Deposition Date
2013-12-10
Release Date
2014-03-12
Last Version Date
2024-02-28
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
4NYI
Keywords:
Title:
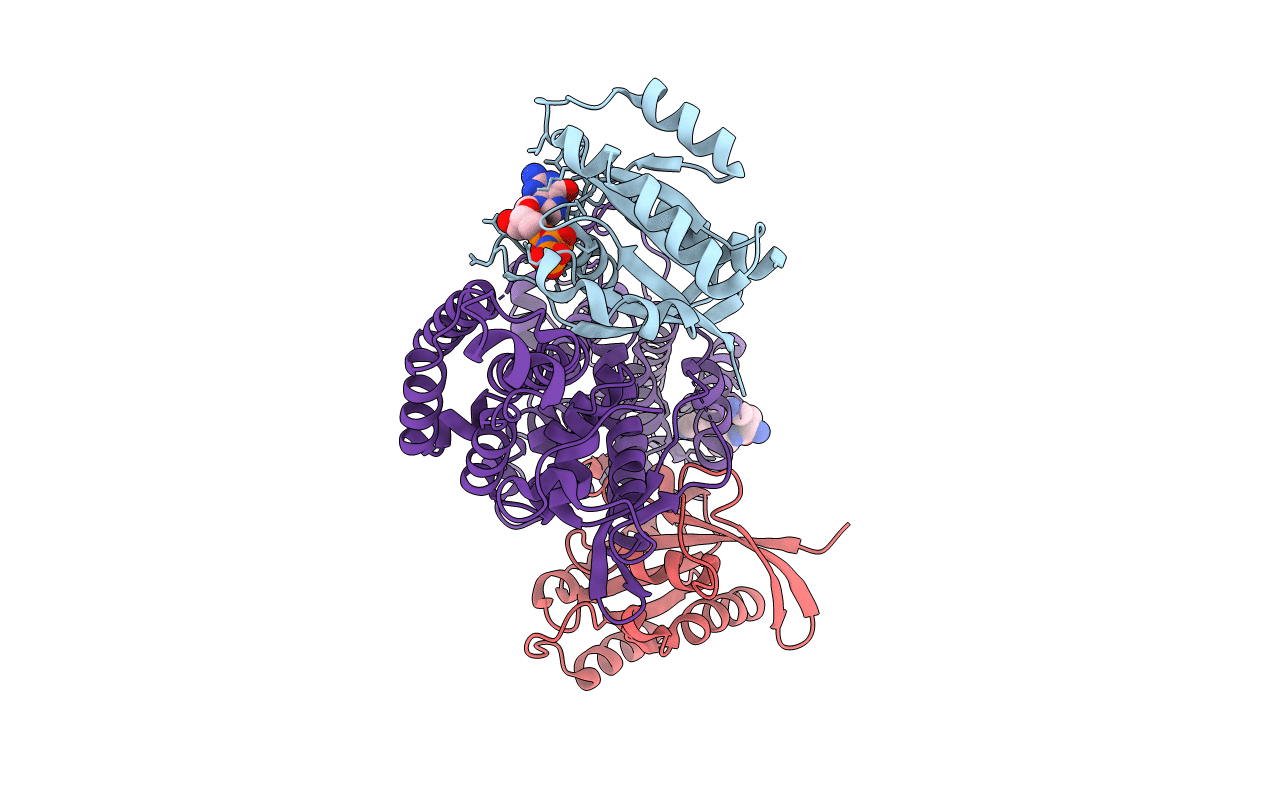
Approach for Targeting Ras with Small Molecules that Activate SOS-Mediated Nucleotide Exchange
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
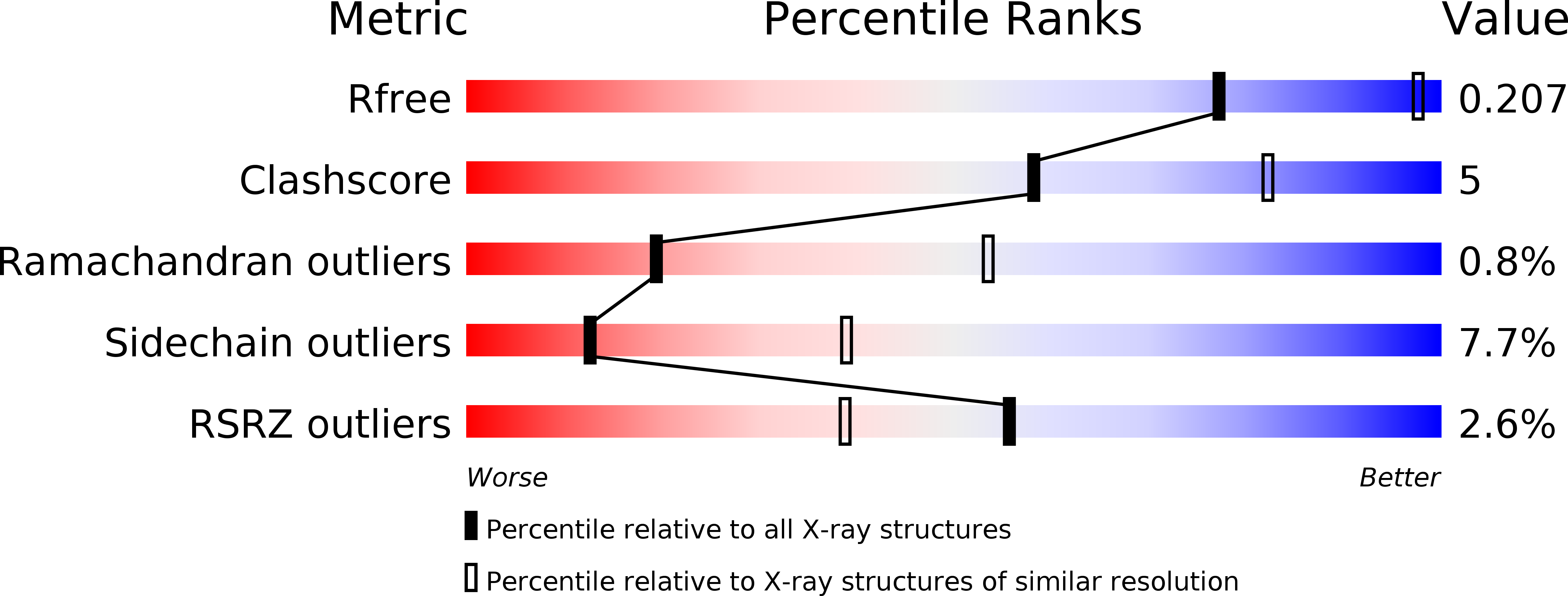
Resolution:
2.96 Å
R-Value Free:
0.20
R-Value Work:
0.16
R-Value Observed:
0.16
Space Group:
I 4 2 2