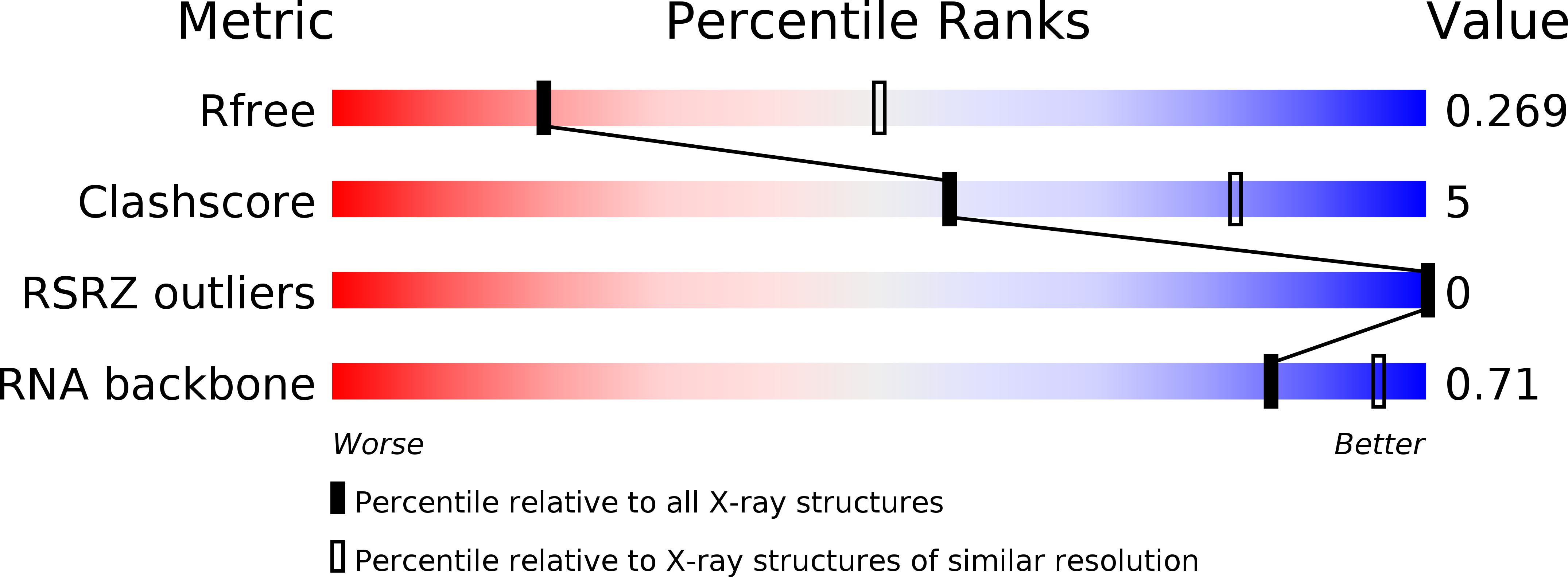
Deposition Date
2015-10-16
Release Date
2016-02-24
Last Version Date
2023-09-27
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
5EAO
Keywords:
Title:
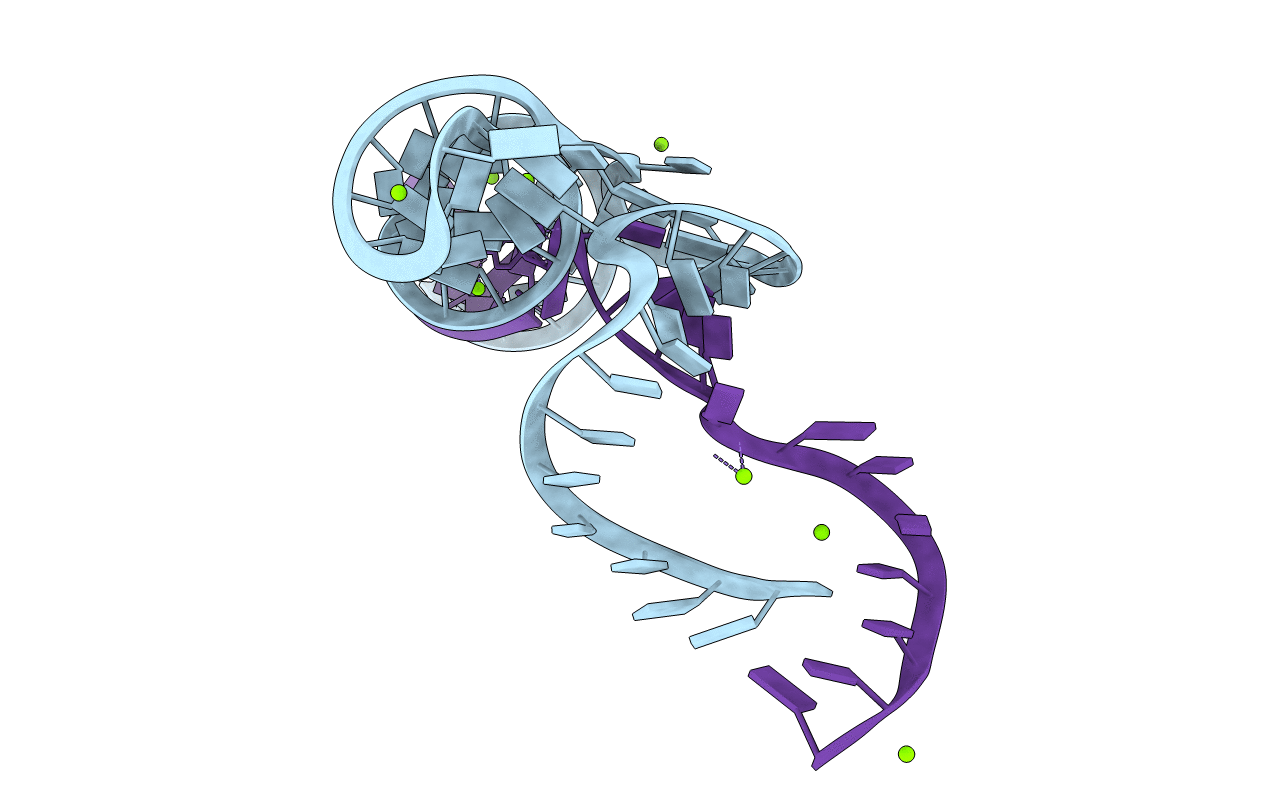
Two active site divalent ion in the crystal structure of the hammerhead ribozyme bound to a transition state analog-Mg2+
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
synthetic construct (Taxon ID: 32630)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
2.99 Å
R-Value Free:
0.26
R-Value Work:
0.22
R-Value Observed:
0.23
Space Group:
C 2 2 21