Deposition Date
2014-01-08
Release Date
2014-01-22
Last Version Date
2024-02-28
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
4OCB
Keywords:
Title:
Z-DNA dodecamer d(CGCGCGCGCGCG)2 at 0.75 A resolution solved by P-SAD
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
0.75 Å
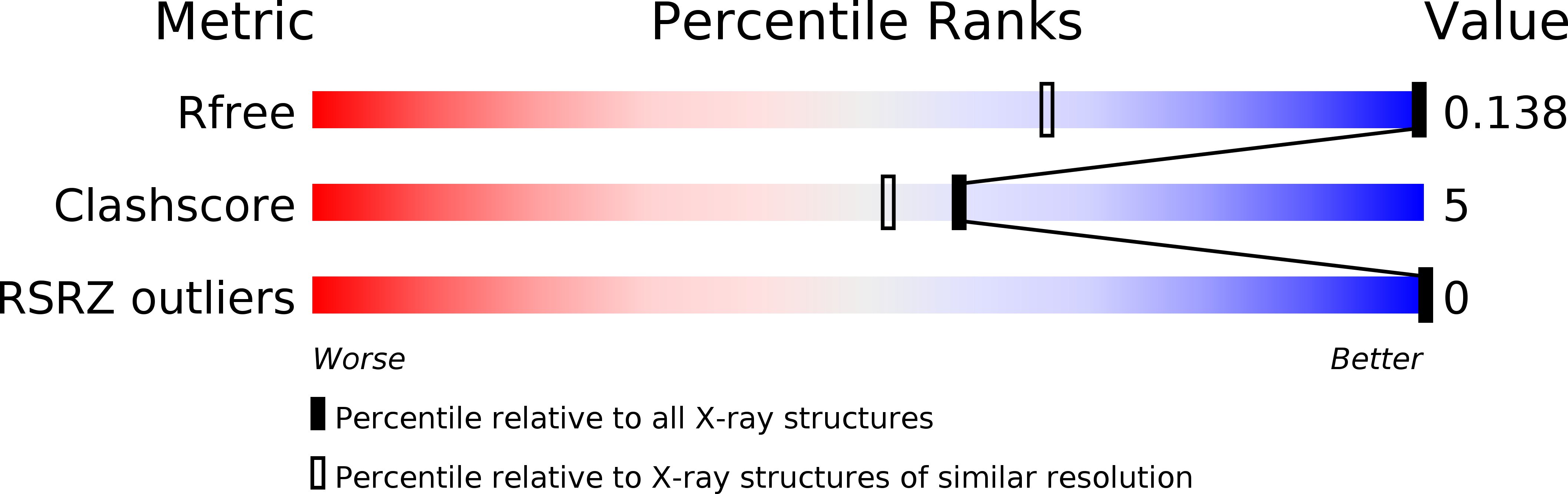
R-Value Free:
0.13
R-Value Work:
0.12
R-Value Observed:
0.12
Space Group:
C 1 2 1