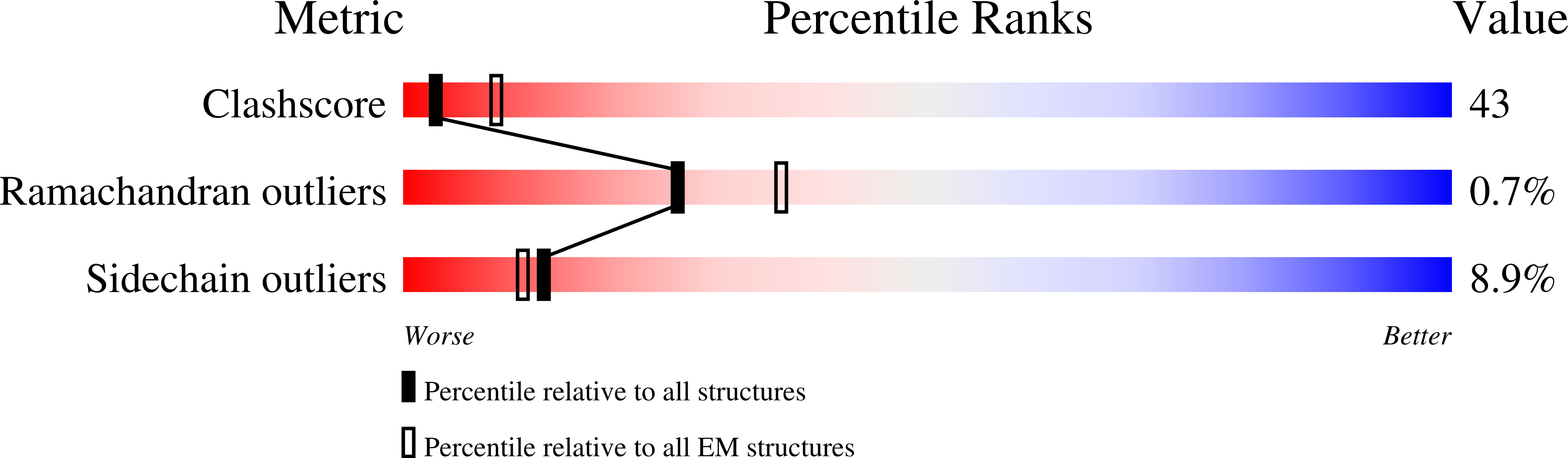
Deposition Date
2011-07-19
Release Date
2011-11-09
Last Version Date
2024-05-08
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
3ZUH
Keywords:
Title:
