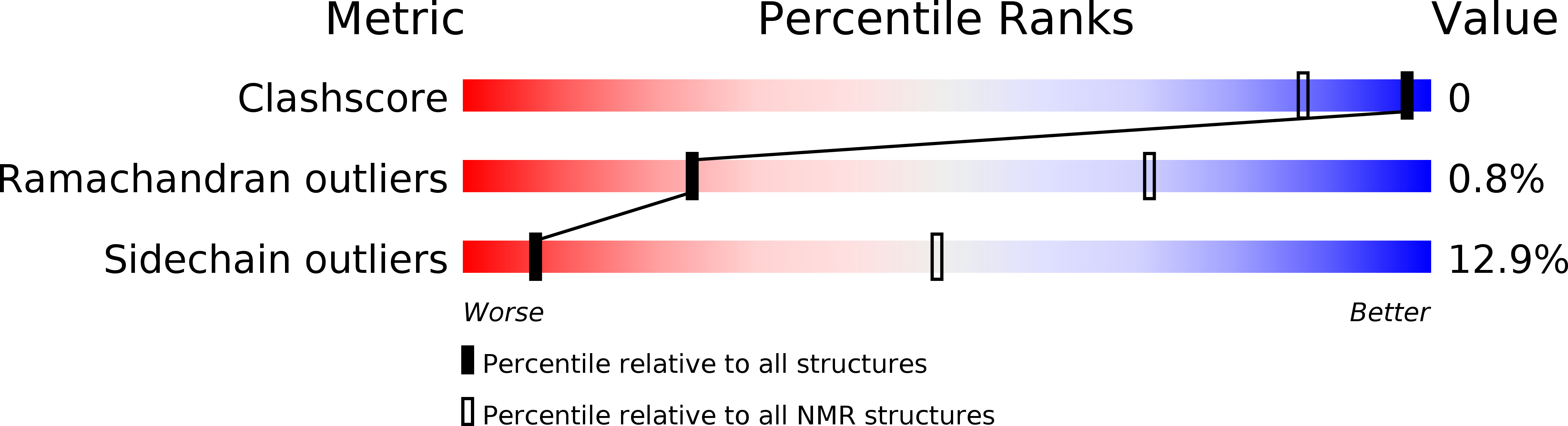
Deposition Date
2016-05-04
Release Date
2016-08-17
Last Version Date
2025-12-17
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
5JPW
Keywords:
Title:
Molecular basis for protein recognition specificity of the DYNLT1/Tctex1 canonical binding groove. Characterization of the interaction with activin receptor IIB
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
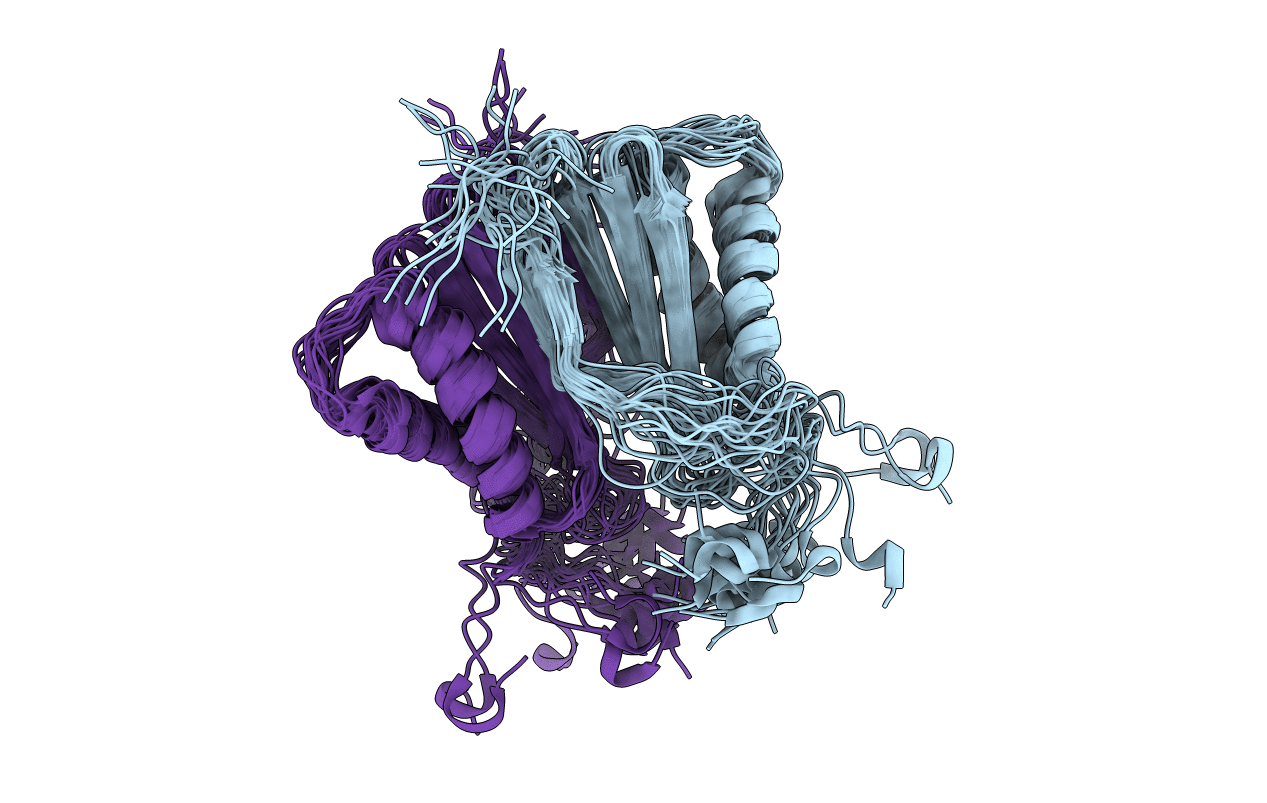
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
100
Conformers Submitted:
20
Selection Criteria:
structures with the lowest energy