Deposition Date
2012-06-26
Release Date
2013-08-07
Last Version Date
2023-12-20
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
4AZM
Keywords:
Title:
Human epidermal fatty acid-binding protein (FABP5) in complex with the inhibitor BMS-309413
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
HOMO SAPIENS (Taxon ID: 9606)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
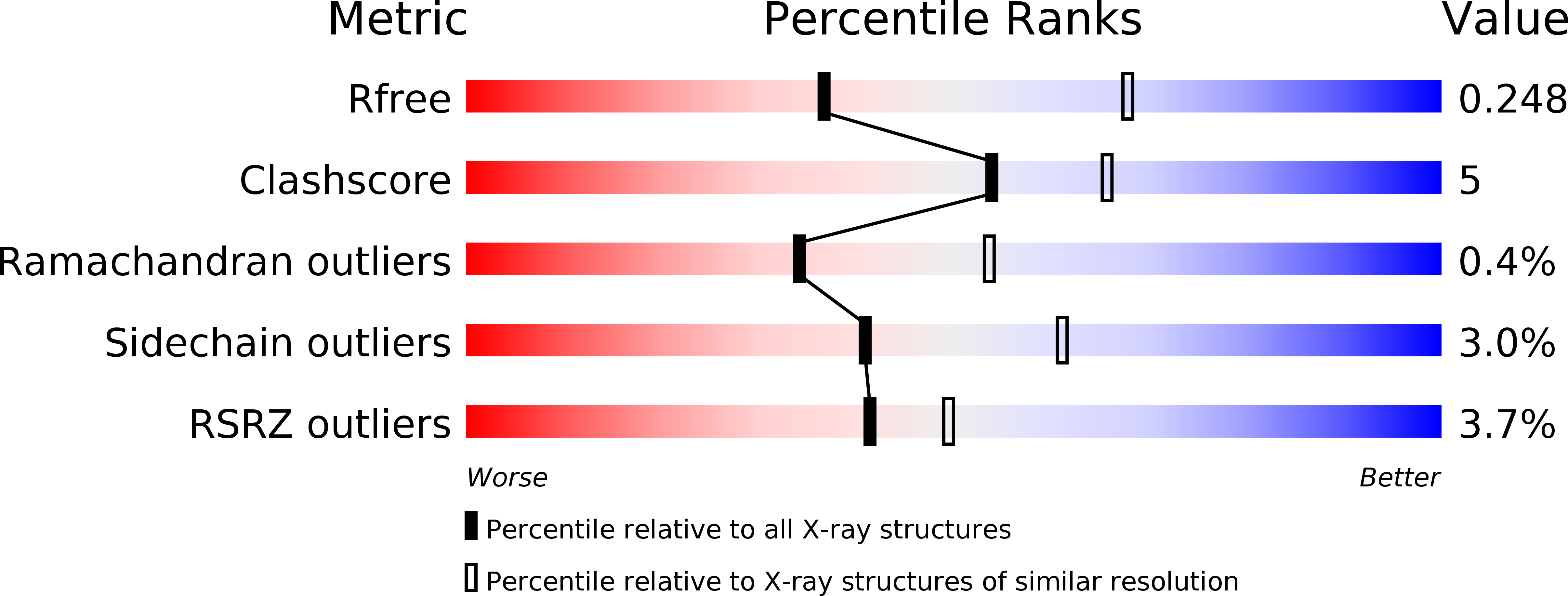
Resolution:
2.75 Å
R-Value Free:
0.25
R-Value Work:
0.20
R-Value Observed:
0.20
Space Group:
P 4 21 2