Deposition Date
2012-05-29
Release Date
2012-06-27
Last Version Date
2024-02-28
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
4FE5
Keywords:
Title:
Crystal structure of the xpt-pbuX guanine riboswitch aptamer domain in complex with hypoxanthine
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
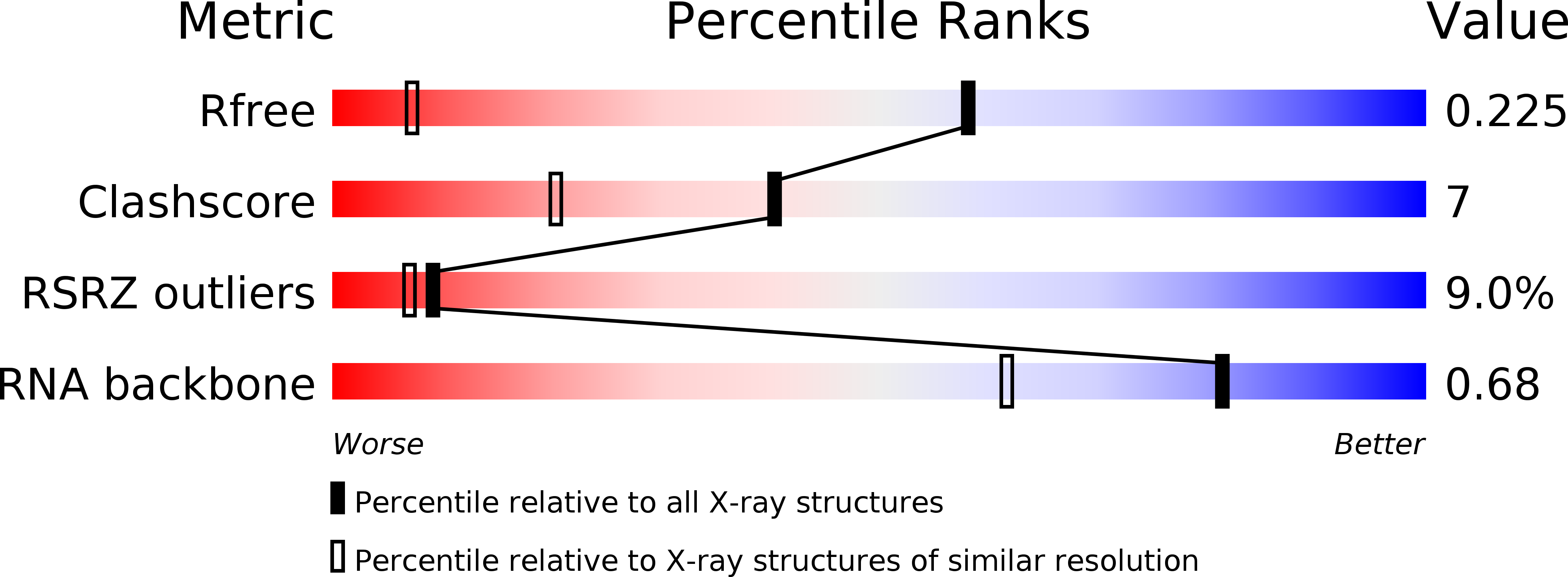
Resolution:
1.32 Å
R-Value Free:
0.22
R-Value Work:
0.19
R-Value Observed:
0.19
Space Group:
C 1 2 1