Deposition Date
2013-08-30
Release Date
2014-07-23
Last Version Date
2023-12-06
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
4MI3
Keywords:
Title:
Crystal structure of Gpb in complex with SUGAR (N-{(2R)-2-METHYL-3-[4-(PROPAN-2-YL)PHENYL]PROPANOYL}-BETA-D-GLUCOPYRANOSYLAMINE) (S21)
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Oryctolagus cuniculus (Taxon ID: 9986)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
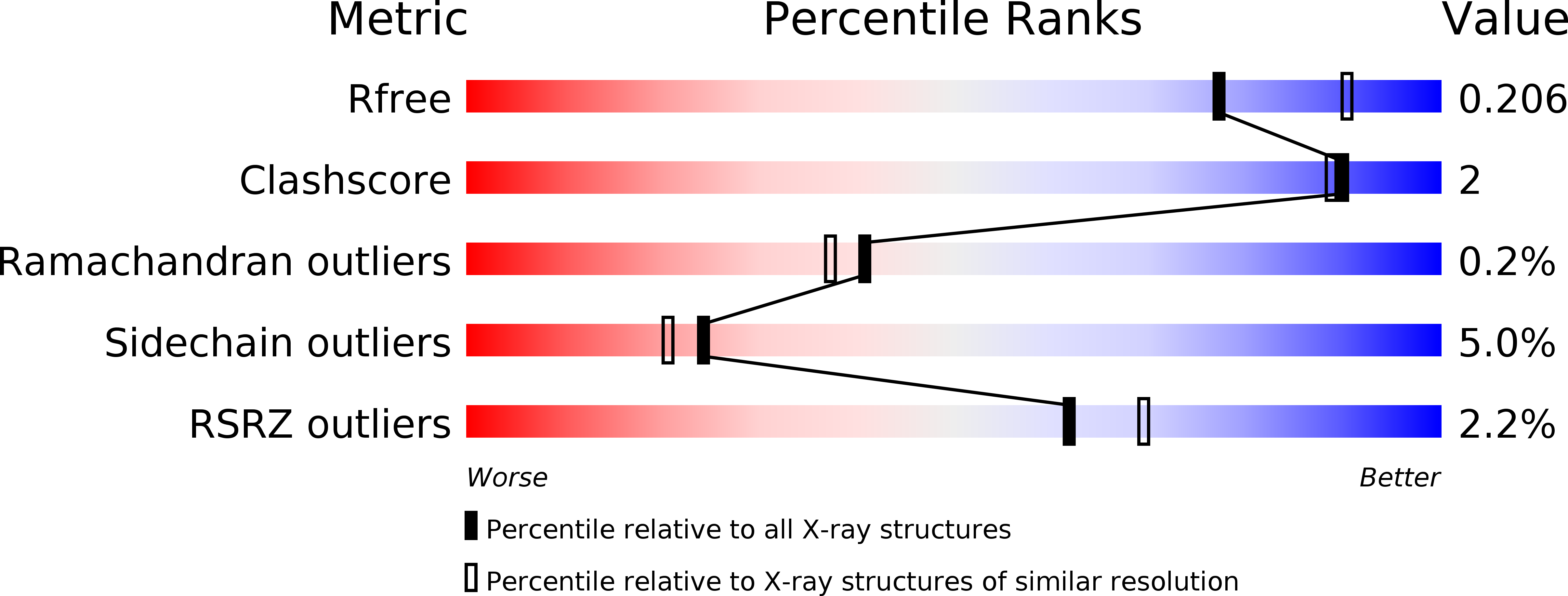
Resolution:
2.15 Å
R-Value Free:
0.20
R-Value Work:
0.16
R-Value Observed:
0.16
Space Group:
P 43 21 2