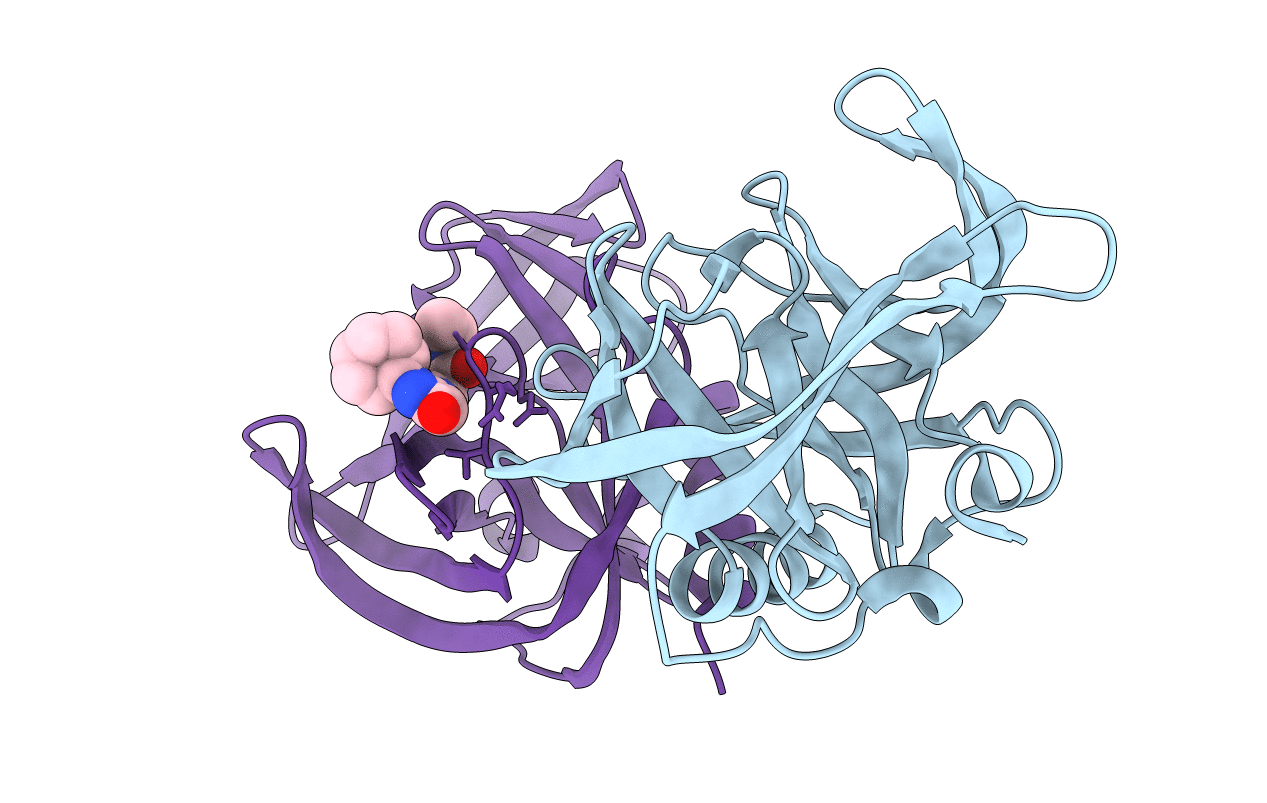
Deposition Date
2016-03-24
Release Date
2016-10-05
Last Version Date
2025-10-01
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
5IYT
Keywords:
Title:
Complex structure of EV-B93 main protease 3C with N-Ethyl 4-((1-cycloheptyl-1,2-dihydropyrazol-3-one-5-yl)-amino)-4-oxo-2Z-butenamide
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Echovirus 1 (strain Human/Egypt/Farouk/1951) (Taxon ID: 103908)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
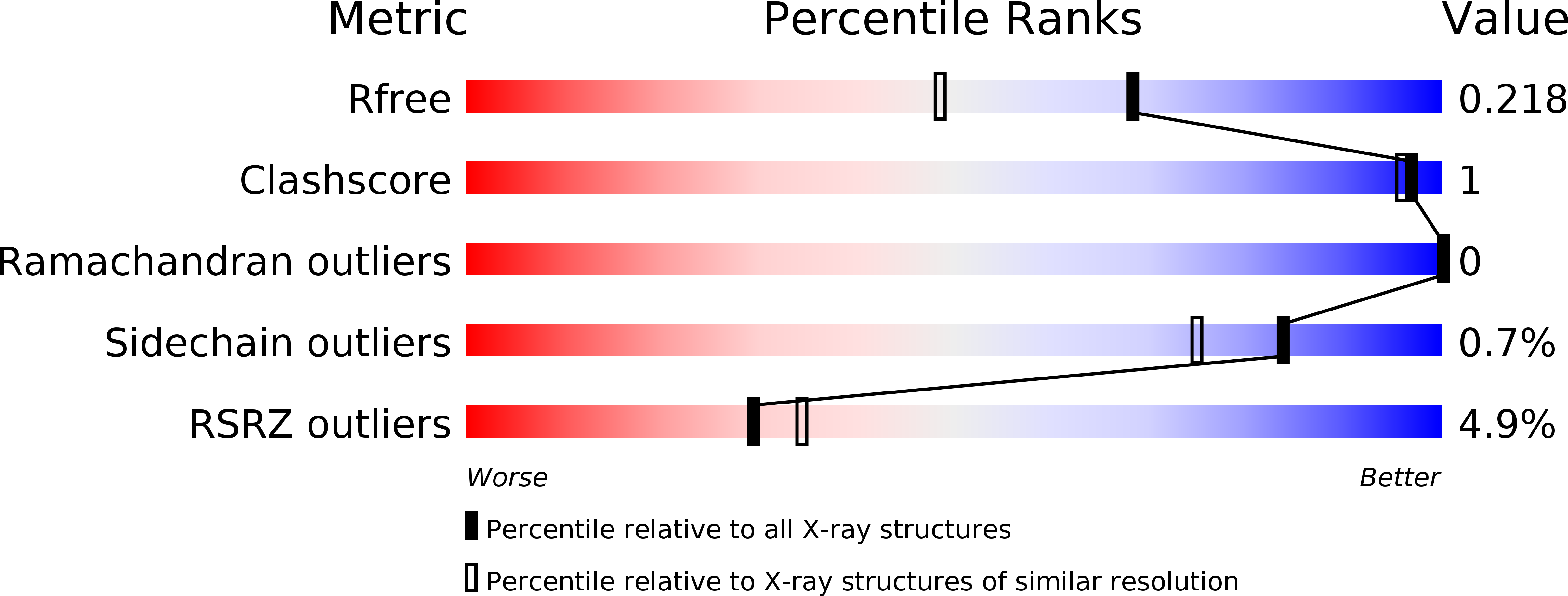
Resolution:
1.73 Å
R-Value Free:
0.21
R-Value Work:
0.18
R-Value Observed:
0.18
Space Group:
P 1 21 1