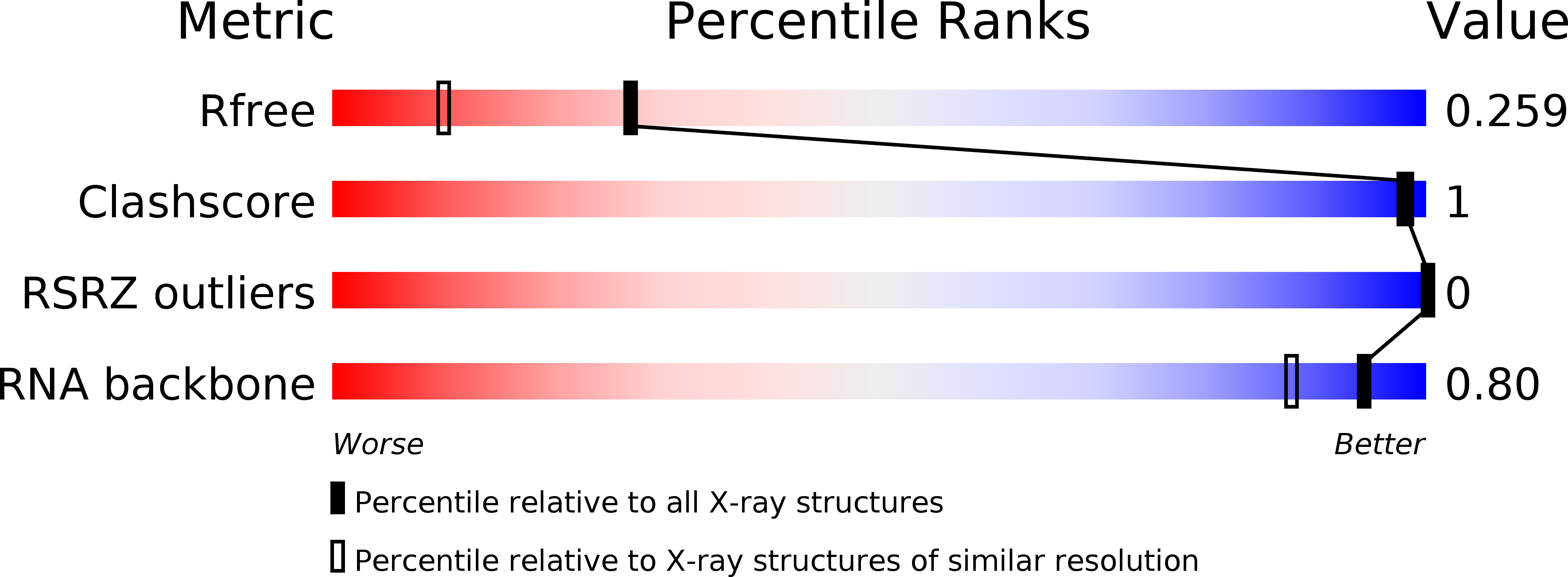Deposition Date
2013-10-31
Release Date
2014-07-02
Last Version Date
2024-02-28
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
4NFP
Keywords:
Title:
Crystal Structure Analysis of the 16mer GCAGNCUUAAGUCUGC containing 8-aza-7-deaza-7-ethynyl Adenosine
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
1.85 Å
R-Value Free:
0.24
R-Value Work:
0.22
R-Value Observed:
0.22
Space Group:
C 1 2 1