Deposition Date
2014-03-18
Release Date
2015-08-26
Last Version Date
2023-09-20
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
4PVZ
Keywords:
Title:
Structure of yeast importin a bound to the membrane protein Nuclear Localization Signal sequence of INM protein Heh2
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288c (Taxon ID: 559292)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
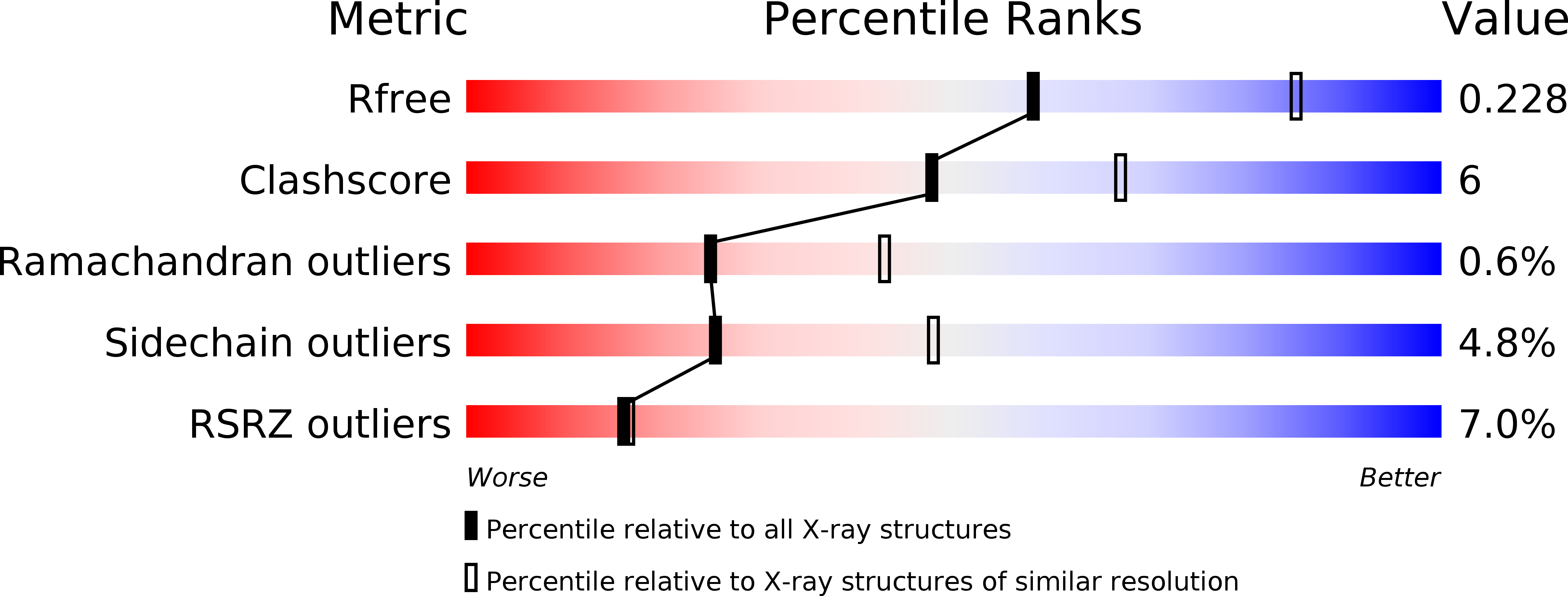
Resolution:
2.50 Å
R-Value Free:
0.22
R-Value Work:
0.19
R-Value Observed:
0.19
Space Group:
P 21 21 21