Deposition Date
2015-03-20
Release Date
2015-07-15
Last Version Date
2023-11-08
Entry Detail
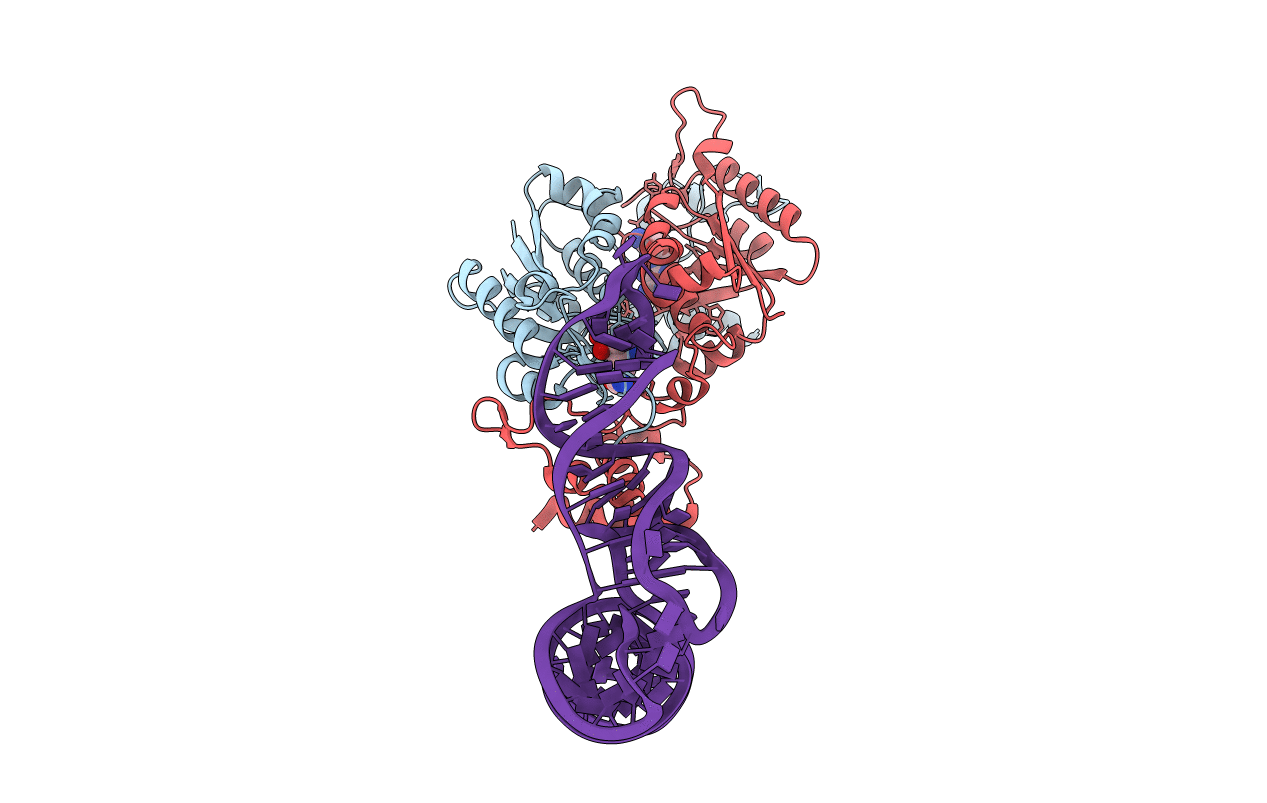
PDB ID:
4YVI
Keywords:
Title:
Crystal Structure of H. influenzae TrmD in complex with sinefungin and tRNA
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Haemophilus influenzae (strain ATCC 51907 / DSM 11121 / KW20 / Rd) (Taxon ID: 71421)
Thermotoga maritima MSB8 (Taxon ID: 243274)
Thermotoga maritima MSB8 (Taxon ID: 243274)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
3.01 Å
R-Value Free:
0.28
R-Value Work:
0.21
R-Value Observed:
0.22
Space Group:
P 41 21 2


