Deposition Date
2012-08-01
Release Date
2012-10-03
Last Version Date
2023-09-13
Entry Detail
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Staphylococcus aureus (Taxon ID: 158879)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
3.20 Å
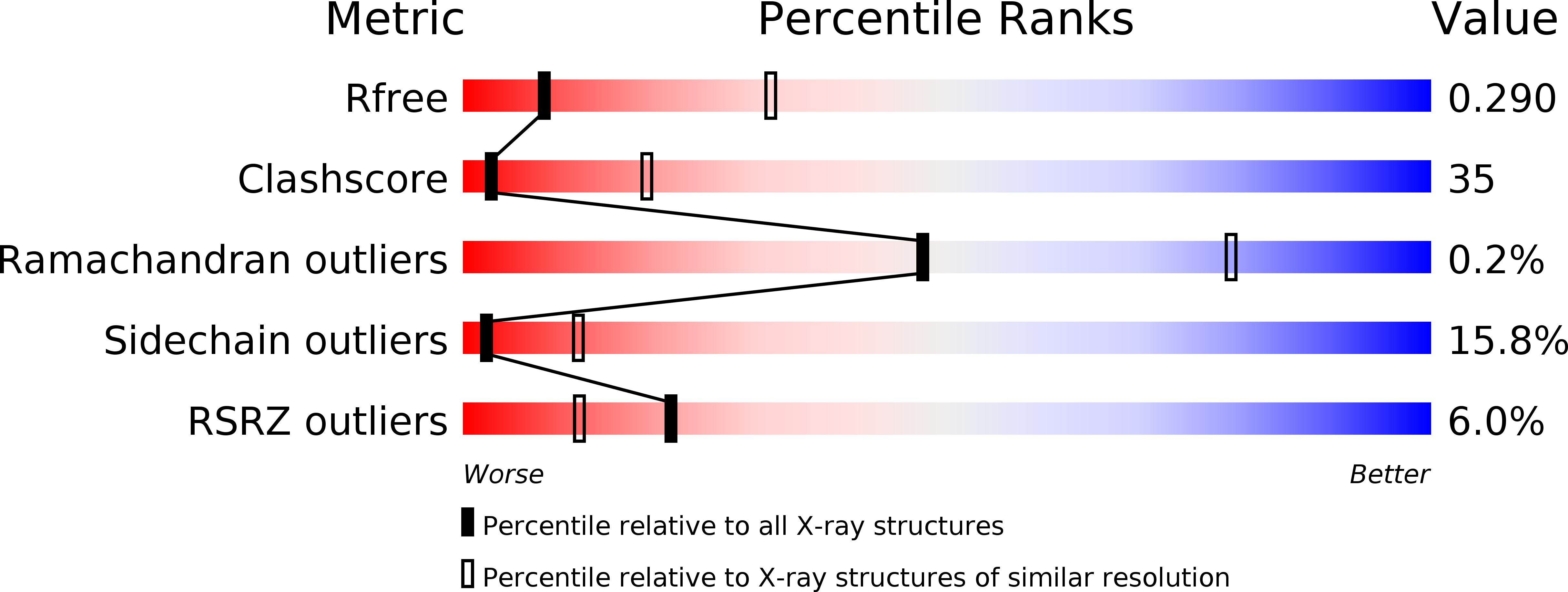
R-Value Free:
0.29
R-Value Work:
0.25
R-Value Observed:
0.25
Space Group:
P 62 2 2