Deposition Date
2016-01-26
Release Date
2016-04-13
Last Version Date
2024-03-06
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
5HSZ
Keywords:
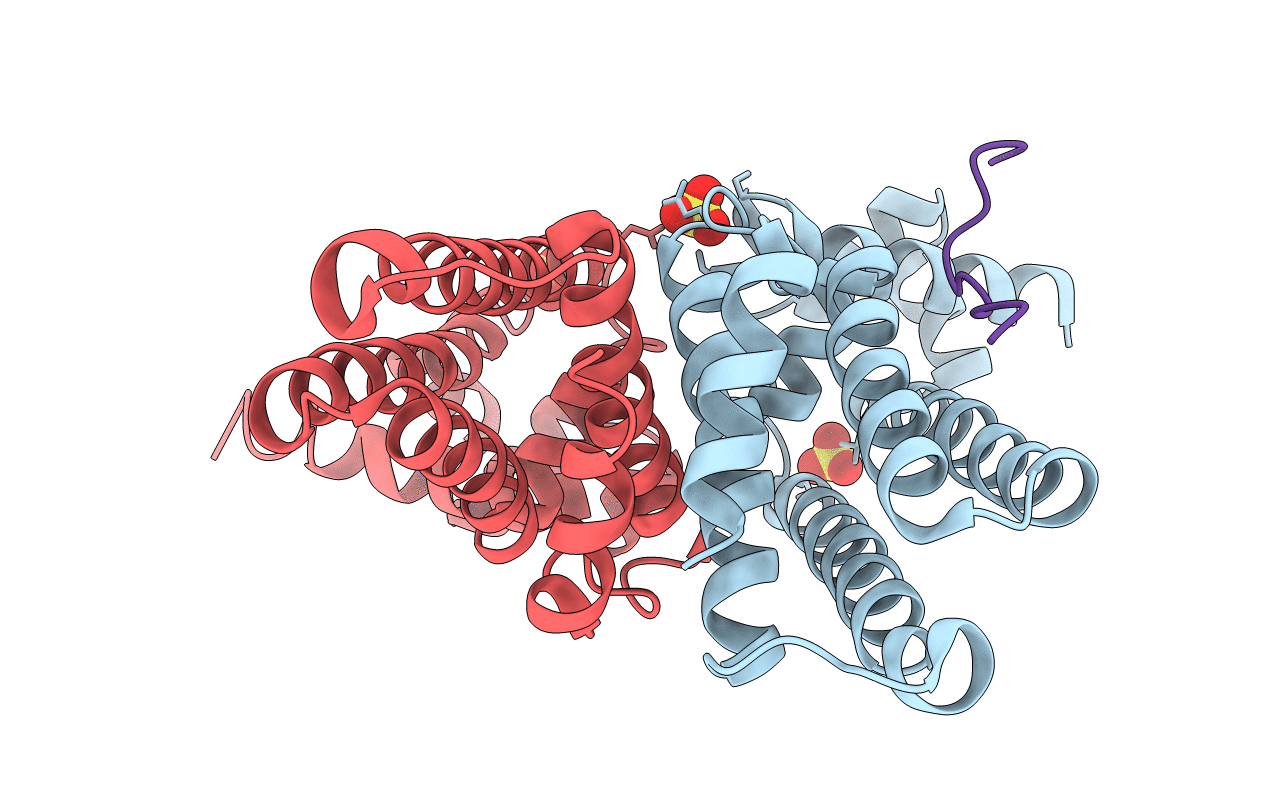
Title:
Structure of the K. pneumonia SlmA protein bound to the C-terminal tail of the cytoskeletal cell division protein FtsZ
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Klebsiella pneumoniae subsp. pneumoniae (strain ATCC 700721 / MGH 78578) (Taxon ID: 272620)
synthetic construct (Taxon ID: 32630)
synthetic construct (Taxon ID: 32630)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
2.30 Å
R-Value Free:
0.26
R-Value Work:
0.21
R-Value Observed:
0.22
Space Group:
P 65 2 2


