Deposition Date
2012-08-28
Release Date
2013-02-27
Last Version Date
2024-11-06
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
4GSU
Keywords:
Title:
Structural basis for the inhibition of Mycobacterium tuberculosis L,D-transpeptidase by meropenem, a drug effective against extensively drug-resistant strains
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Taxon ID: 1773)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
2.00 Å
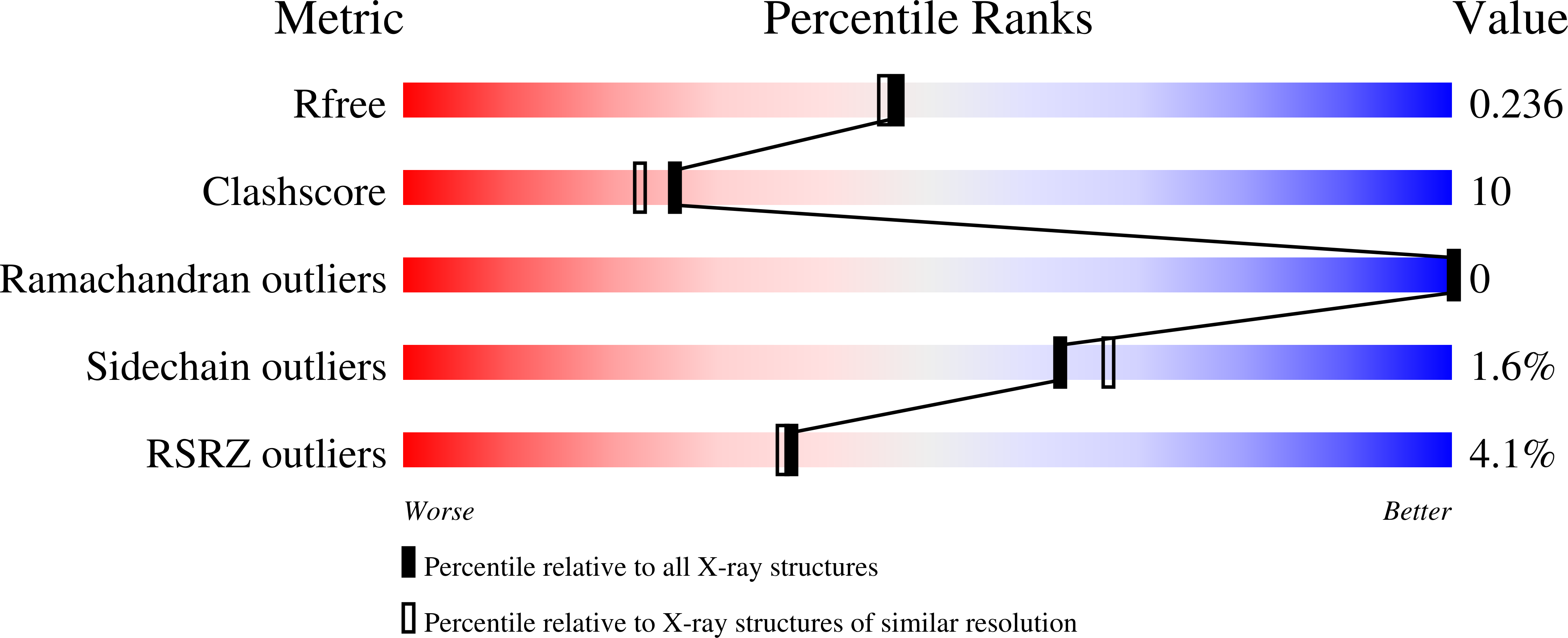
R-Value Free:
0.23
R-Value Work:
0.18
R-Value Observed:
0.18
Space Group:
P 21 21 21