Deposition Date
2013-11-26
Release Date
2014-05-14
Last Version Date
2024-05-01
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
4CGW
Keywords:
Title:
Second TPR of Spaghetti (RPAP3) bound to HSP90 peptide SRMEEVD
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
HOMO SAPIENS (Taxon ID: 9606)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
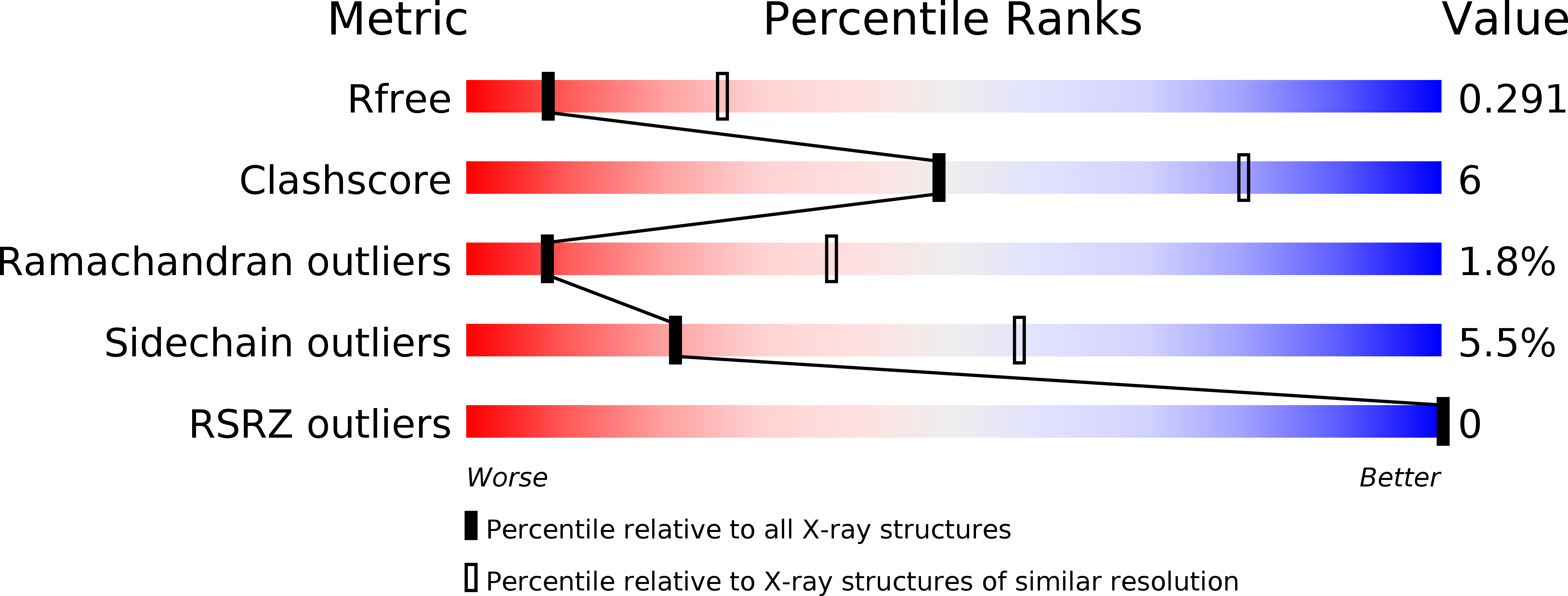
Resolution:
3.00 Å
R-Value Free:
0.29
R-Value Work:
0.24
R-Value Observed:
0.24
Space Group:
P 21 21 21