Deposition Date
2015-11-30
Release Date
2016-03-16
Last Version Date
2024-10-30
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
5F1C
Keywords:
Title:
Crystal structure of an invertebrate P2X receptor from the Gulf Coast tick in the presence of ATP and Zn2+ ion at 2.9 Angstroms
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Amblyomma maculatum (Taxon ID: 34609)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
2.90 Å
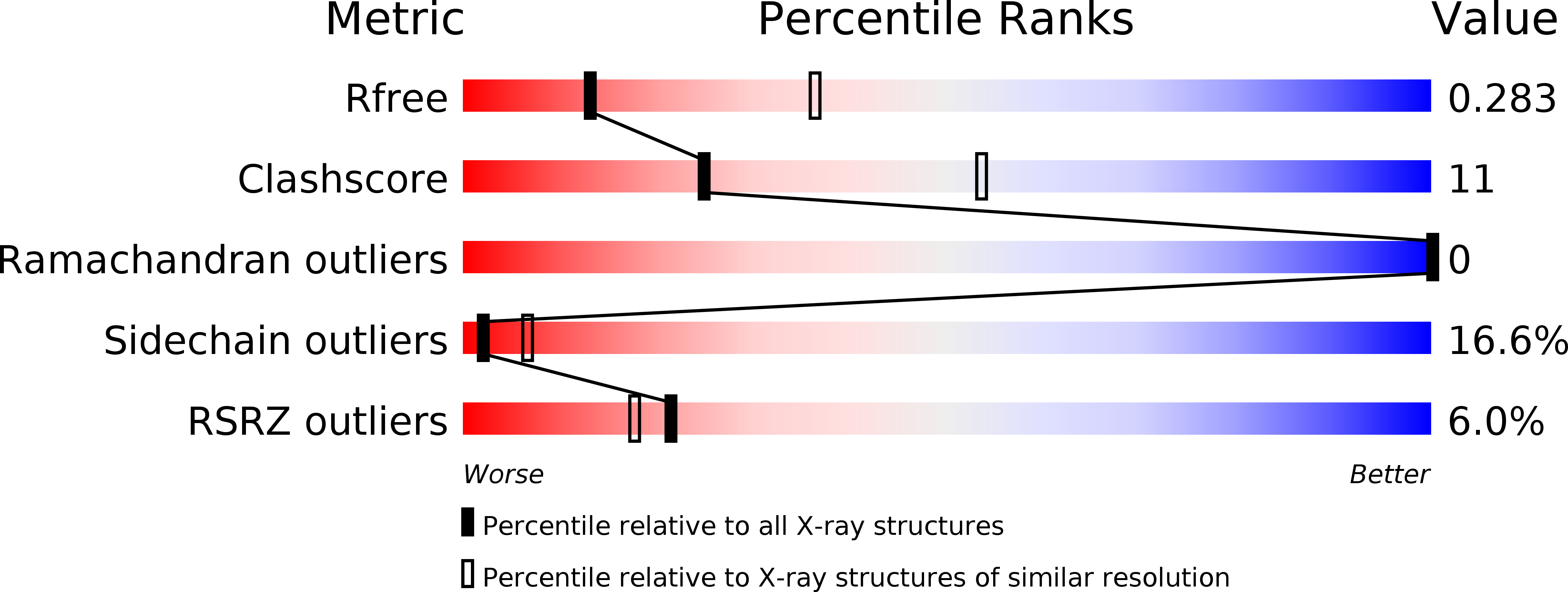
R-Value Free:
0.28
R-Value Work:
0.25
R-Value Observed:
0.25
Space Group:
P 21 21 21