Deposition Date
2014-07-07
Release Date
2014-10-01
Last Version Date
2024-10-16
Entry Detail
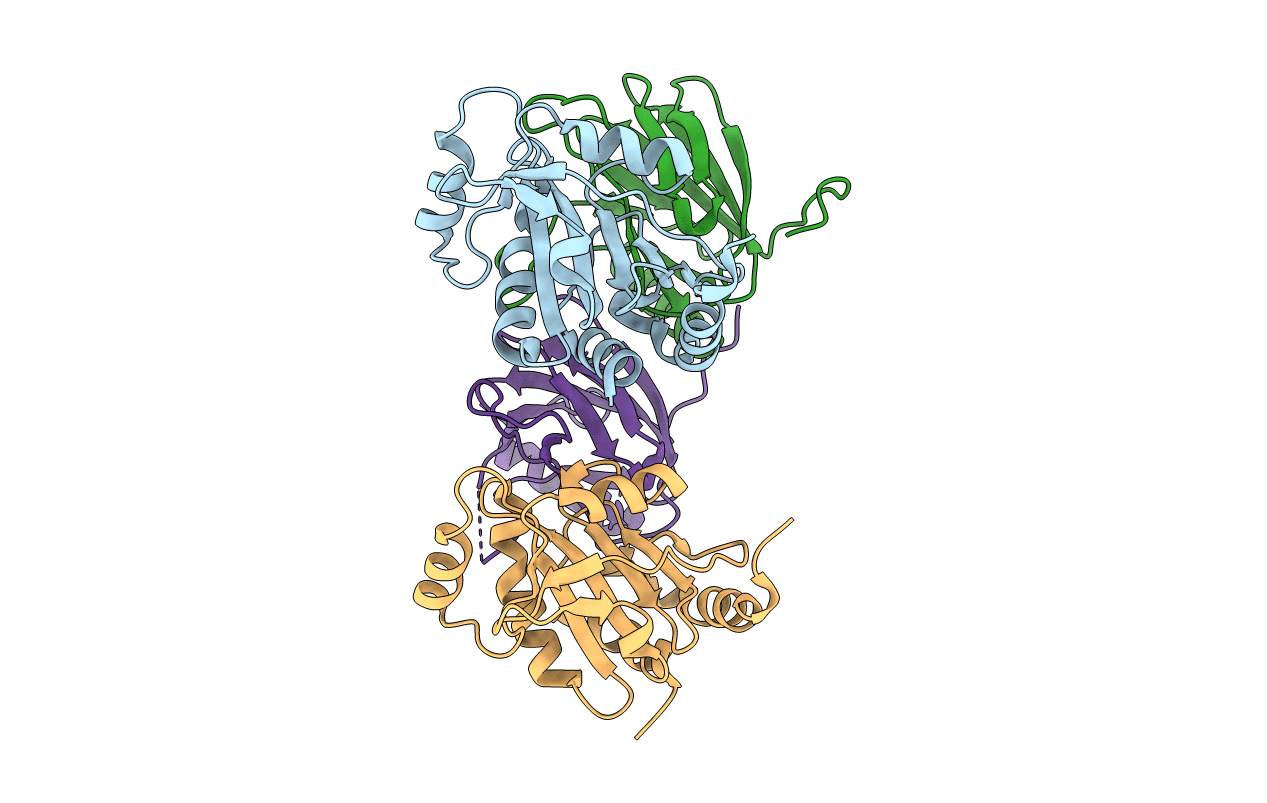
PDB ID:
4TXV
Keywords:
Title:
Crystal structure of the mixed disulfide intermediate between thioredoxin-like TlpAs(C110S) and subunit II of cytochrome c oxidase CoxBPD (C233S)
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Bradyrhizobium diazoefficiens (Taxon ID: 224911)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
2.00 Å
R-Value Free:
0.21
R-Value Work:
0.16
R-Value Observed:
0.16
Space Group:
P 21 21 21


