Deposition Date
2016-05-12
Release Date
2017-03-29
Last Version Date
2024-03-06
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
5JWQ
Keywords:
Title:
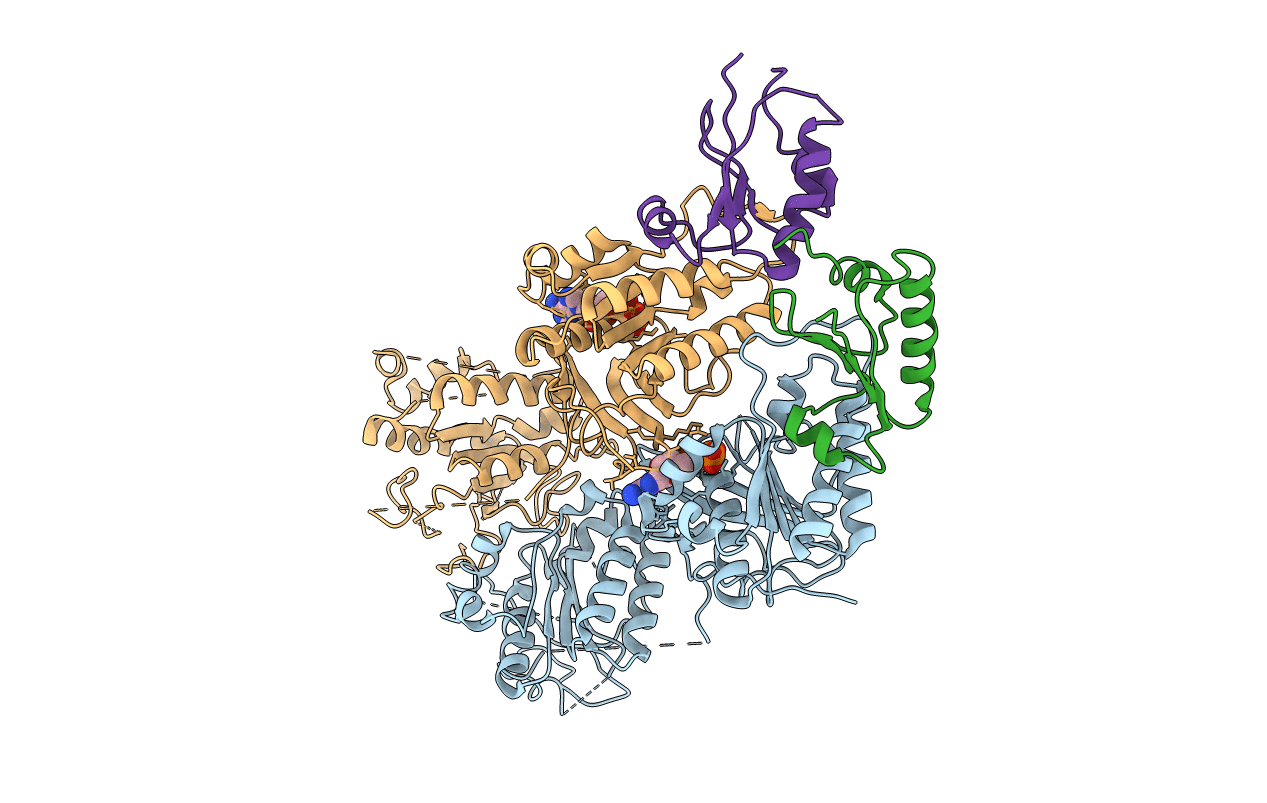
Crystal structure of KaiC S431E in complex with foldswitch-stabilized KaiB from Thermosynechococcus elongatus
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Thermosynechococcus elongatus (strain BP-1) (Taxon ID: 197221)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
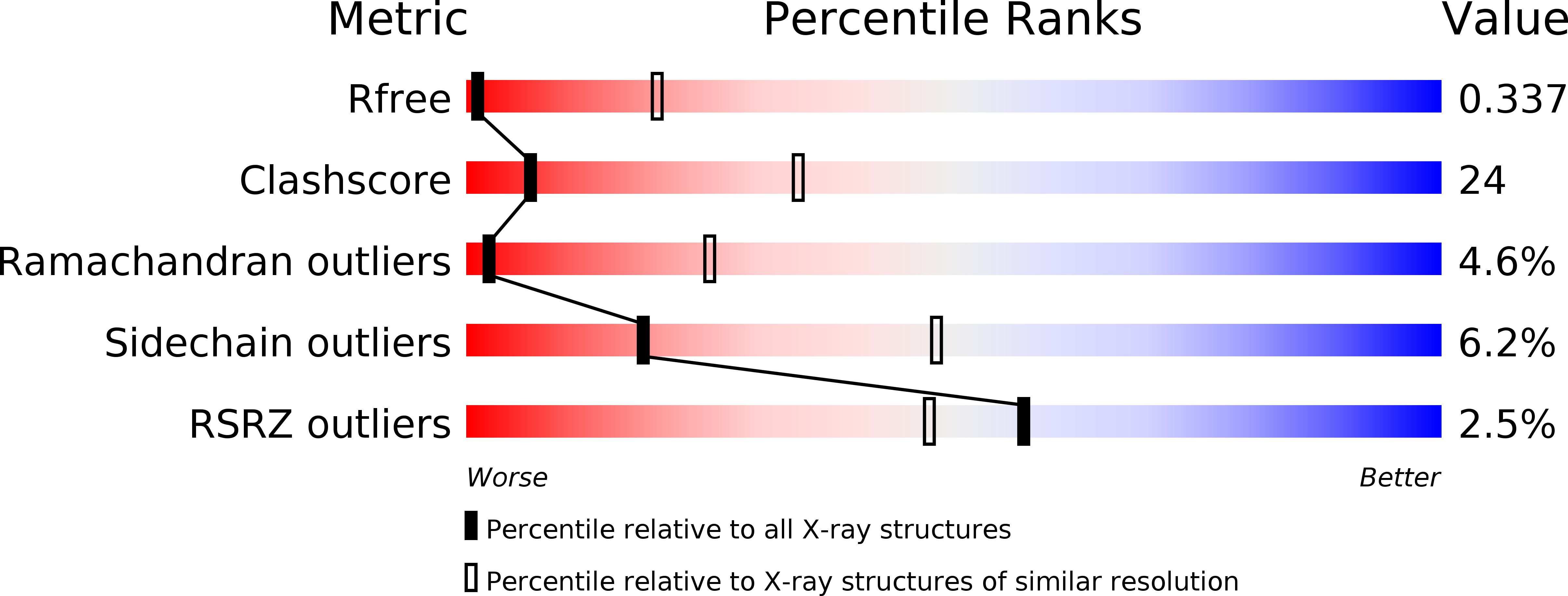
Resolution:
3.87 Å
R-Value Free:
0.34
R-Value Work:
0.32
R-Value Observed:
0.32
Space Group:
P 21 3