Deposition Date
2014-06-06
Release Date
2015-11-11
Last Version Date
2024-11-06
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
4QKM
Keywords:
Title:
Influenza A M2 wild type TM domain at low pH in the lipidic cubic phase under room temperature diffraction conditions
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Influenza A virus (Taxon ID: 385599)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
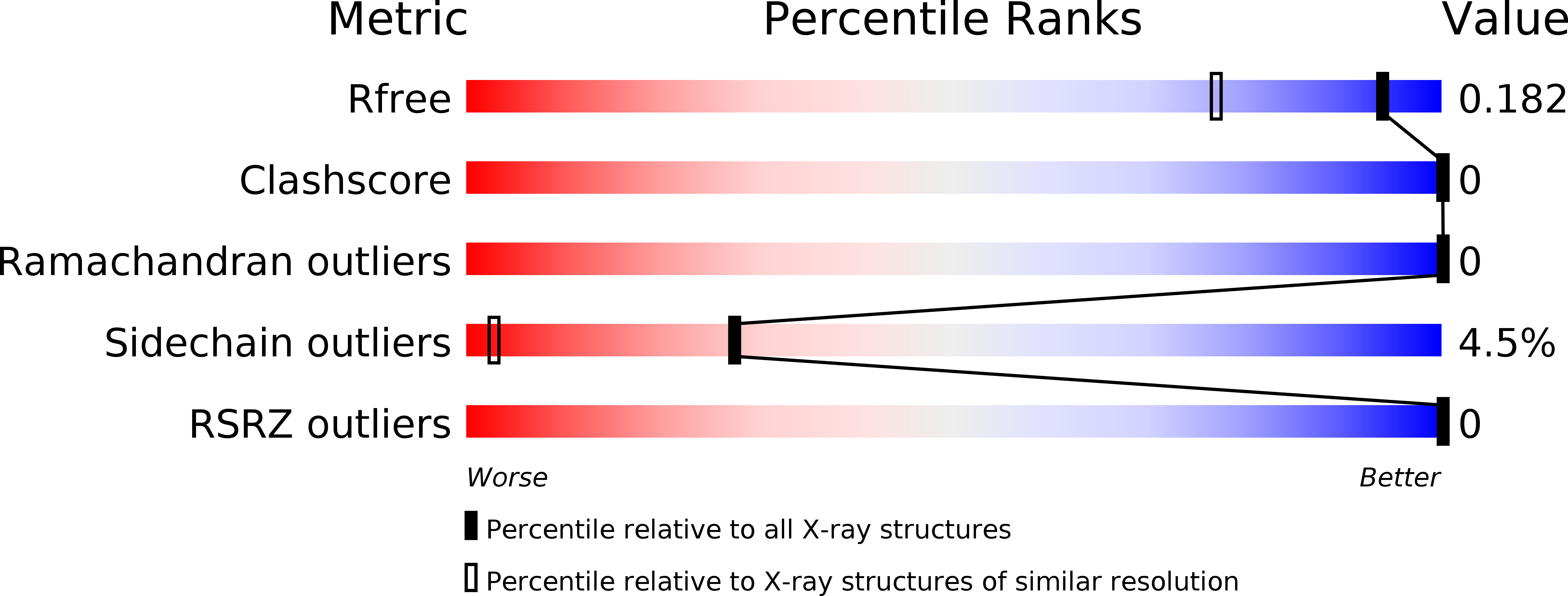
Resolution:
1.44 Å
R-Value Free:
0.18
R-Value Work:
0.14
R-Value Observed:
0.15
Space Group:
I 4