Deposition Date
2013-07-01
Release Date
2013-09-18
Last Version Date
2023-12-20
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
4BWC
Keywords:
Title:
X-ray structure of a phospholiapse B like protein 1 from bovine kidneys
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
BOS TAURUS (Taxon ID: 9913)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
1.89 Å
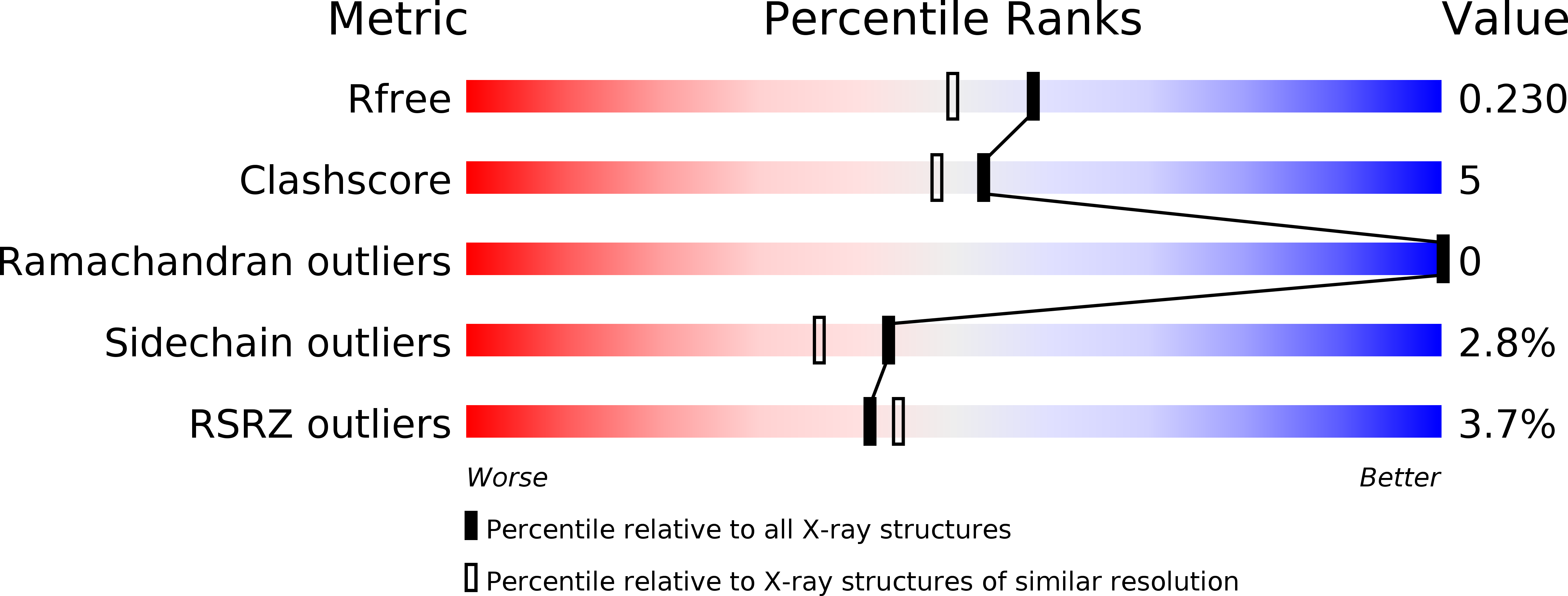
R-Value Free:
0.23
R-Value Work:
0.18
R-Value Observed:
0.19
Space Group:
P 31 2 1