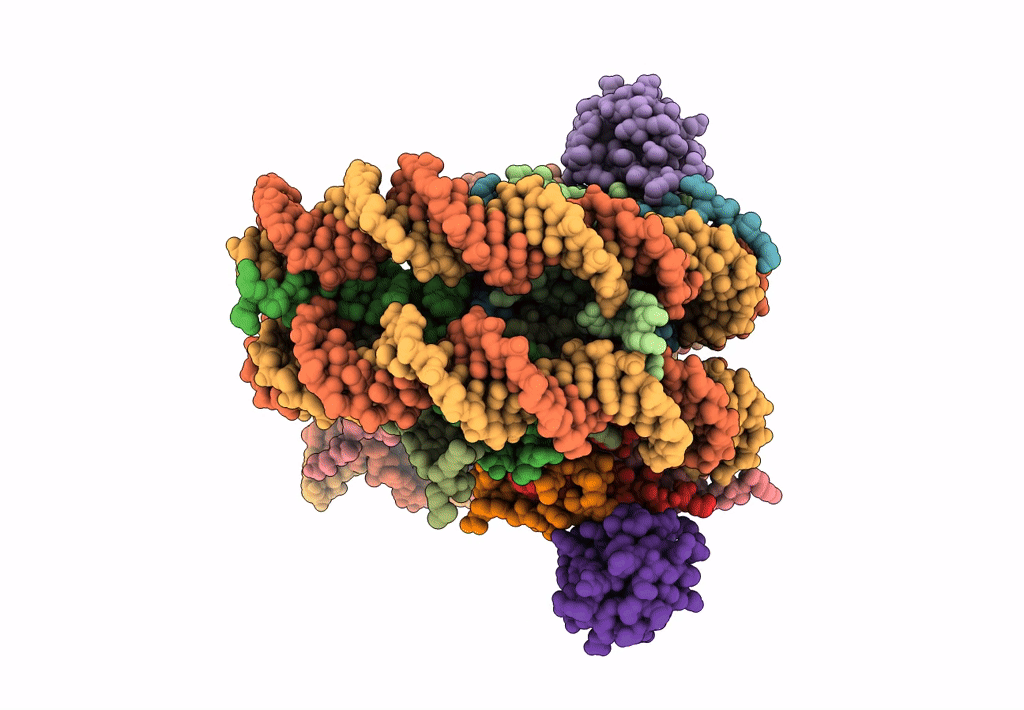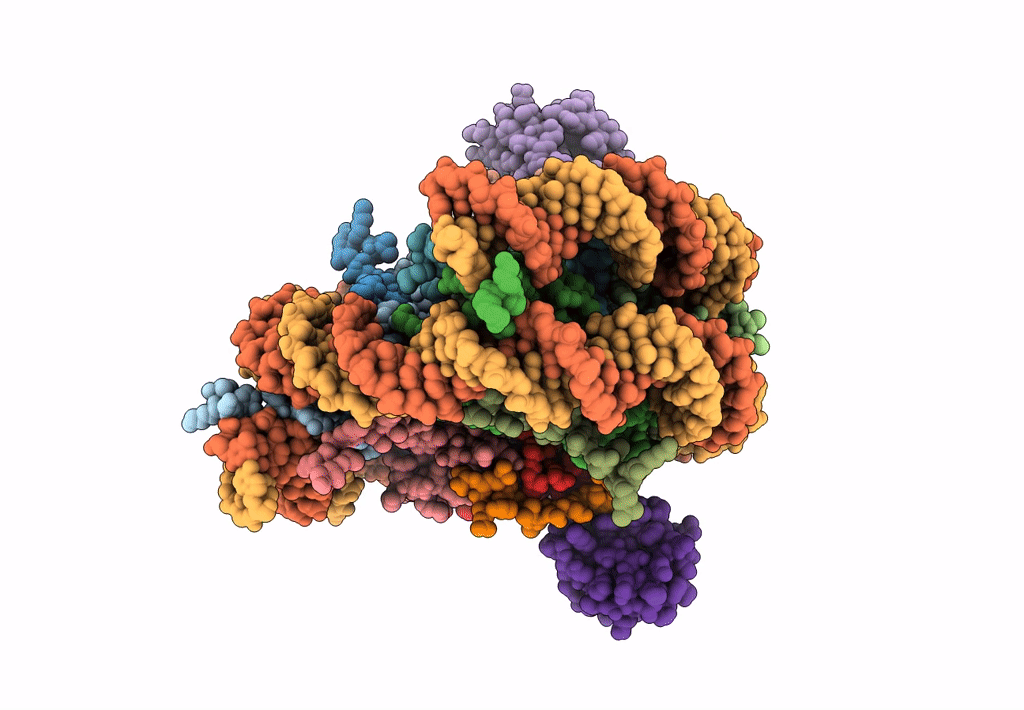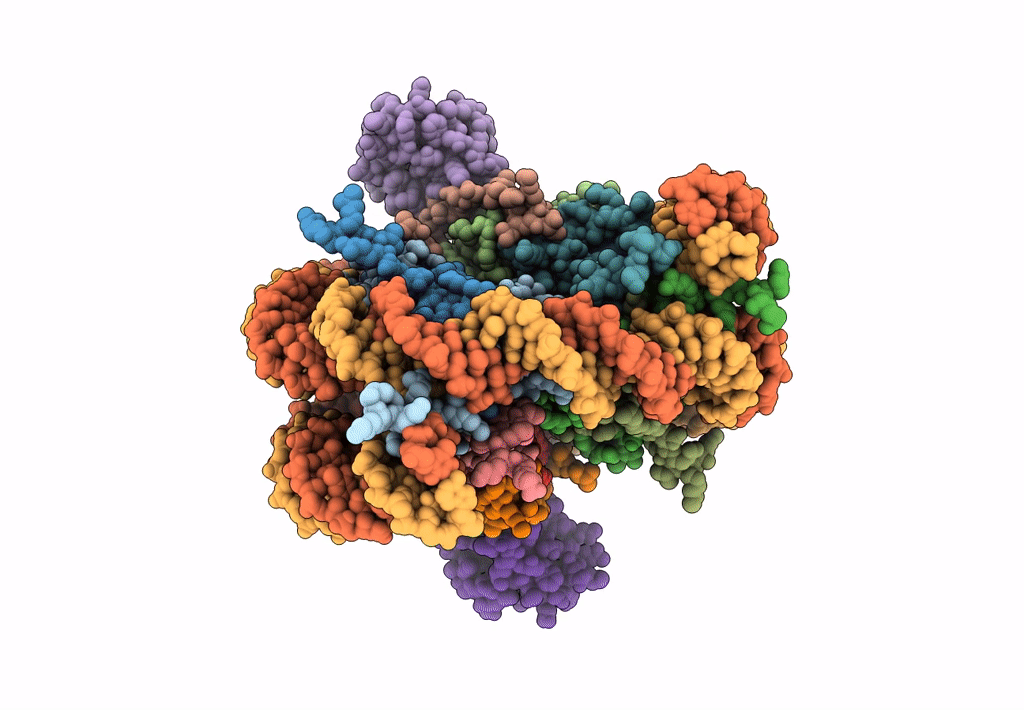
Title:
Structural model of 53BP1 bound to a ubiquitylated and methylated nucleosome, at 4.5 A resolution
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Xenopus laevis (Taxon ID: 8355)
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
synthetic construct (Taxon ID: 32630)
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
synthetic construct (Taxon ID: 32630)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
4.54 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE


