Deposition Date
2013-11-19
Release Date
2014-05-07
Last Version Date
2023-12-20
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
4CFR
Keywords:
Title:
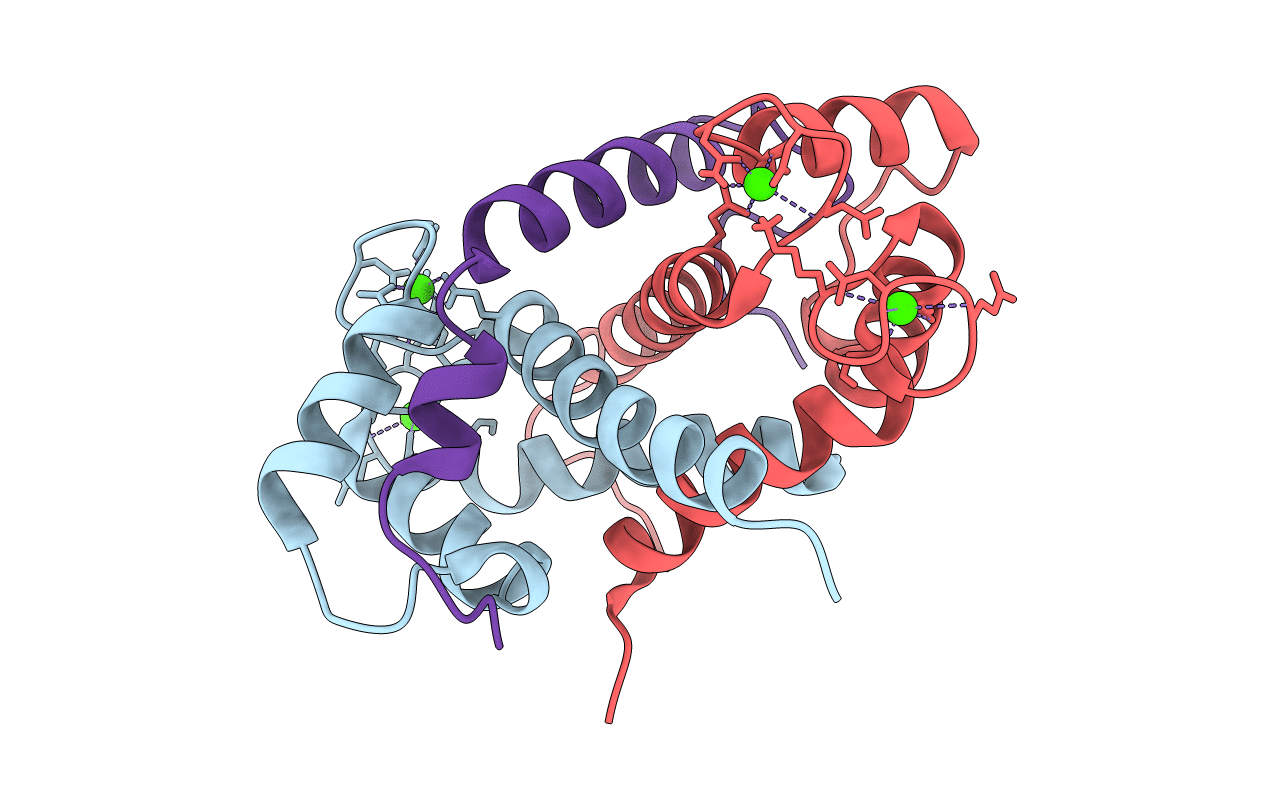
Ca-bound S100A4 C3S, C81S, C86S and F45W mutant complexed with non- muscle myosin IIA
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
HOMO SAPIENS (Taxon ID: 9606)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
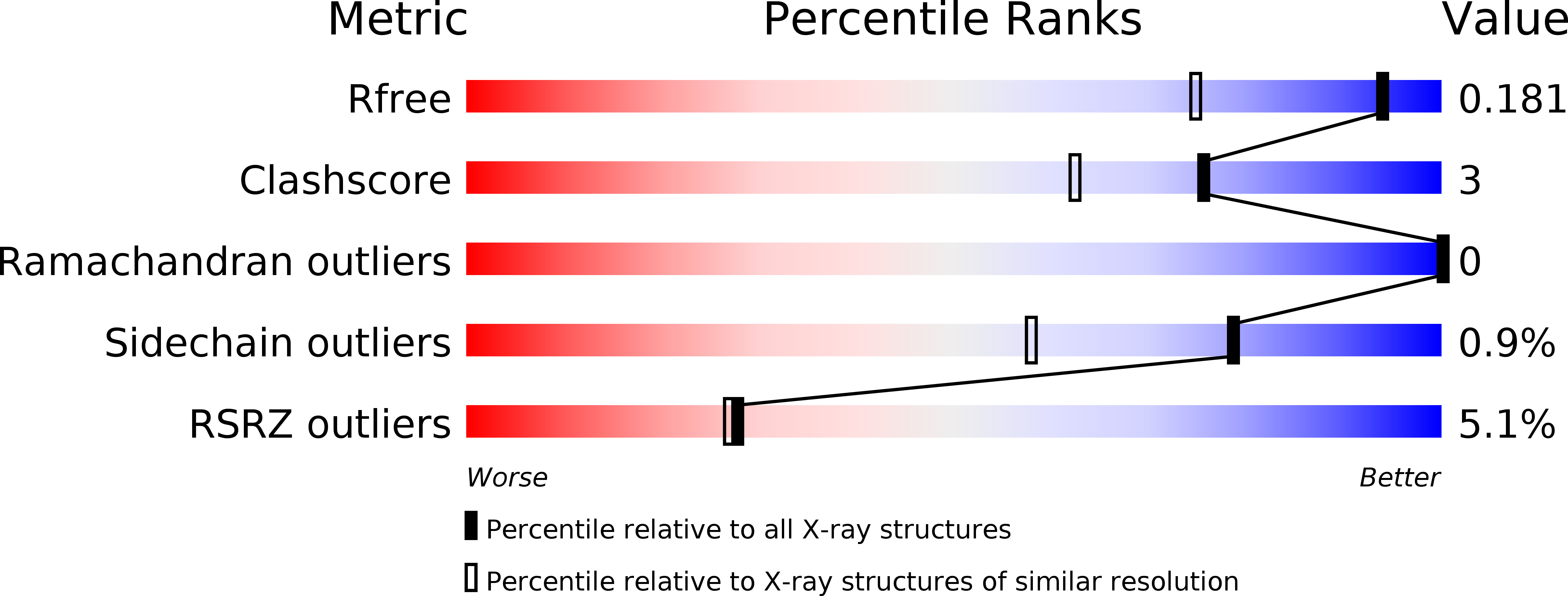
Resolution:
1.40 Å
R-Value Free:
0.17
R-Value Work:
0.16
R-Value Observed:
0.16
Space Group:
P 41 21 2