Deposition Date
2013-03-27
Release Date
2013-09-25
Last Version Date
2024-10-09
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
4JW3
Keywords:
Title:
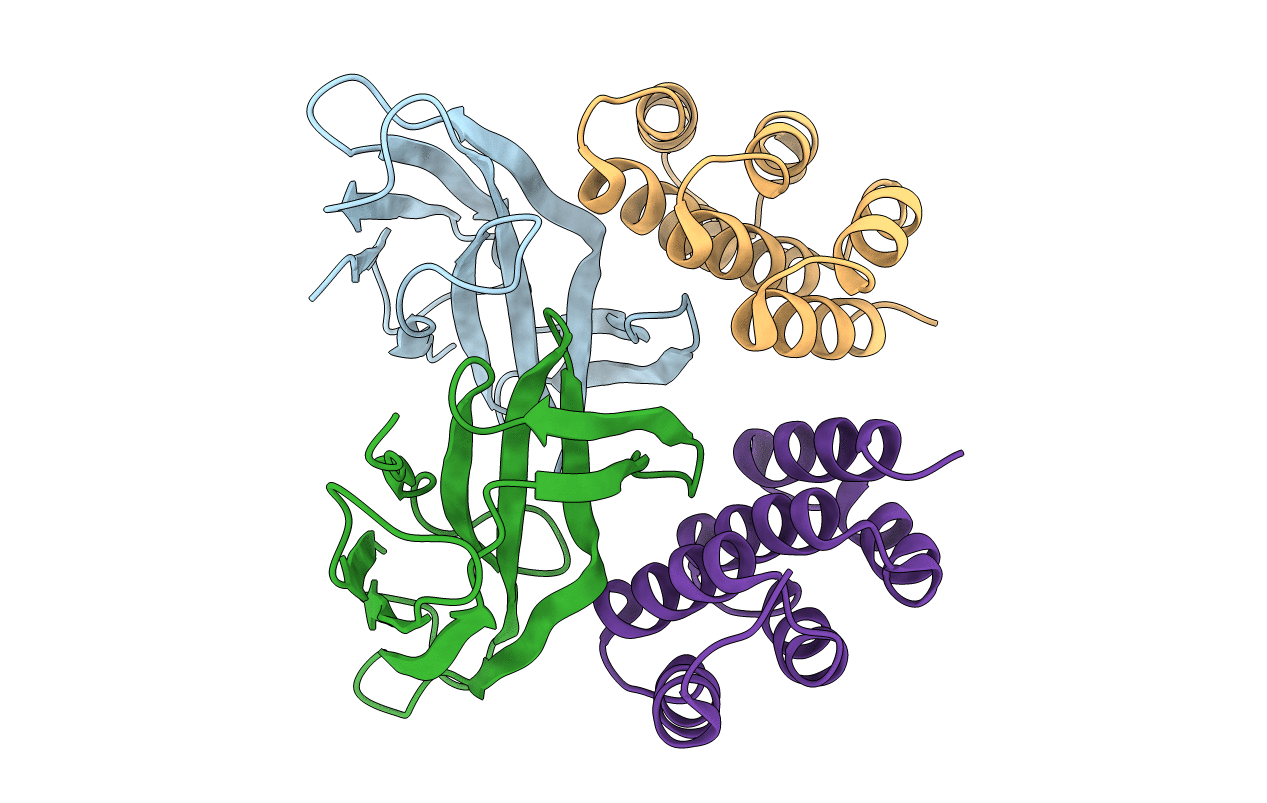
Selection of specific protein binders for pre-defined targets from an optimized library of artificial helicoidal repeat proteins (alphaRep)
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Streptomyces malayensis (Taxon ID: 1918)
synthetic construct (Taxon ID: 32630)
synthetic construct (Taxon ID: 32630)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
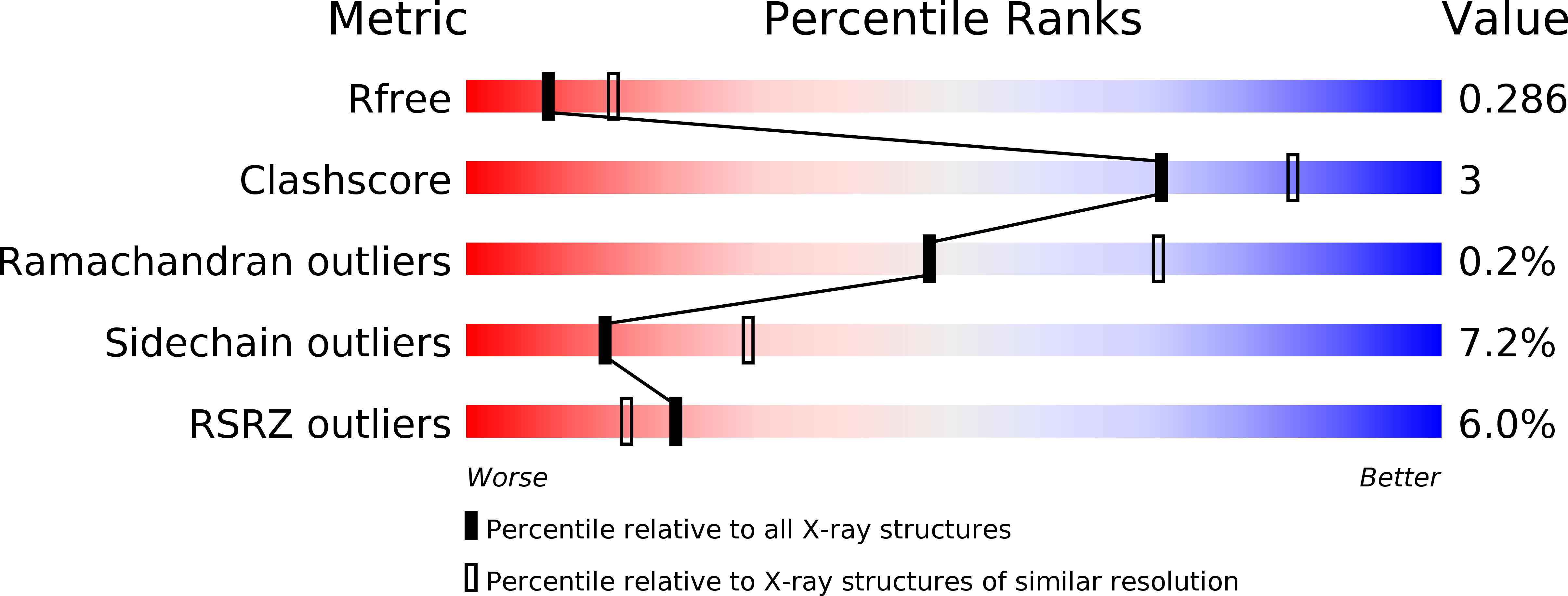
Resolution:
2.60 Å
R-Value Free:
0.26
R-Value Work:
0.22
R-Value Observed:
0.22
Space Group:
P 21 21 2