Deposition Date
1998-01-26
Release Date
1998-04-29
Last Version Date
2023-08-09
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
4DAA
Keywords:
Title:
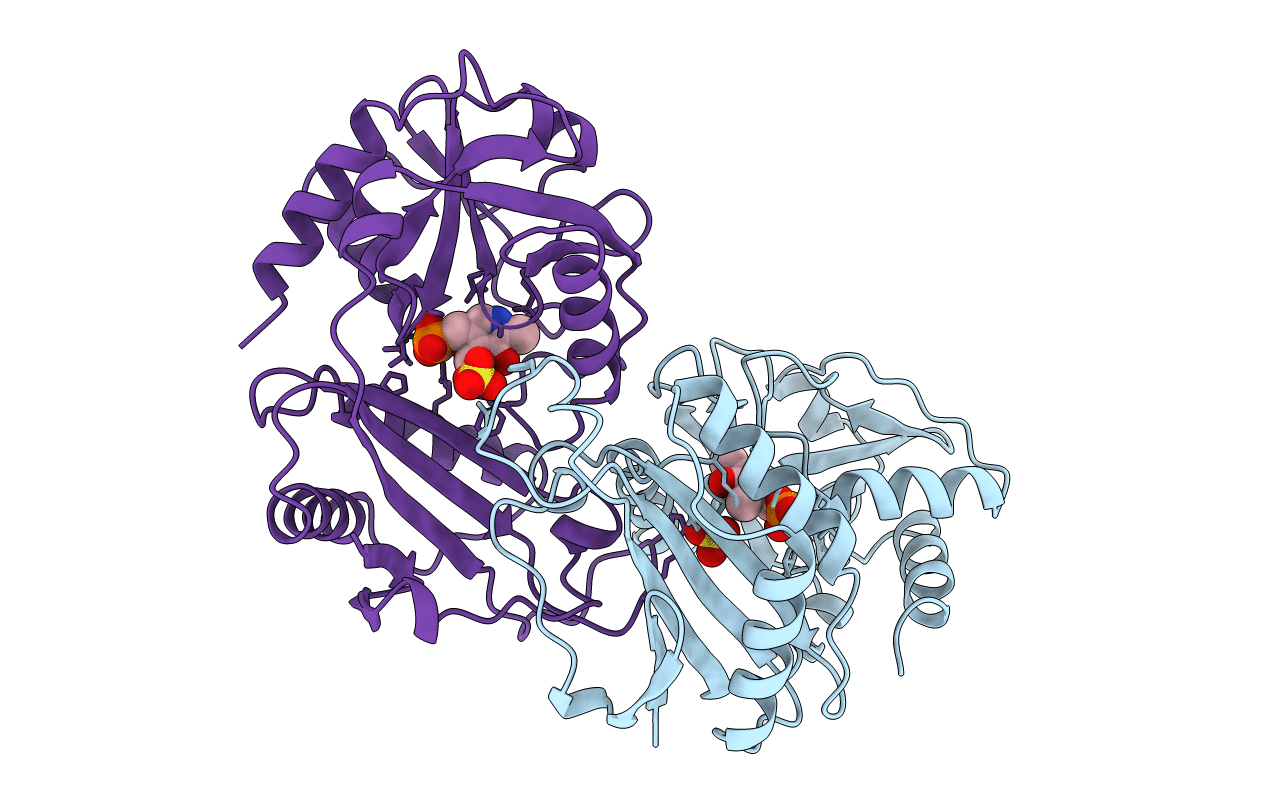
CRYSTALLOGRAPHIC STRUCTURE OF D-AMINO ACID AMINOTRANSFERASE IN PYRIDOXAL-5'-PHOSPHATE (PLP) FORM
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Bacillus sp. (Taxon ID: 72579)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
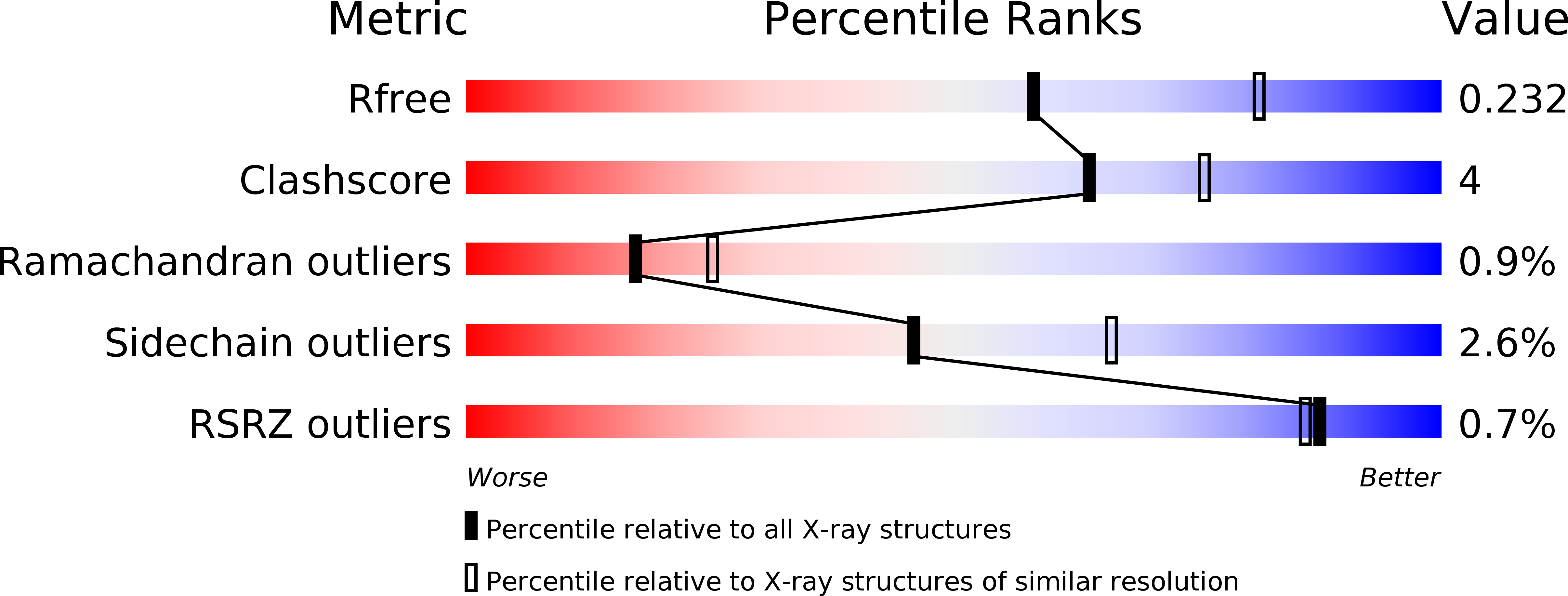
Resolution:
2.40 Å
R-Value Free:
0.24
R-Value Work:
0.18
R-Value Observed:
0.18
Space Group:
C 1 2 1