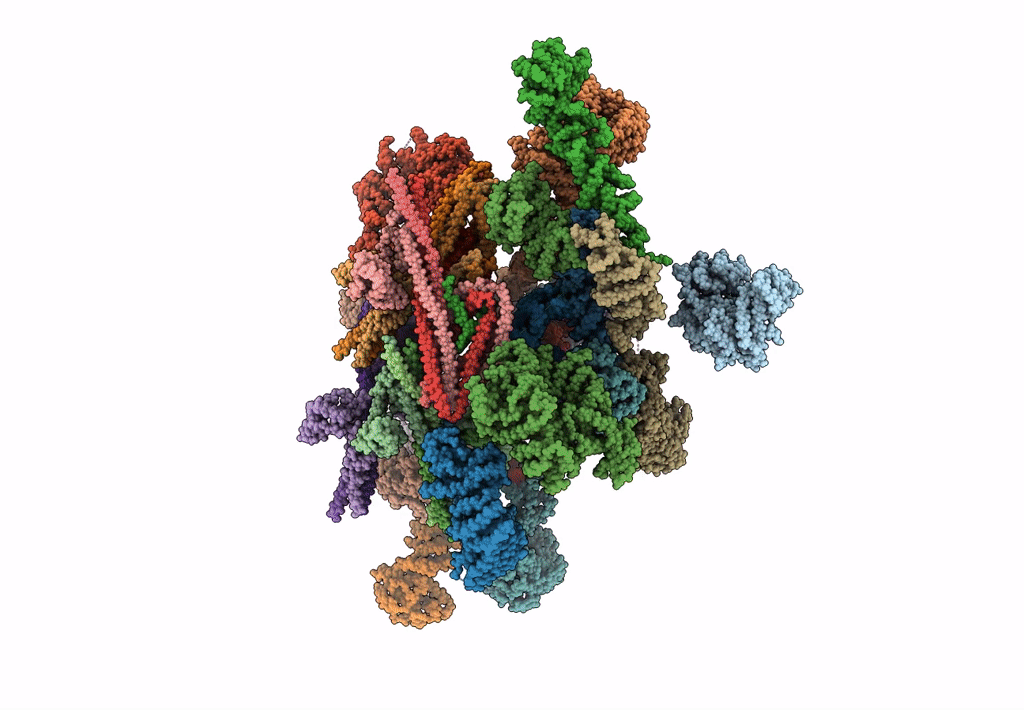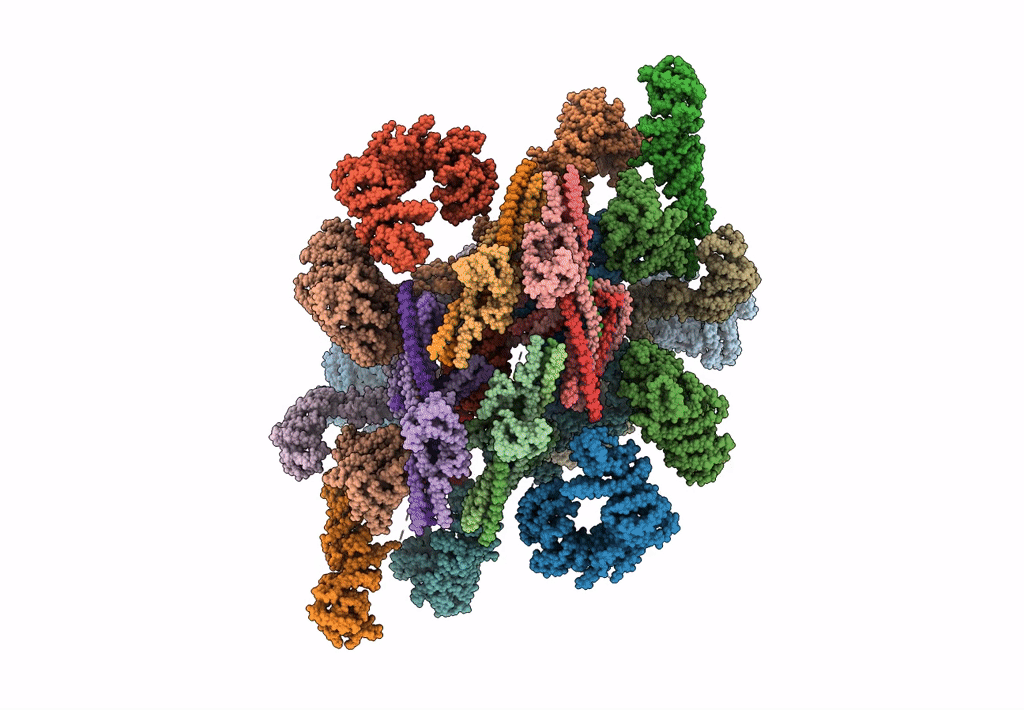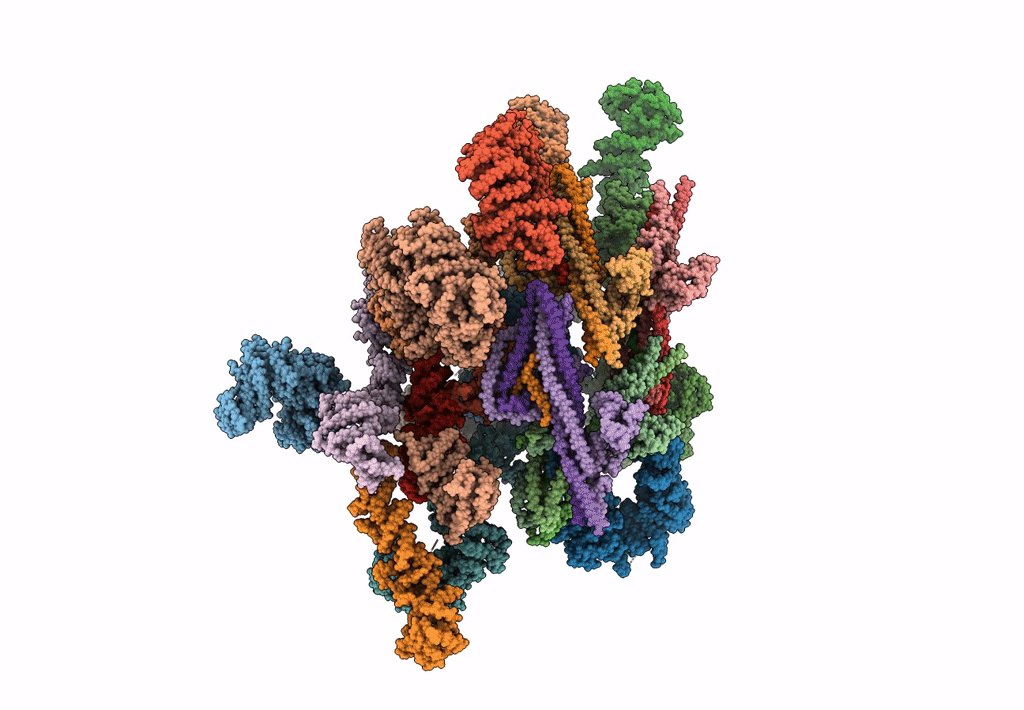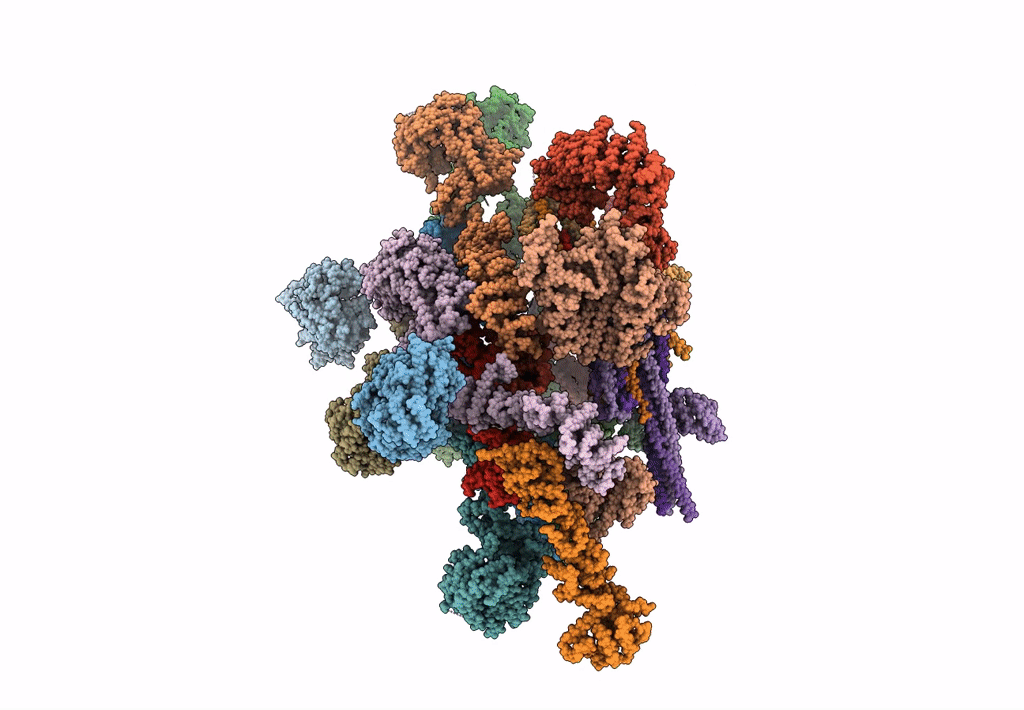
Deposition Date
2016-03-02
Release Date
2016-04-27
Last Version Date
2024-05-08
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
5IJO
Keywords:
Title:
Alternative composite structure of the inner ring of the human nuclear pore complex (16 copies of Nup188, 16 copies of Nup205)
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
21.40 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SUBTOMOGRAM AVERAGING


