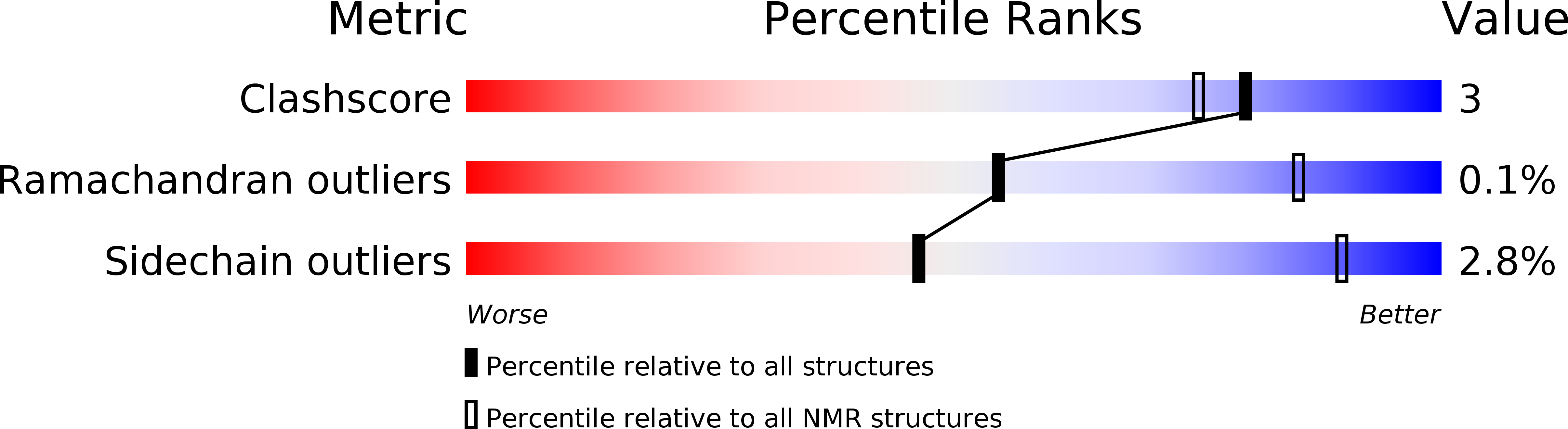Deposition Date
2016-05-09
Release Date
2016-08-24
Last Version Date
2024-05-01
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
5JTM
Keywords:
Title:
The structure of chaperone SecB in complex with unstructured PhoA binding site a
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Escherichia coli (strain 55989 / EAEC) (Taxon ID: 585055)
Escherichia coli (strain K12) (Taxon ID: 83333)
Escherichia coli (strain K12) (Taxon ID: 83333)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
100
Conformers Submitted:
20
Selection Criteria:
target function