Deposition Date
2012-06-06
Release Date
2012-09-26
Last Version Date
2024-10-30
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
4FHN
Keywords:
Title:
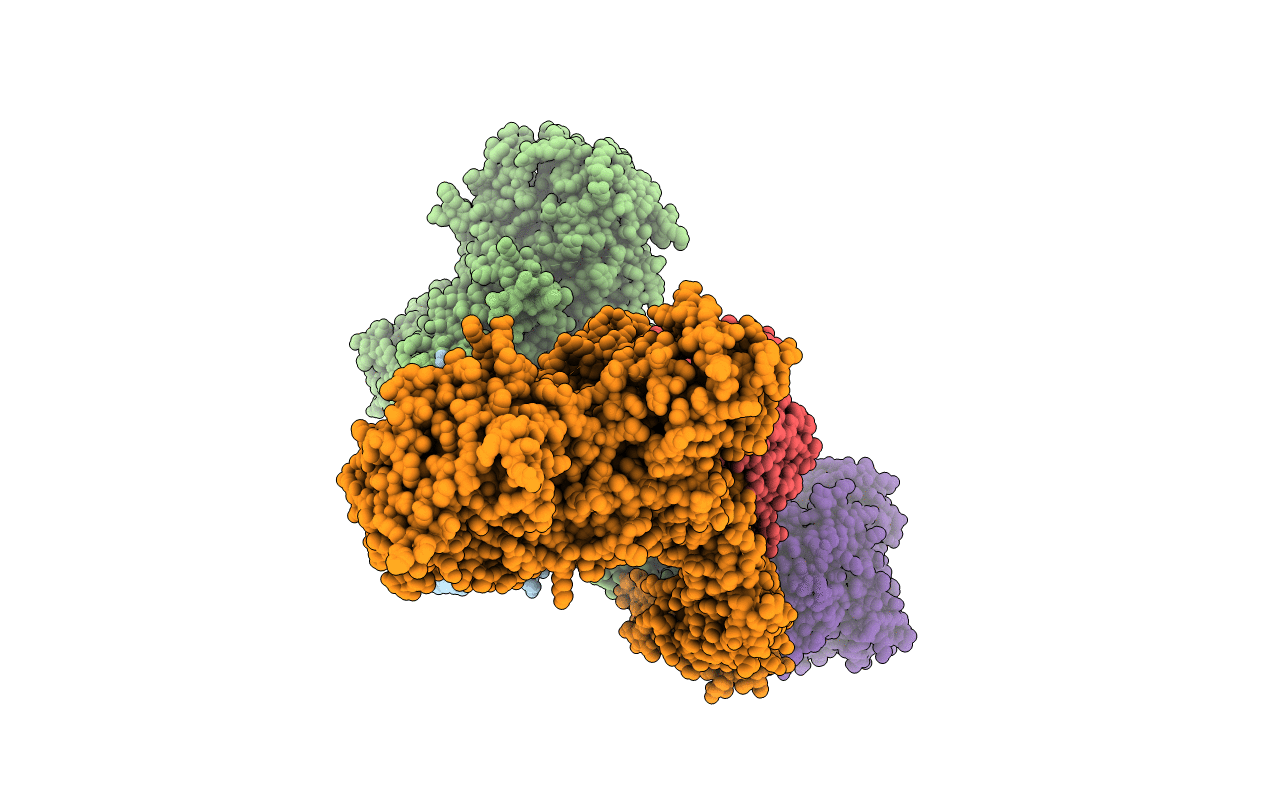
Nup37-Nup120 full-length complex from Schizosaccharomyces pombe
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Schizosaccharomyces pombe 972h- (Taxon ID: 284812)
Escherichia coli O157:H7 (Taxon ID: 83334)
Escherichia coli O157:H7 (Taxon ID: 83334)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
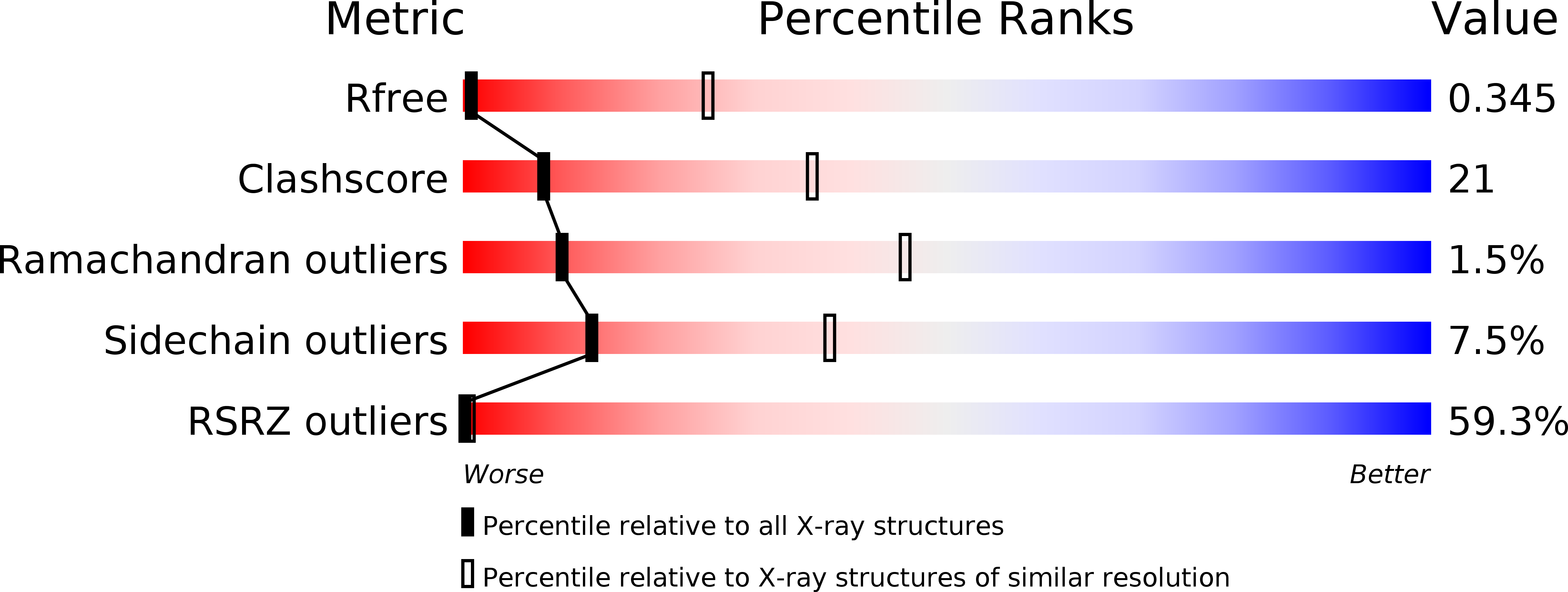
Resolution:
6.99 Å
R-Value Free:
0.34
R-Value Work:
0.28
R-Value Observed:
0.28
Space Group:
P 63 2 2