Deposition Date
1991-04-11
Release Date
1992-10-15
Last Version Date
2024-02-28
Entry Detail
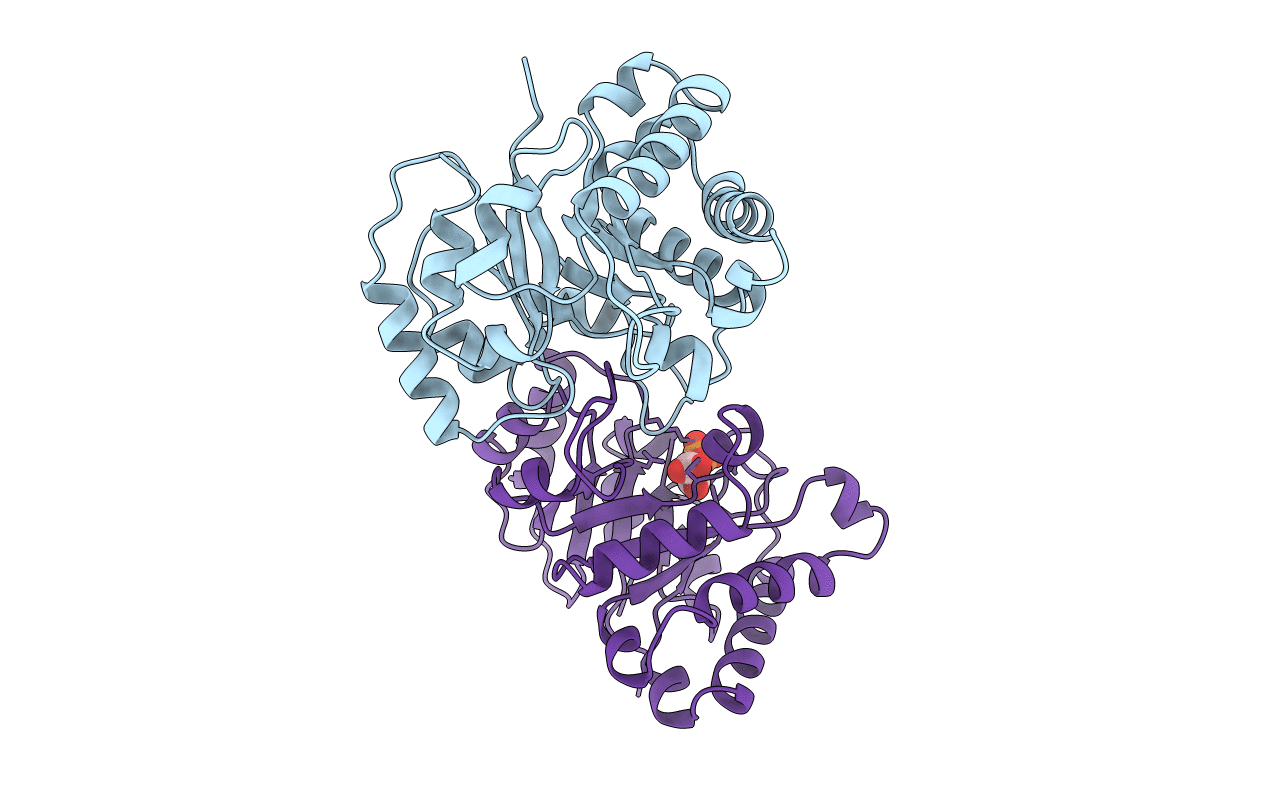
PDB ID:
4TIM
Keywords:
Title:
CRYSTALLOGRAPHIC AND MOLECULAR MODELING STUDIES ON TRYPANOSOMAL TRIOSEPHOSPHATE ISOMERASE: A CRITICAL ASSESSMENT OF THE PREDICTED AND OBSERVED STRUCTURES OF THE COMPLEX WITH 2-PHOSPHOGLYCERATE
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Trypanosoma brucei brucei (Taxon ID: 5702)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
2.40 Å
R-Value Observed:
0.14
Space Group:
P 21 21 21


