Deposition Date
2016-05-20
Release Date
2016-12-14
Last Version Date
2024-01-10
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
5K3W
Keywords:
Title:
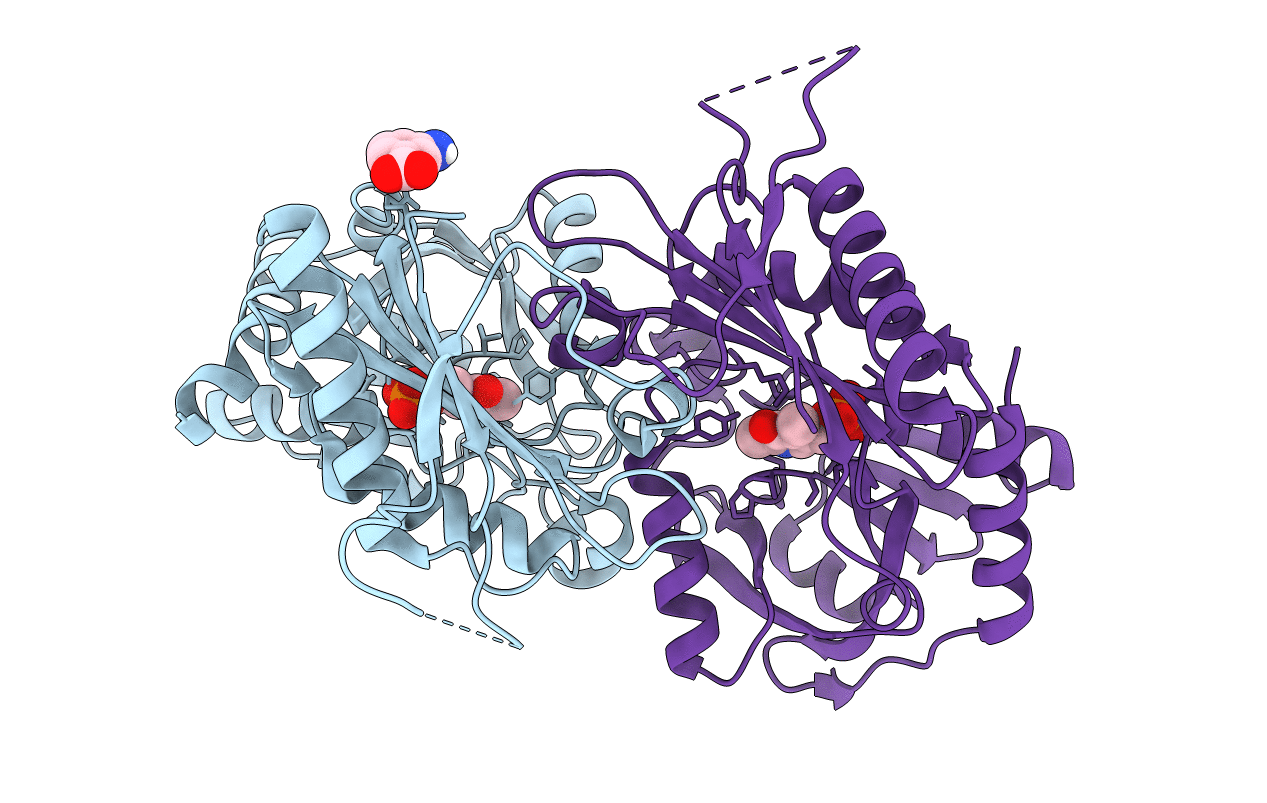
Structural characterisation of fold IV-transaminase, CpuTA1, from Curtobacterium pusillum
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Curtobacterium pusillum (Taxon ID: 69373)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
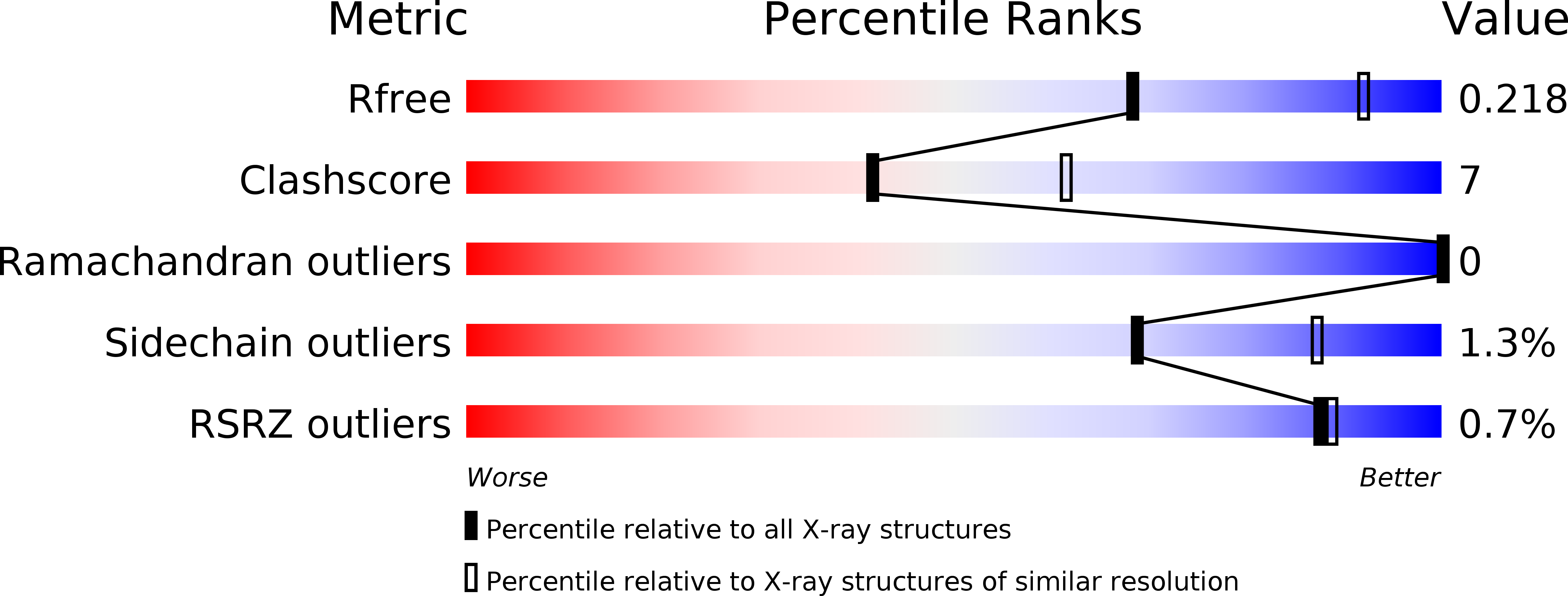
Resolution:
2.50 Å
R-Value Free:
0.21
R-Value Work:
0.16
R-Value Observed:
0.16
Space Group:
P 62