Deposition Date
2015-10-12
Release Date
2016-05-11
Last Version Date
2024-01-10
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
5FJS
Keywords:
Title:
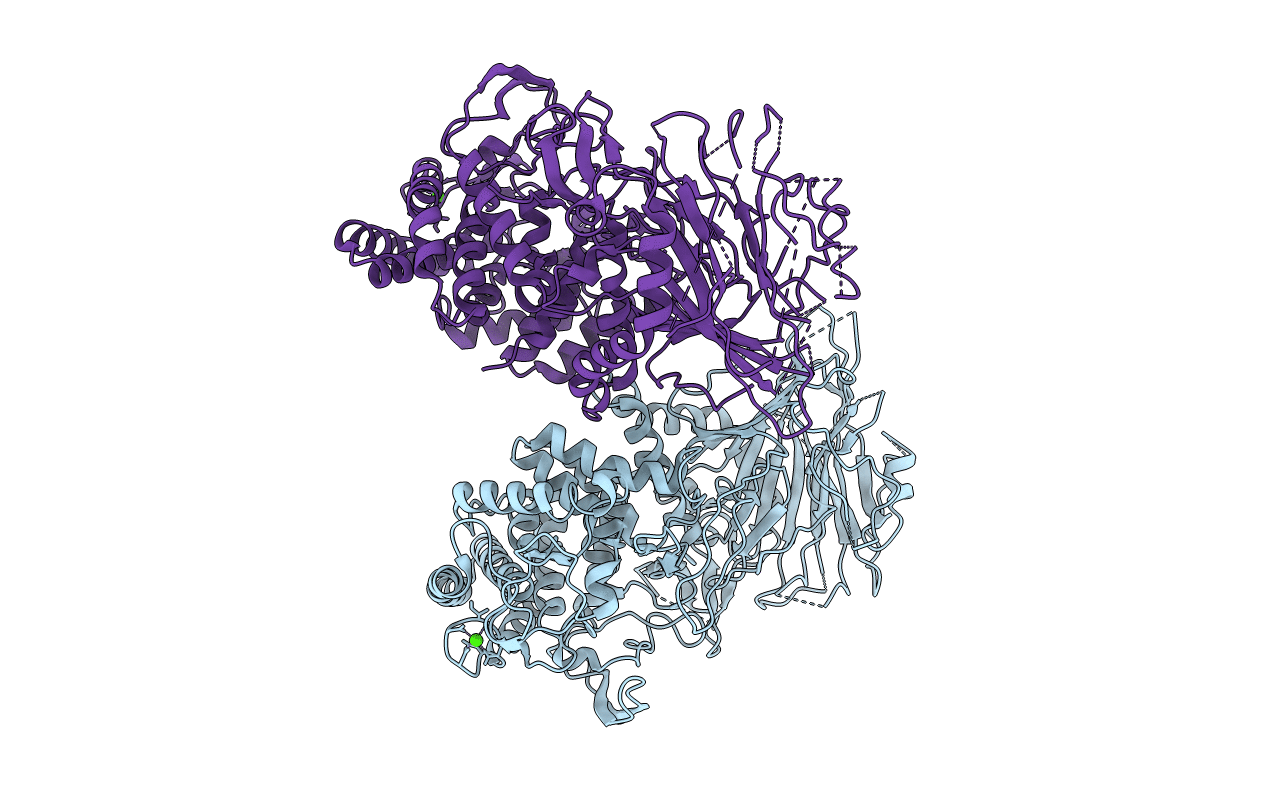
Bacterial beta-glucosidase reveals the structural and functional basis of genetic defects in human glucocerebrosidase 2 (GBA2)
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
THERMOANAEROBACTERIUM XYLANOLYTICUM (Taxon ID: 858215)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
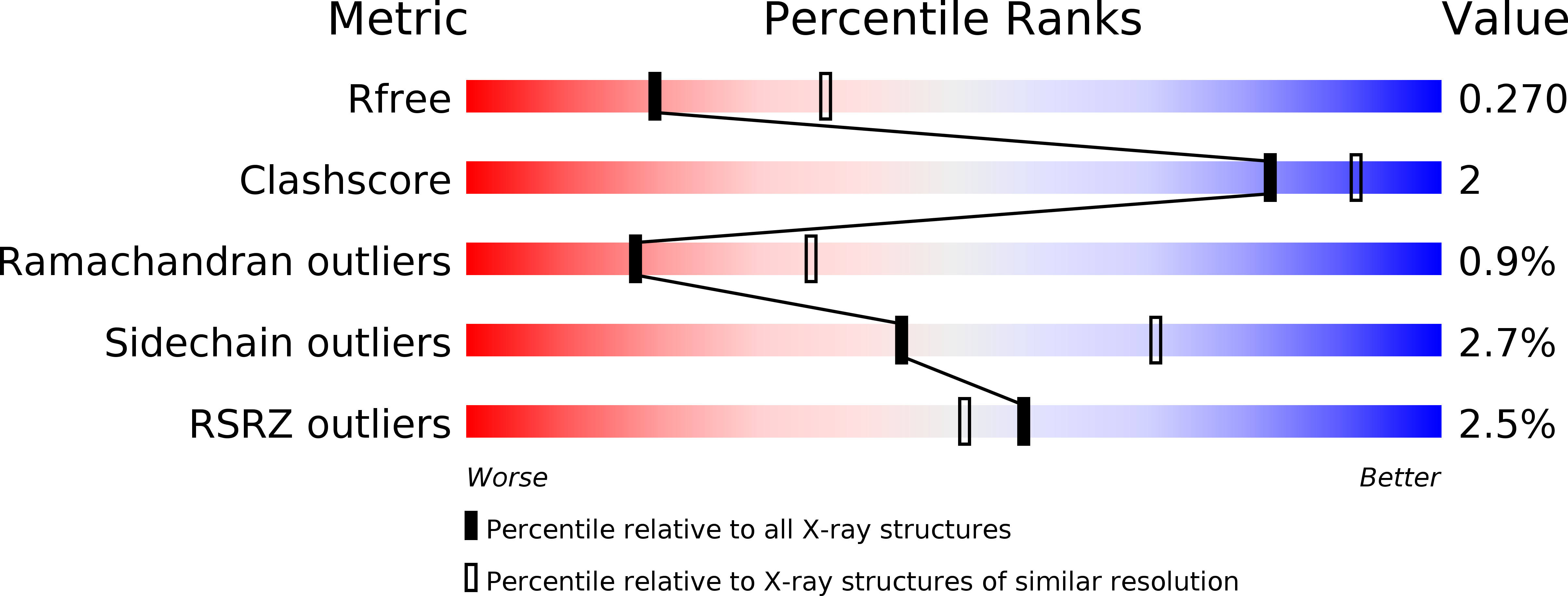
Resolution:
2.60 Å
R-Value Free:
0.26
R-Value Work:
0.20
R-Value Observed:
0.20
Space Group:
P 61