Deposition Date
2014-02-05
Release Date
2015-01-28
Last Version Date
2025-03-26
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
4OPB
Keywords:
Title:
AA13 Lytic polysaccharide monooxygenase from Aspergillus oryzae
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Aspergillus oryzae (Taxon ID: 510516)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
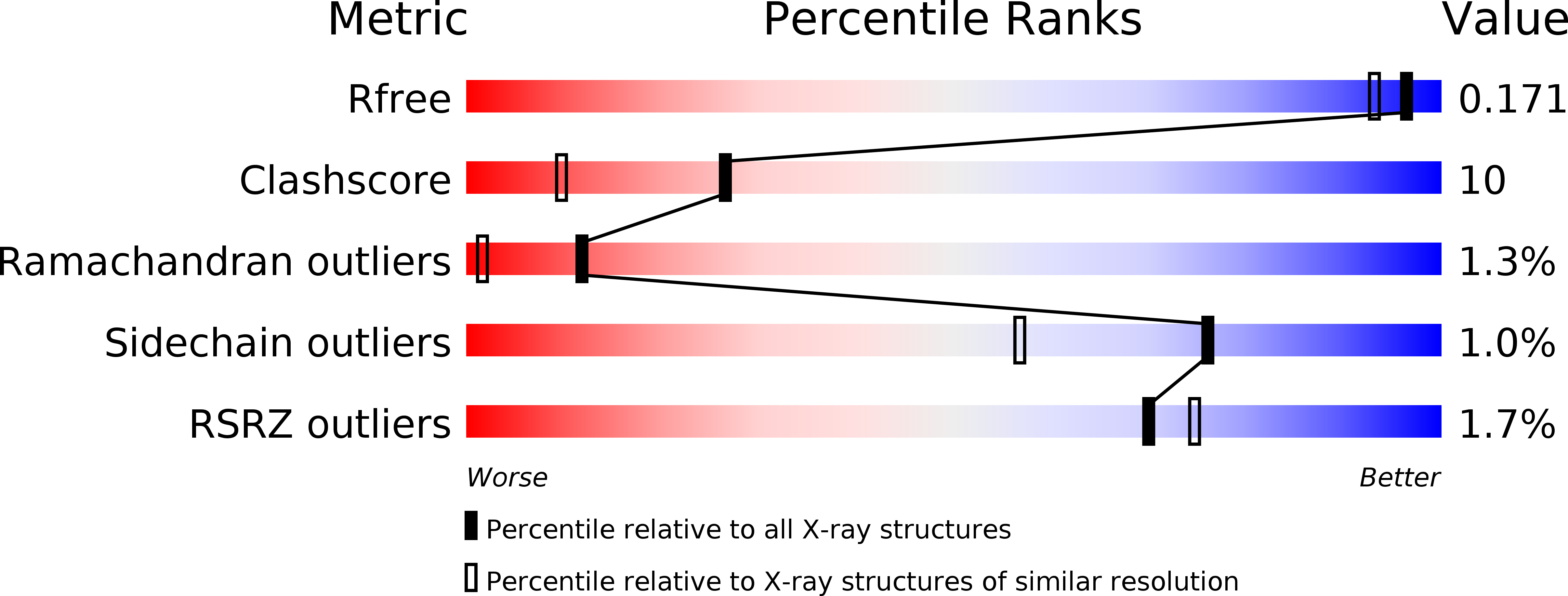
Resolution:
1.50 Å
R-Value Free:
0.16
R-Value Work:
0.11
R-Value Observed:
0.12
Space Group:
P 21 21 21