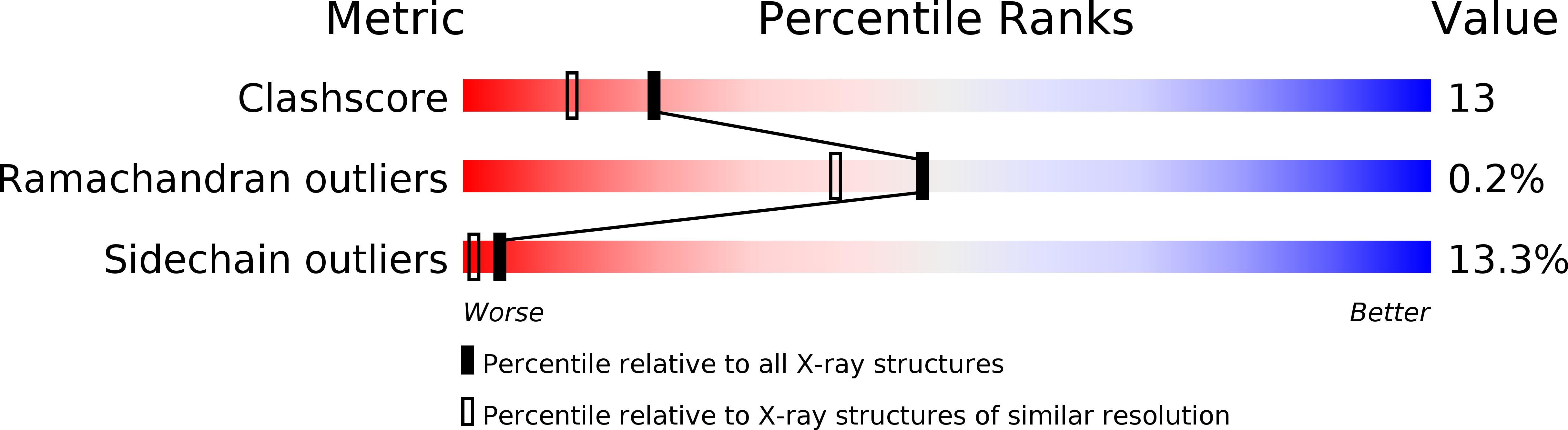Deposition Date
1989-11-16
Release Date
1990-10-15
Last Version Date
2024-03-06
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
5CTS
Keywords:
Title:
PROPOSED MECHANISM FOR THE CONDENSATION REACTION OF CITRATE SYNTHASE. 1.9-ANGSTROMS STRUCTURE OF THE TERNARY COMPLEX WITH OXALOACETATE AND CARBOXYMETHYL COENZYME A
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Gallus gallus (Taxon ID: 9031)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
1.90 Å
R-Value Observed:
0.18
Space Group:
C 1 2 1