Deposition Date
2016-03-07
Release Date
2016-12-28
Last Version Date
2023-09-27
Entry Detail
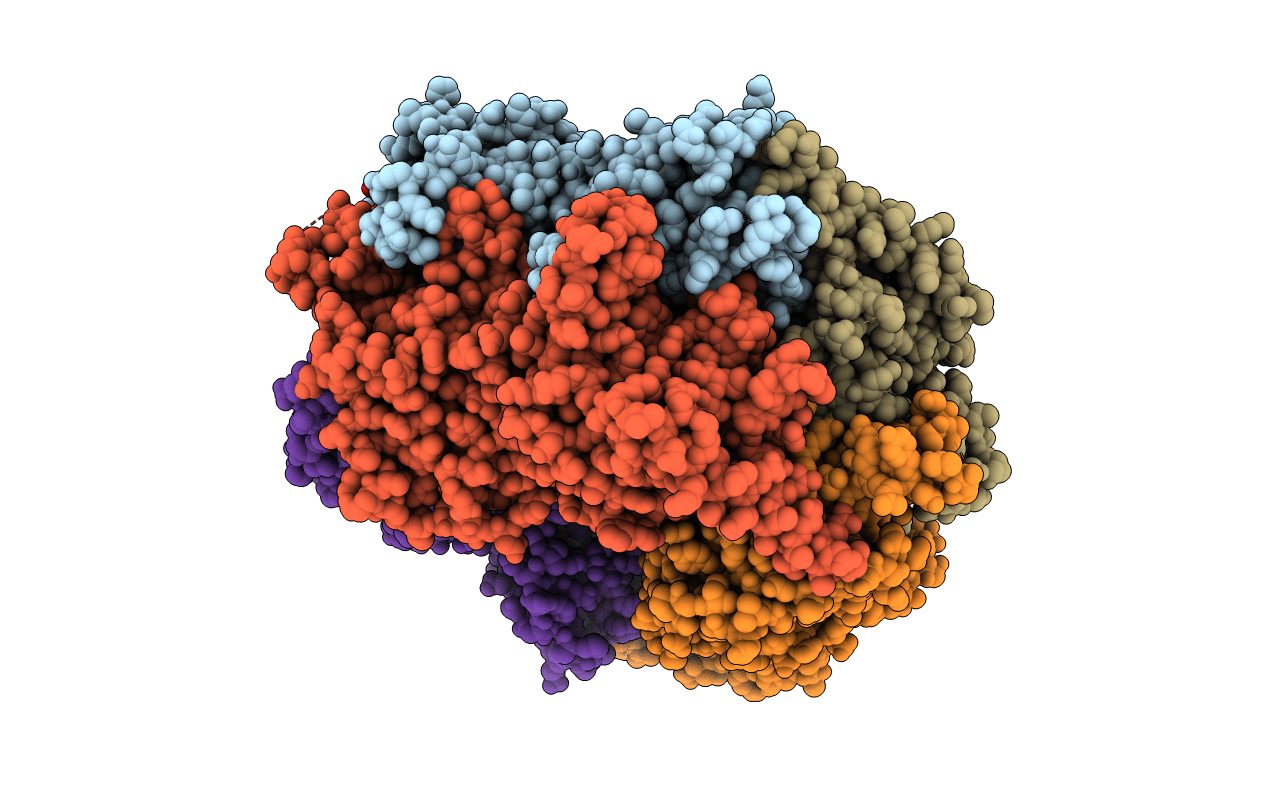
PDB ID:
5INI
Keywords:
Title:
Structural basis for acyl-CoA carboxylase-mediated assembly of unusual polyketide synthase extender units incorporated into the stambomycin antibiotics
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Streptomyces ambofaciens ATCC 23877 (Taxon ID: 278992)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
2.85 Å
R-Value Free:
0.23
R-Value Work:
0.17
R-Value Observed:
0.17
Space Group:
P 21 21 21


