Abstact
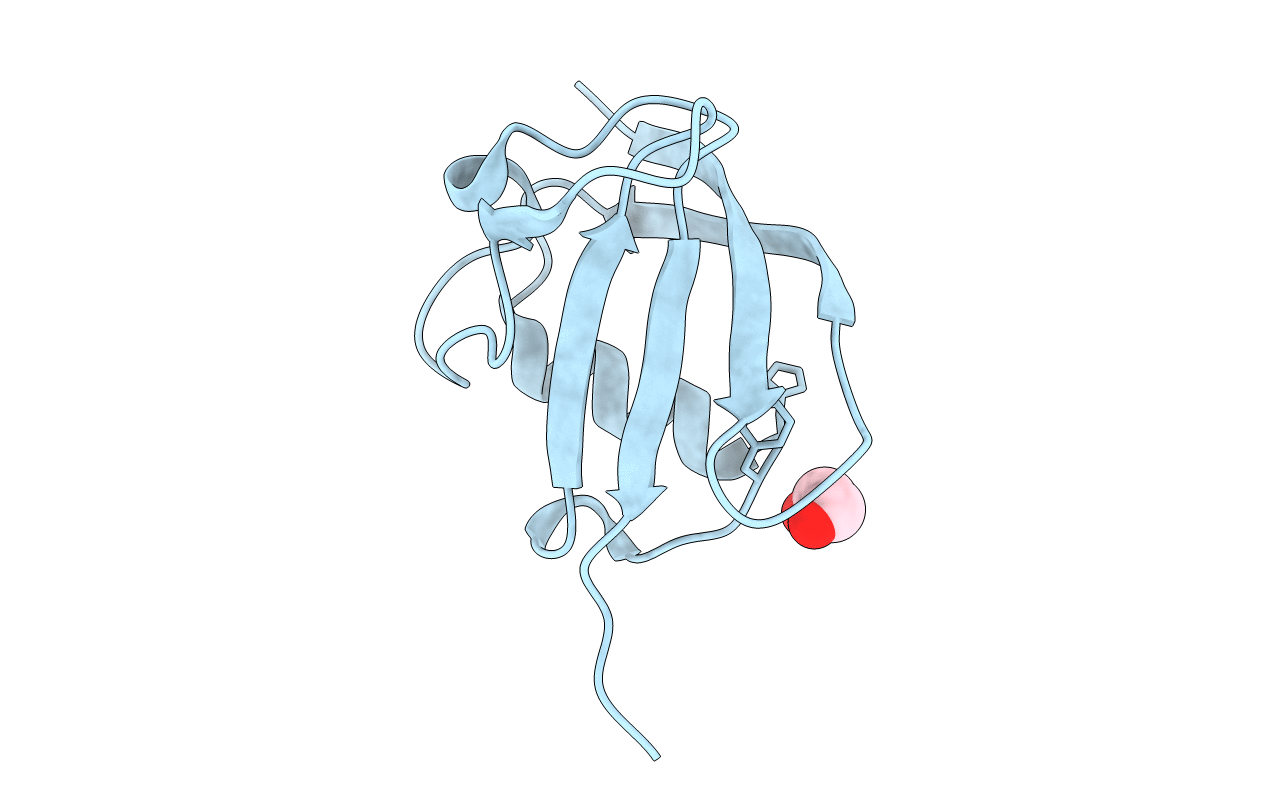
Tubulin-binding cofactor (TBC)-B is implicated in the presentation of α-tubulin ready to polymerize, and at the correct levels to form microtubules. Bioinformatics analyses, including secondary structure prediction, CD, and crystallography, were combined to characterize the molecular architecture of Trypanosoma brucei TBC-B. An efficient recombinant expression system was prepared, material-purified, and characterized by CD. Extensive crystallization screening, allied with the use of limited proteolysis, led to structures of the N-terminal ubiquitin-like and C-terminal cytoskeleton-associated protein with glycine-rich segment domains at 2.35-Å and 1.6-Å resolution, respectively. These are compact globular domains that appear to be linked by a flexible segment. The ubiquitin-like domain contains two lysines that are spatially conserved with residues known to participate in ubiquitinylation, and so may represent a module that, through covalent attachment, regulates the signalling and/or protein degradation associated with the control of microtubule assembly, catastrophe, or function. The TBC-B C-terminal cytoskeleton-associated protein with glycine-rich segment domain, a known tubulin-binding structure, is the only such domain encoded by the T. brucei genome. Interestingly, in the crystal structure, the peptide-binding groove of this domain forms intermolecular contacts with the C-terminus of a symmetry-related molecule, an association that may mimic interactions with the C-terminus of α-tubulin or other physiologically relevant partners. The interaction of TBC-B with the α-tubulin C-terminus may, in particular, protect from post-translational modifications, or simply assist in the shepherding of the protein into polymerization.