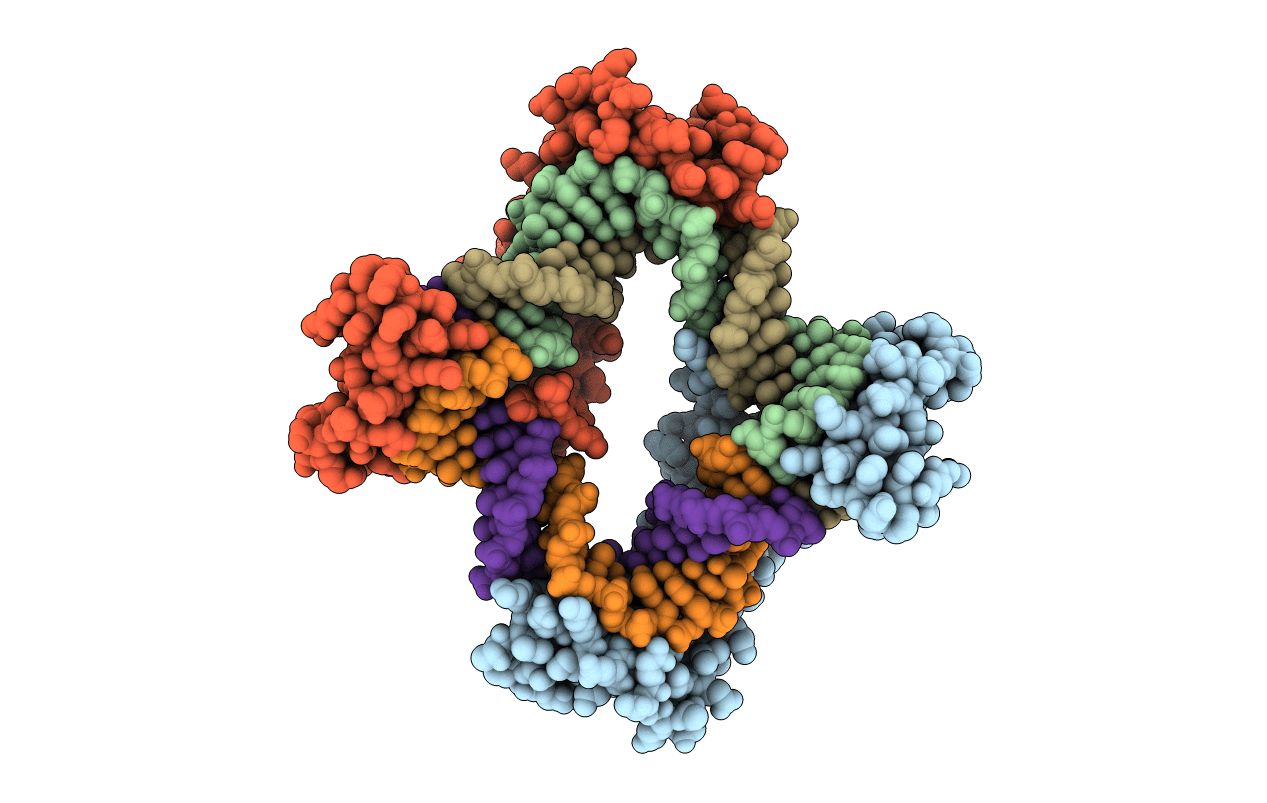
Deposition Date
2016-04-20
Release Date
2017-02-08
Last Version Date
2024-05-01
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
5JH0
Keywords:
Title:
Crystal structure of the mitochondrial DNA packaging protein Abf2p in complex with DNA at 2.18 Angstrom resolution
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Taxon ID: 559292)
Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Taxon ID: 4932)
Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Taxon ID: 4932)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
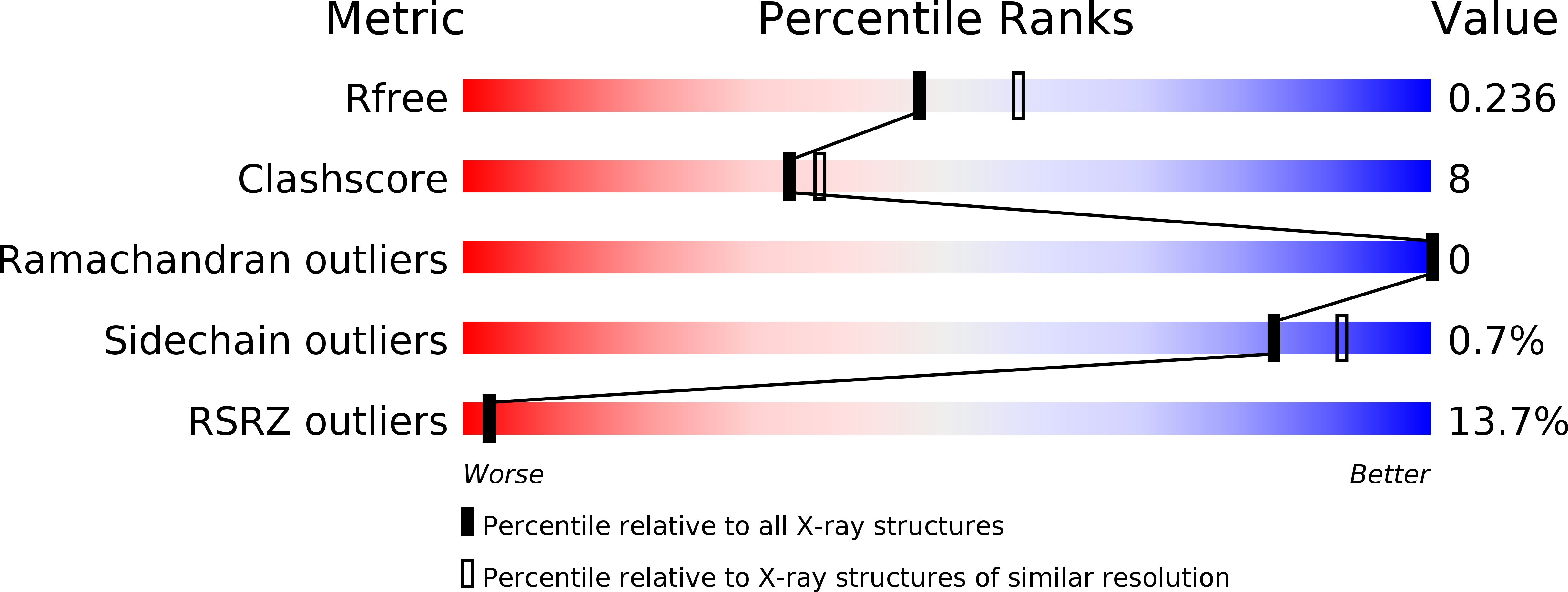
Resolution:
2.18 Å
R-Value Free:
0.23
R-Value Work:
0.20
R-Value Observed:
0.21
Space Group:
C 1 2 1