Deposition Date
2014-01-28
Release Date
2014-04-02
Last Version Date
2023-12-20
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
4COH
Keywords:
Title:
Crystal structure of Trypanosoma cruzi CYP51 bound to the sulfonamide derivative of the 4-aminopyridyl-based inhibitor
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
TRYPANOSOMA CRUZI (Taxon ID: 5693)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
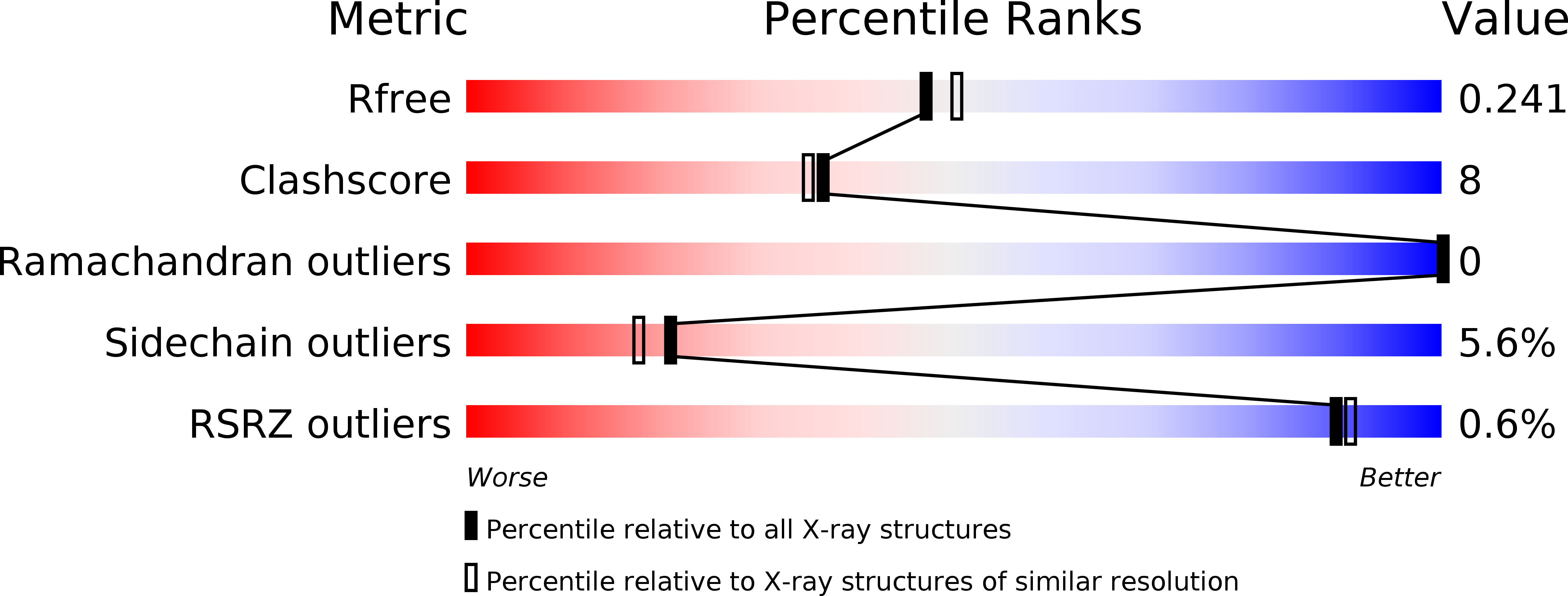
Resolution:
2.08 Å
R-Value Free:
0.24
R-Value Work:
0.17
R-Value Observed:
0.17
Space Group:
P 21 21 21