Deposition Date
2013-02-27
Release Date
2014-01-15
Last Version Date
2023-12-20
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
3ZPH
Keywords:
Title:
Bacterial chalcone isomerase in closed conformation from Eubacterium ramulus at 2.8 A resolution
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
EUBACTERIUM RAMULUS (Taxon ID: 39490)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
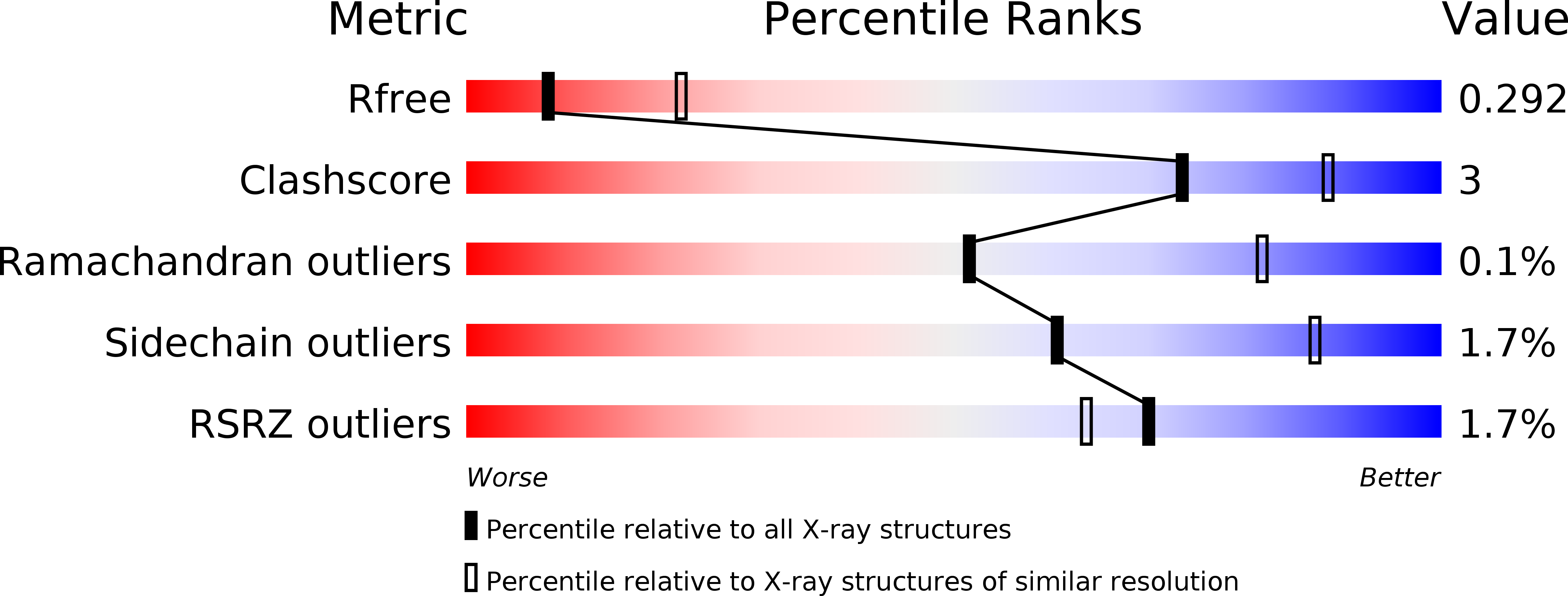
Resolution:
2.80 Å
R-Value Free:
0.29
R-Value Work:
0.24
R-Value Observed:
0.25
Space Group:
I 21 21 21