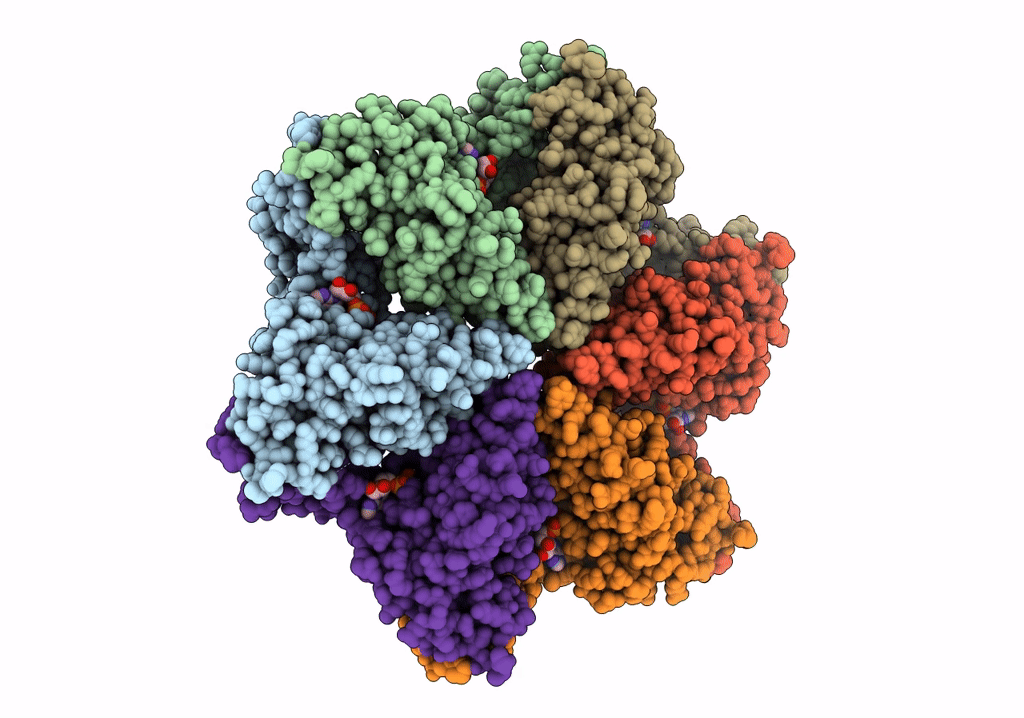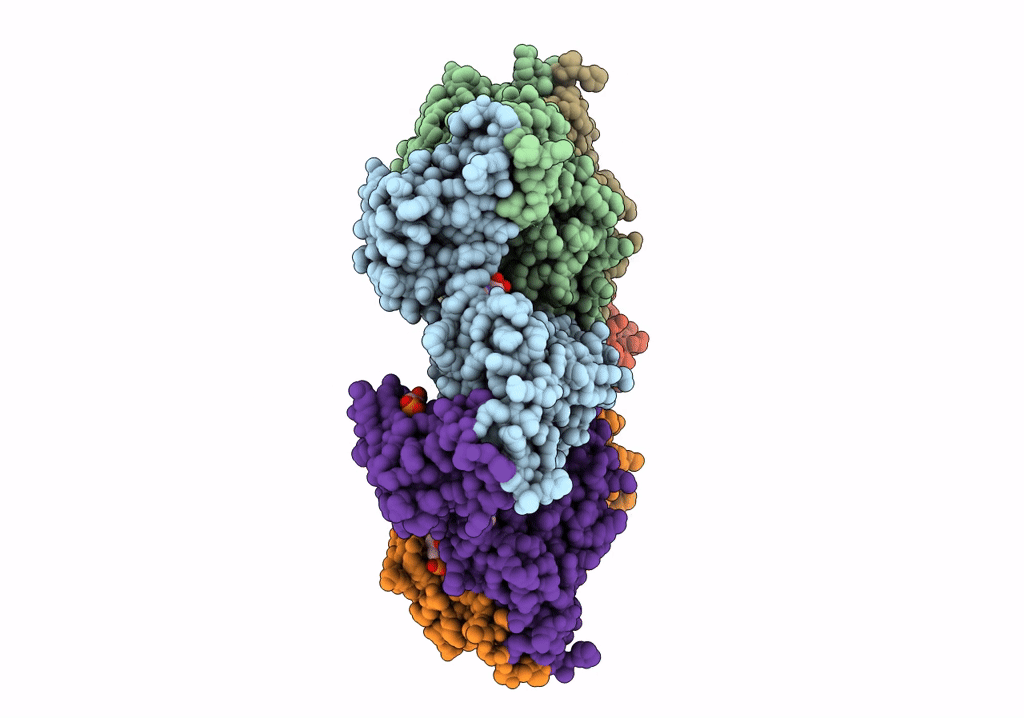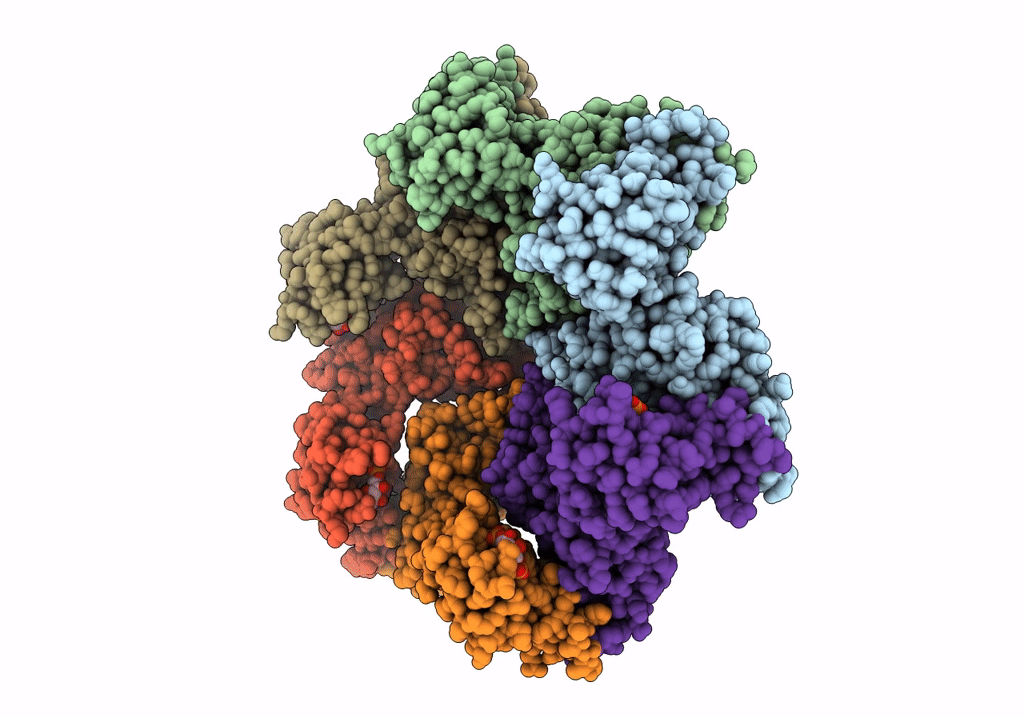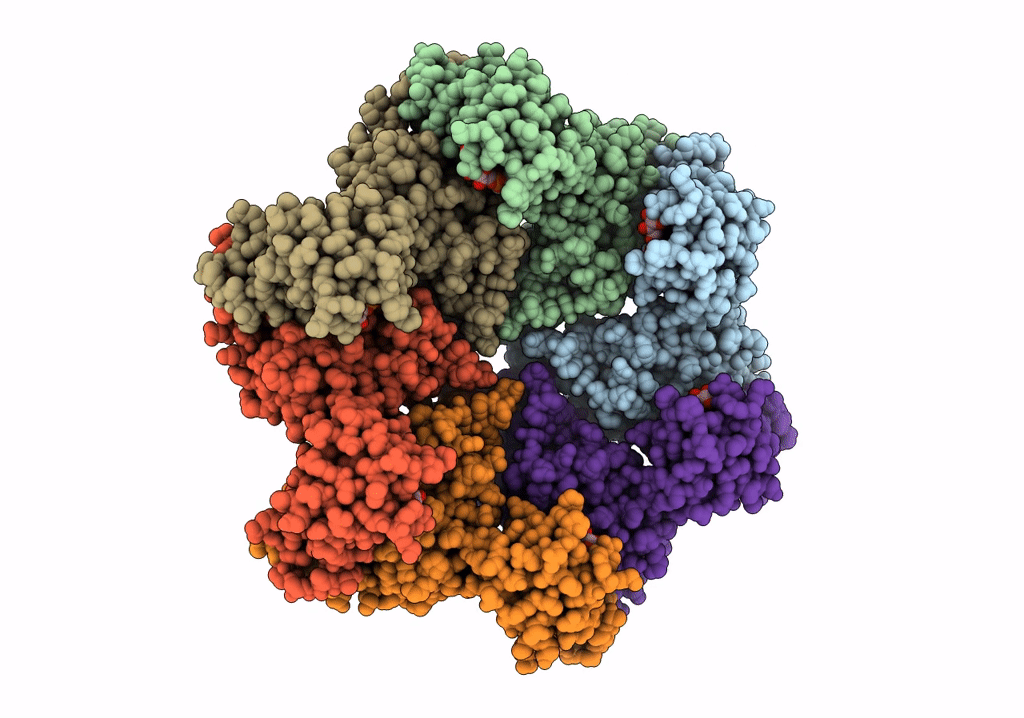
Negative stain EM Map of the AAA protein CbbX, a red-type Rubisco activase from R. sphaeroides
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
RHODOBACTER SPHAEROIDES (Taxon ID: 1063)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
21.00 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE