Deposition Date
2012-07-16
Release Date
2012-10-31
Last Version Date
2025-03-26
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
4G4L
Keywords:
Title:
Crystal structure of the de novo designed peptide alpha4tbA6
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
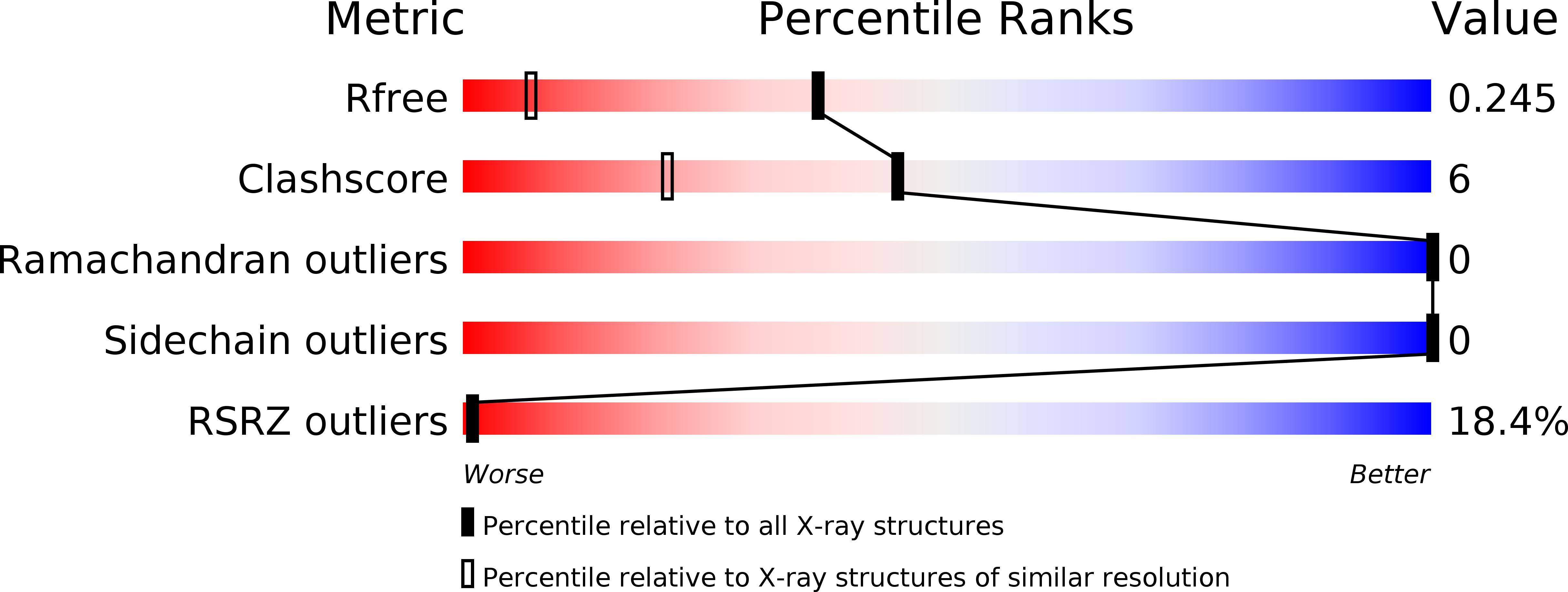
Resolution:
1.54 Å
R-Value Free:
0.24
R-Value Work:
0.24
R-Value Observed:
0.24
Space Group:
P 21 21 2