Deposition Date
2012-03-27
Release Date
2013-05-22
Last Version Date
2024-11-13
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
4EDA
Keywords:
Title:
Structures of monomeric hemagglutinin and its complex with an Fab fragment of a neutralizing antibody that binds to H1 subtype influenza viruses: molecular basis of infectivity of 2009 pandemic H1N1 influenza A viruses
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Influenza A virus (Taxon ID: 644289)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
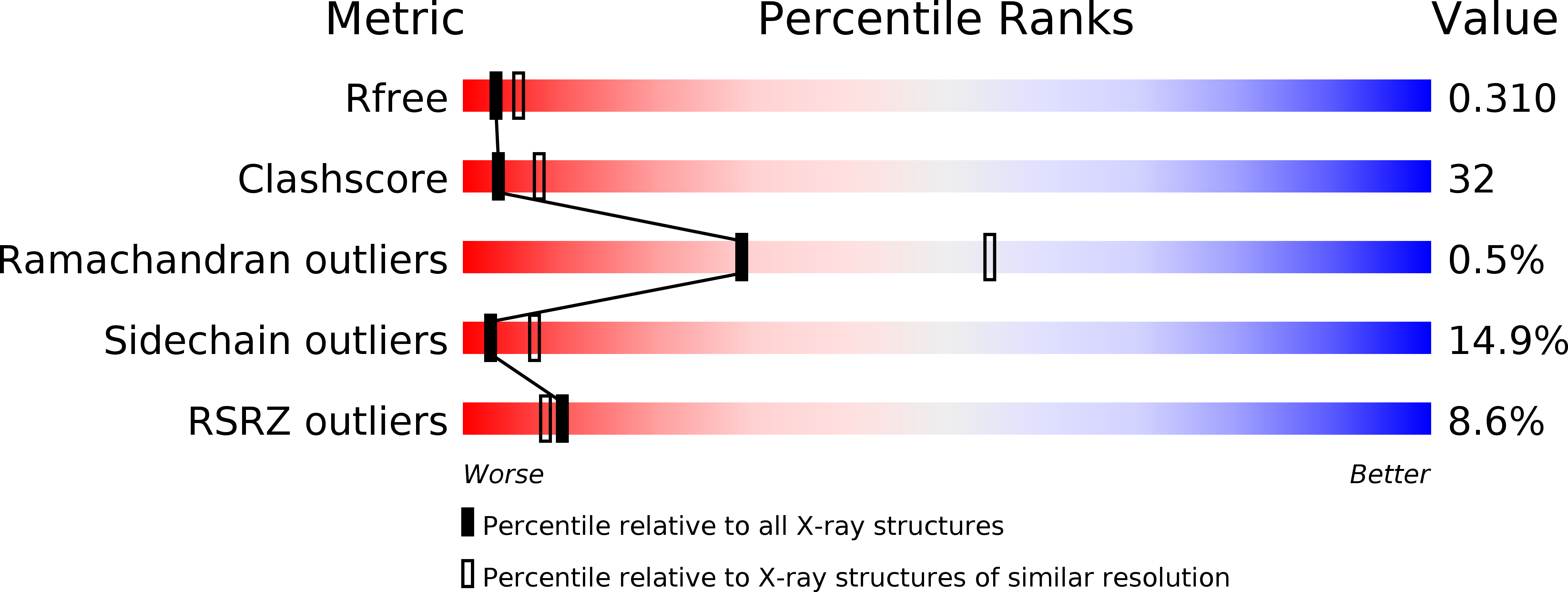
Resolution:
2.70 Å
R-Value Free:
0.28
R-Value Work:
0.23
R-Value Observed:
0.23
Space Group:
P 6